Thin film transistor substrate having bi-layer oxide semiconductor
An oxide semiconductor, thin film transistor technology, applied in transistors, semiconductor devices, electric solid state devices, etc., can solve the problems of thin film transistor deterioration and uncontrollable threshold voltage, and achieve high-speed operation, excellent video quality, and stable threshold voltage. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
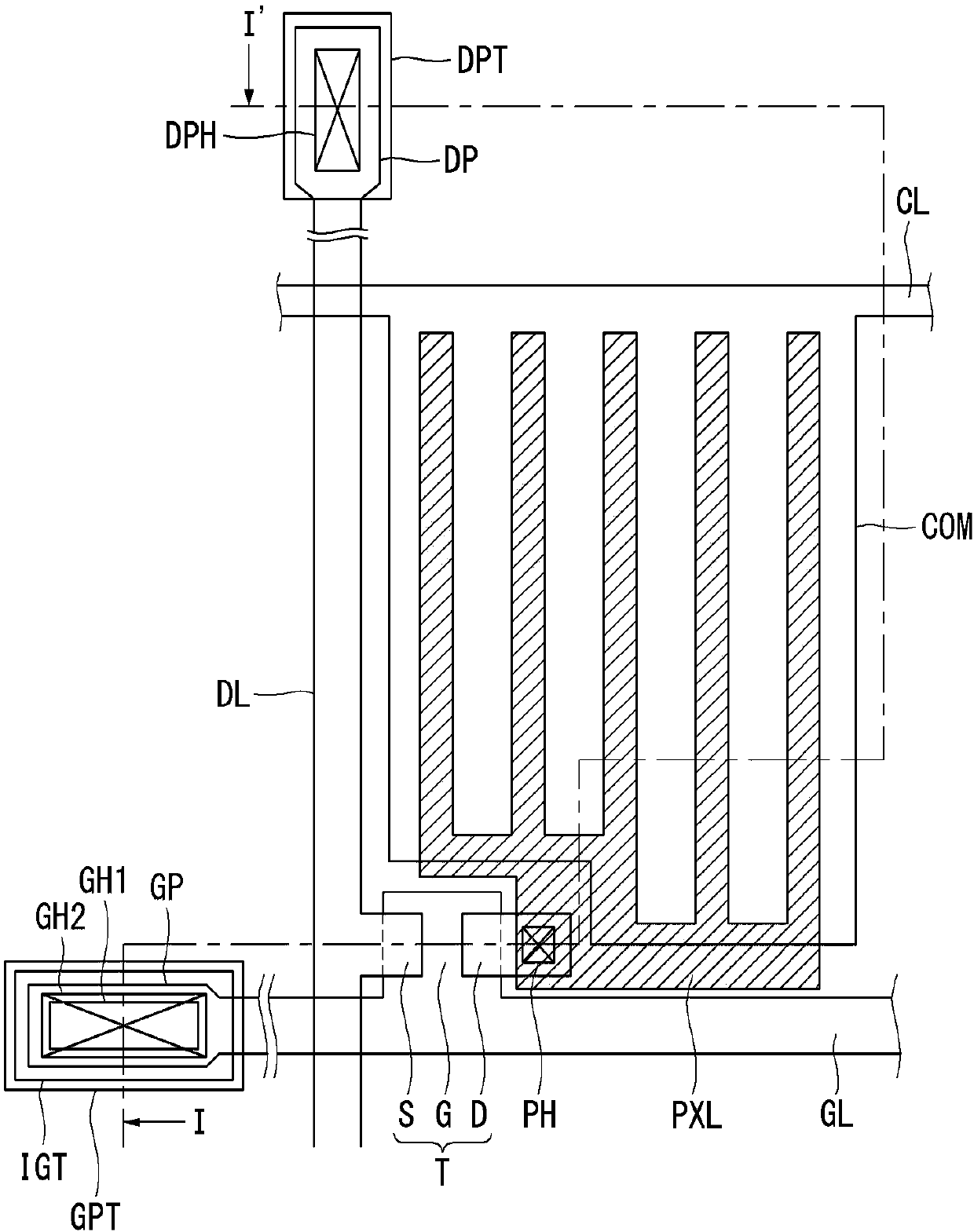
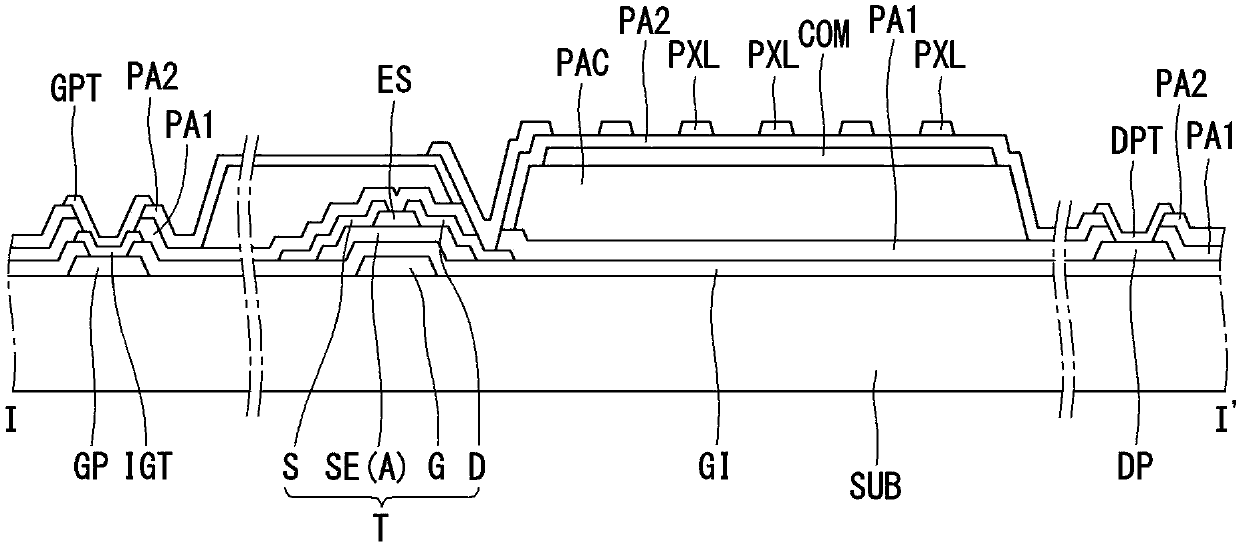
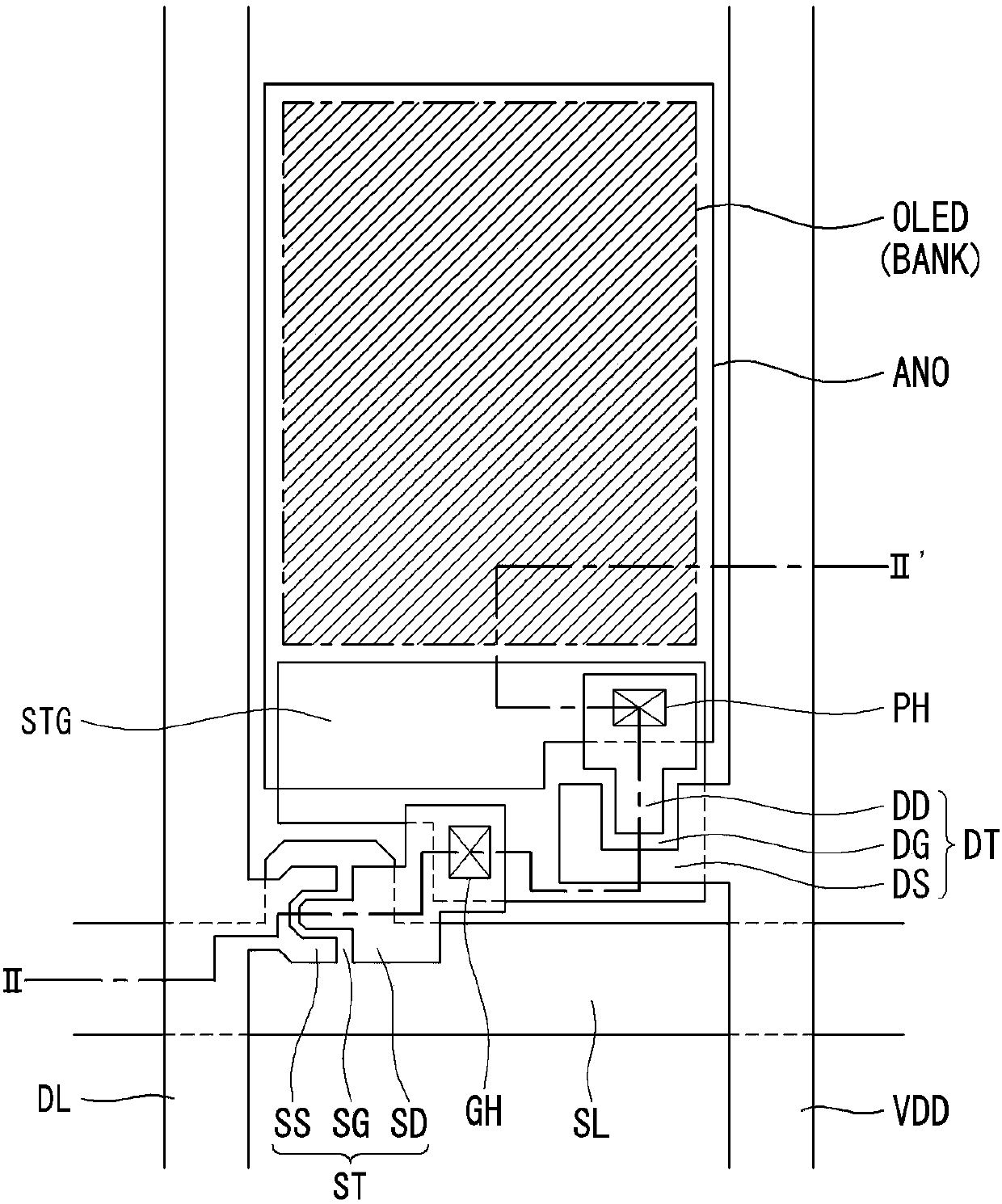
[0055] refer to Figure 5 , we will describe the first embodiment of the present disclosure. Figure 5 is a cross-sectional view showing the structure of the thin film transistor substrate including the oxide semiconductor material according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure. refer to Figure 5 , The thin film transistor substrate according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure includes a plurality of pixel areas including at least one thin film transistor T in each pixel area arranged in a matrix on the substrate SUB. Here, for convenience of explanation, we will mainly explain the structure of the thin film transistor T. FIG.
[0056] On the substrate SUB, a gate G is formed. On the gate G is deposited a gate insulating layer GI covering the entire surface of the substrate SUB. On the gate insulating layer GI, a semiconductor layer A overlapping a middle portion of the gate G is formed. The semiconductor layer A has a stacked structure in whi...
no. 2 approach
[0069] As for the double-layered oxide semiconductor according to the first embodiment, since the channel length is short and has a stable threshold voltage, it is suitable for large-area flat panel displays. However, in the first embodiment, the source S and the drain D directly contact the second oxide semiconductor layer GA. From the viewpoint of electrical characteristics, the resistivity of the second oxide semiconductor layer GA is much larger than that of the first oxide semiconductor layer GO. That is, a thin film transistor having a double-layer oxide semiconductor has greater resistivity and work function than a thin film transistor having a single-layer oxide semiconductor.
[0070] Due to the greater resistivity, contact resistance between the second oxide semiconductor layer GA and the source S and / or between the second oxide semiconductor layer GA and the drain D may be increased. In the first embodiment, a short channel length can be obtained with the double-la...
no. 3 approach
[0078] In the first embodiment and the second embodiment, the source S and the drain D are directly formed on and contact the semiconductor layer A. Referring to FIG. Therefore, the thin film transistor has a back channel etching structure in which the thickness of the channel layer defined between the source S and the drain D of the semiconductor layer A is thinned. In the first embodiment and the second embodiment, only the second oxide semiconductor layer GA is thinned, but the first oxide semiconductor layer GO is not thinned. Therefore, the characteristics of the channel are not affected or deteriorated due to the back channel etch structure. However, for a large-area display panel in which a large number of transistors are disposed on a large-area substrate, it is difficult to form all transistors to have the same or similar conditions and / or dimensions on all regions of the substrate.
[0079] In the third embodiment, we provide a thin film transistor having an etching...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com