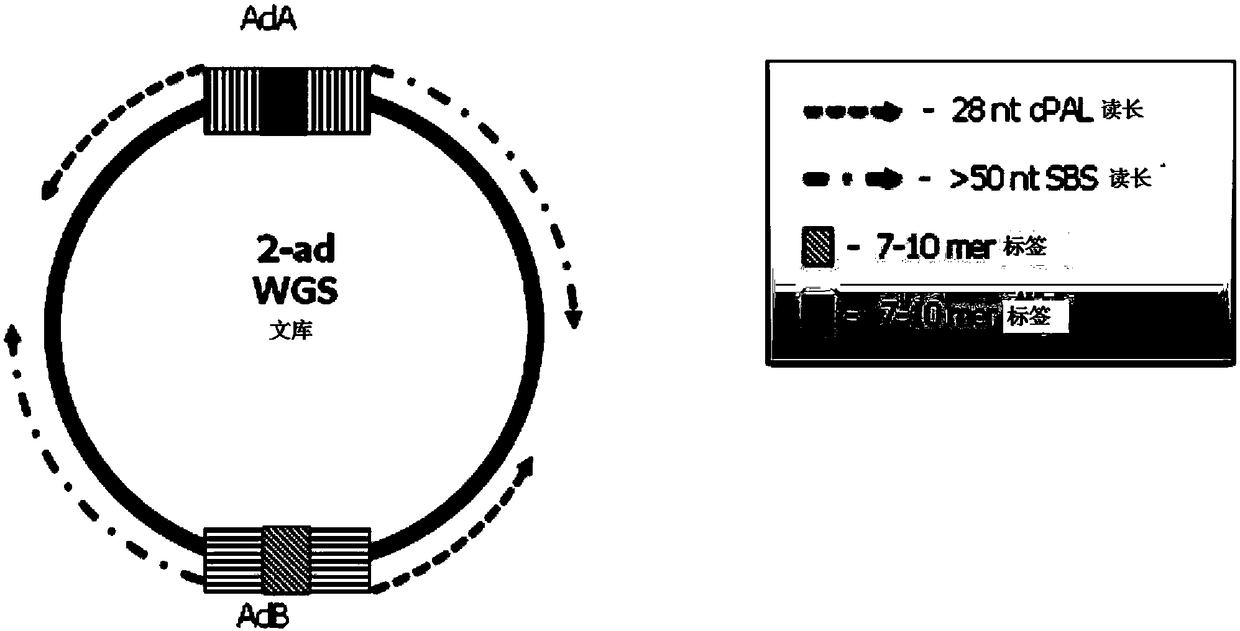
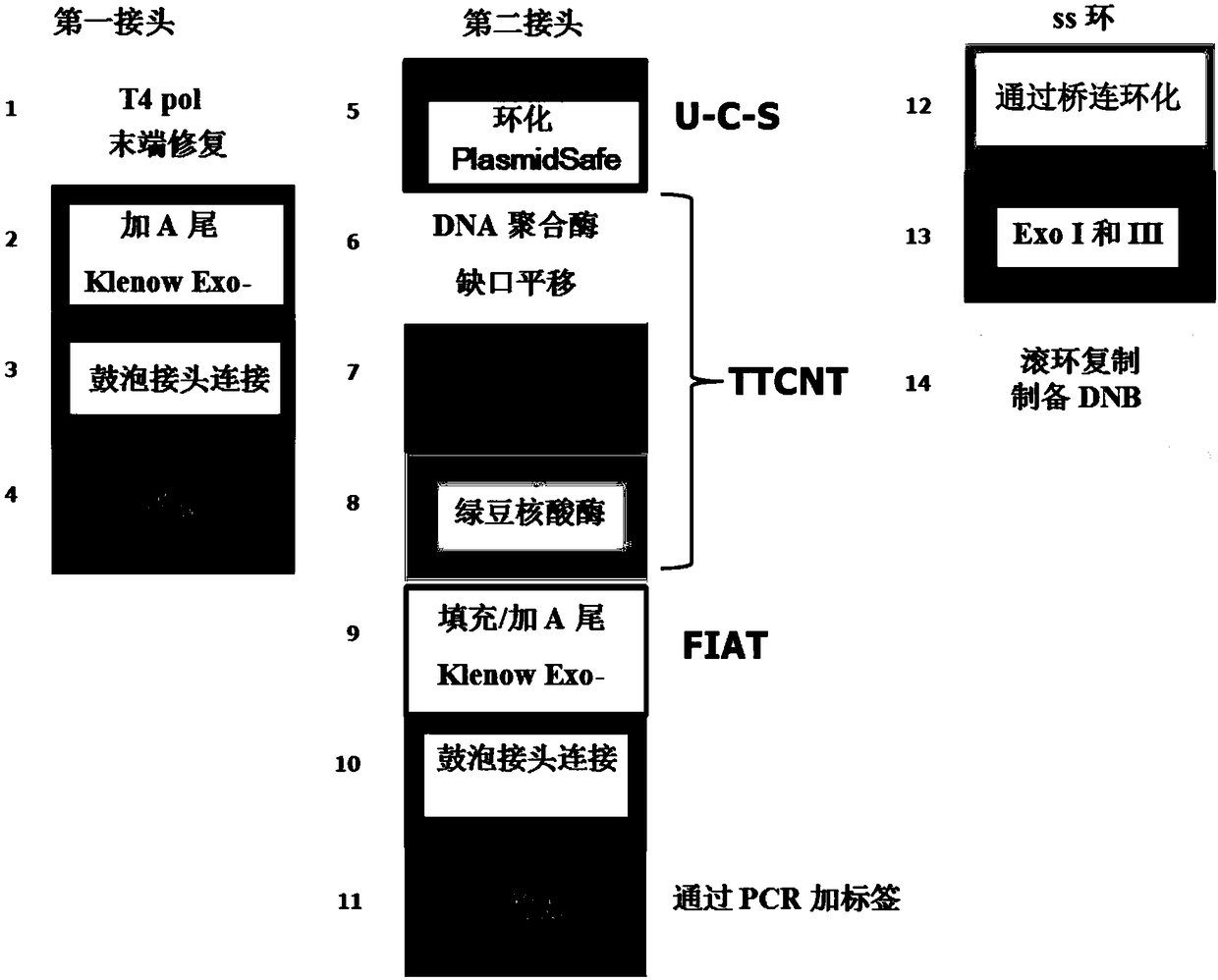
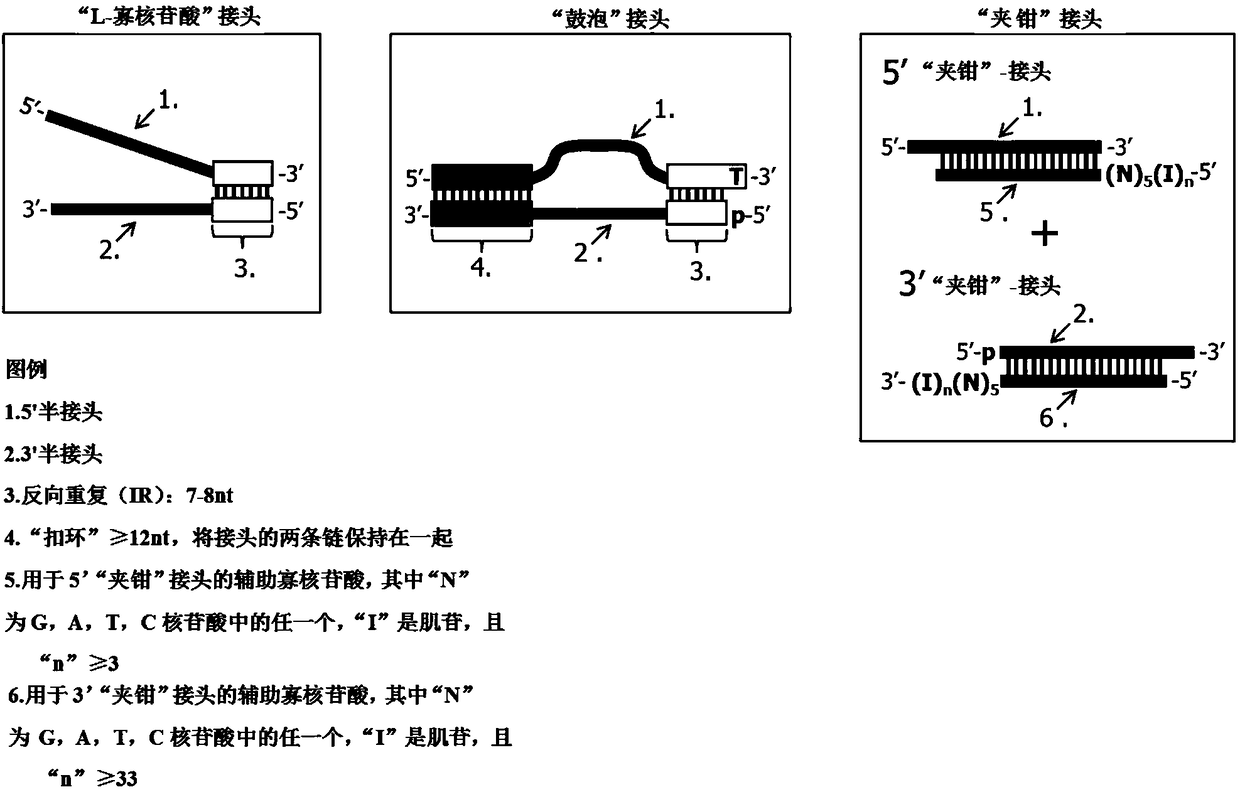
Double chain nucleic acid fragment joint adding method, library constructing method and kit
A double-stranded nucleic acid and library construction technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problem that the library construction efficiency of target nucleic acid fragments needs to be improved, and achieve the effects of simplifying the construction process, reducing the amount of nucleic acid input, and improving the sequencing coverage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0288] Example 1 Construction of a paired library comprising two bubbling adapters
[0289] Figure 19 Depicted how to construct a paired library containing two bubbling adapters. The details are as follows:
[0290] 3ug DNA was fragmented using Covaris to obtain 200-1800bp fragments. The fragmented DNA was then size-selected using magnetic beads to retain fragments of 300-1000 bp with an average size of 650 bp. 500 ng or 1.2 pmol of size-selected DNA was used in library preparation. End repair was performed using T4PNK and T4 DNA polymerase to generate 5' phosphorylated blunt-ended fragments, and dA tailing was added to the fragments. The first bubble adapter Ad203 was ligated to the DNA fragment by A-T ligation. The ligation product was amplified by PCR using uracil-containing primers and PfuCx polymerase, which allows the presence of uracil in the template. With USER enzyme, uracil-specific excision reagent enzyme, uracil DNA glycosylase (abbreviated UDG) and a mixtur...
Embodiment 2
[0291] Example 2 Construction of a paired library comprising two L-oligonucleotide adapters
[0292] Figure 22 Depicted is a schematic diagram of the construction of a paired library comprising two L-oligonucleotide adapters.
[0293] 3ug DNA was fragmented using Covaris to obtain 200-1800bp fragments. The fragmented DNA was then size-selected using magnetic beads to retain fragments of 300-1000 bp with an average size of 650 bp. 500 ng or 1.2 pmol of size-selected DNA was used in library preparation. The fragmented DNA was end-repaired using shrimp alkaline phosphatase and T4 DNA polymerase to obtain dephosphorylated blunt-ended fragments. The first L-oligonucleotide adapter Ad169 was ligated to the DNA fragment in two steps. For the first step, a second oligonucleotide is ligated by blunt ends in the presence of a short helper oligonucleotide with a 3'-end modification. A "heat inactivation" step is used to inactivate the ligase and remove the helper oligonucleotide, t...
Embodiment 3
[0294] Example 3 Construction of a paired library comprising bubbling and clamp junctions
[0295] Figure 23 Depicted is a schematic diagram of the construction of a paired library comprising a bubble adapter as the first adapter and a clamp adapter as the second adapter.
[0296] 3 μg of DNA was fragmented using Covaris to generate 200-1800 bp fragments. The fragmented DNA was then size-selected using magnetic beads to retain fragments of 300-1000 bp with an average size of 650 bp. 500 ng or 1.2 pmol of size-selected DNA was used in library preparation. End repair was performed using T4PNK and T4 DNA polymerase to generate 5' phosphorylated blunt-ended fragments, and dA tailing was added to the fragments. The first adapter, bubble adapter Ad201, was ligated to the DNA fragment by A-T ligation. The ligation product was amplified by PCR using uracil-containing primers and PfuCx polymerase, which allows the presence of uracil in the template. With USER enzyme, uracil-speci...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com