NMF-based micro-seismic weak signal recognition method
A recognition method and weak signal technology, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve the problems of limited resolution, no localization ability in time domain, frequency aliasing end effect, etc., and achieve the effect of accurate classification results, comprehensive feature set, convenient real-time performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
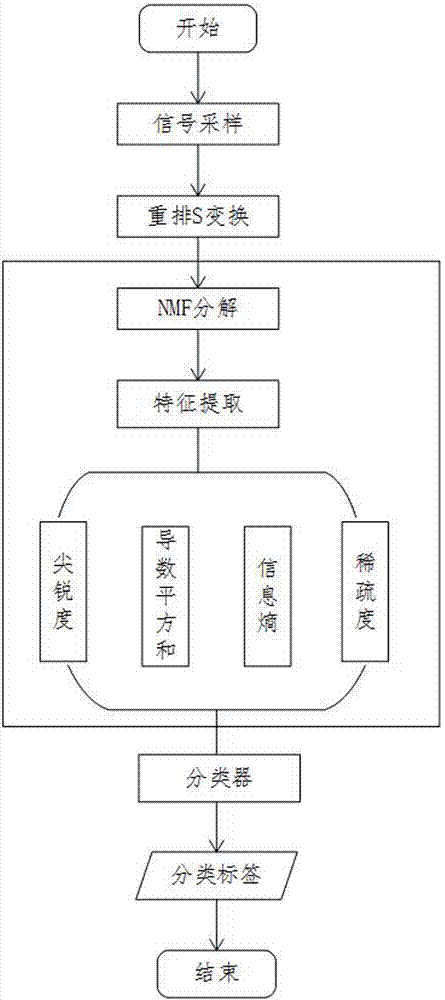
[0056] A method for distinguishing weak signals of microseisms based on NMF, the flow chart is as follows figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0057] (1) The microseismic data collected in a coal mine is x=x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x n T .
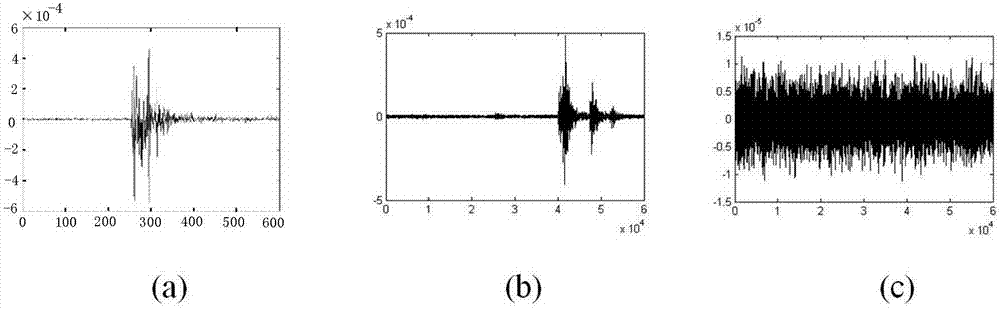
[0058] (2) Sampling the collected data at equal intervals plotted with matlab such as figure 2 Its waveform diagram is shown.
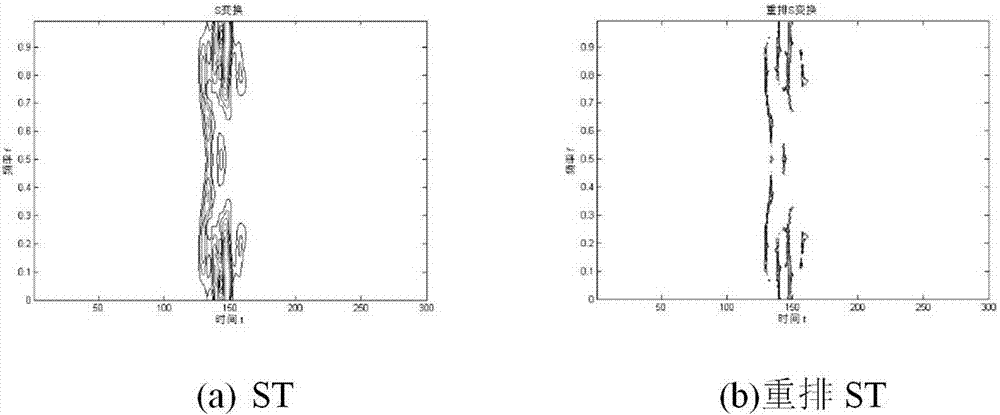
[0059] (3) Perform rearrangement S transformation on the signal x(n).
[0060] (4) If the column of x is greater than the row, go to step (5), otherwise go to step (6).
[0061] (5) Transpose x and assign it to A itself x=x T ; Guarantee that x is a column vector.
[0062] (6) If the number of input parameters is 1, go to step (7), otherwise go to step (8).
[0063] (7) Let the minimum sampling frequency be f min =0, the maximum sampling frequency f max =f Nyquist , the sampling interval T=1.
[0064] (8) Display parameters: minimum sampling frequency f min , the maximum samplin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com