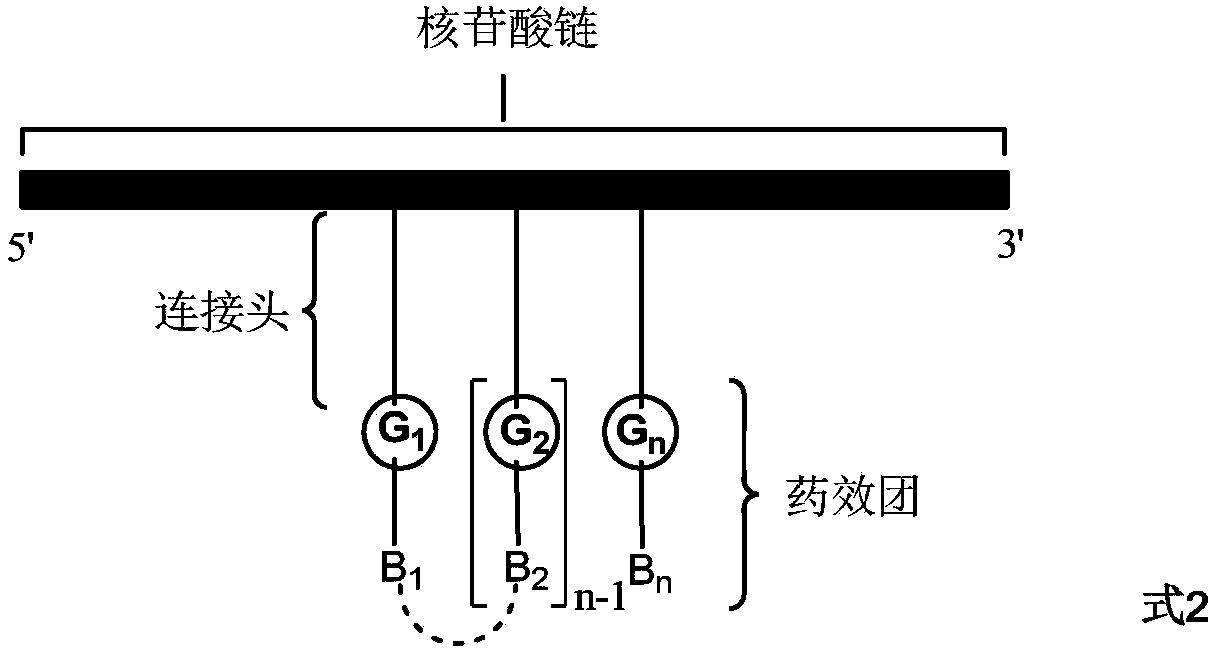
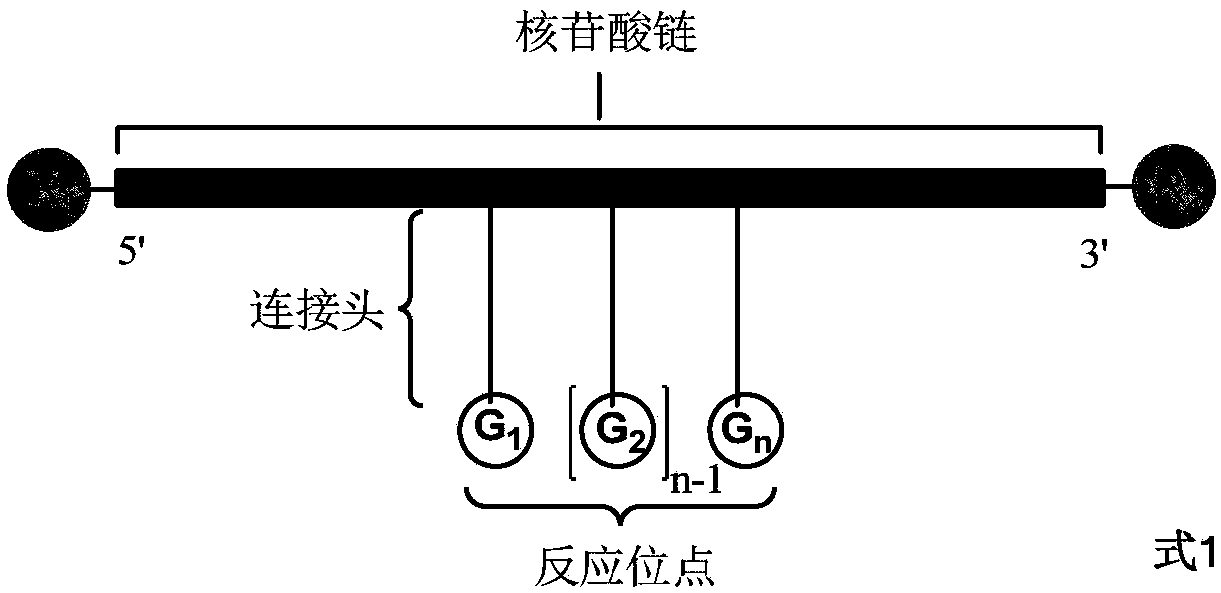
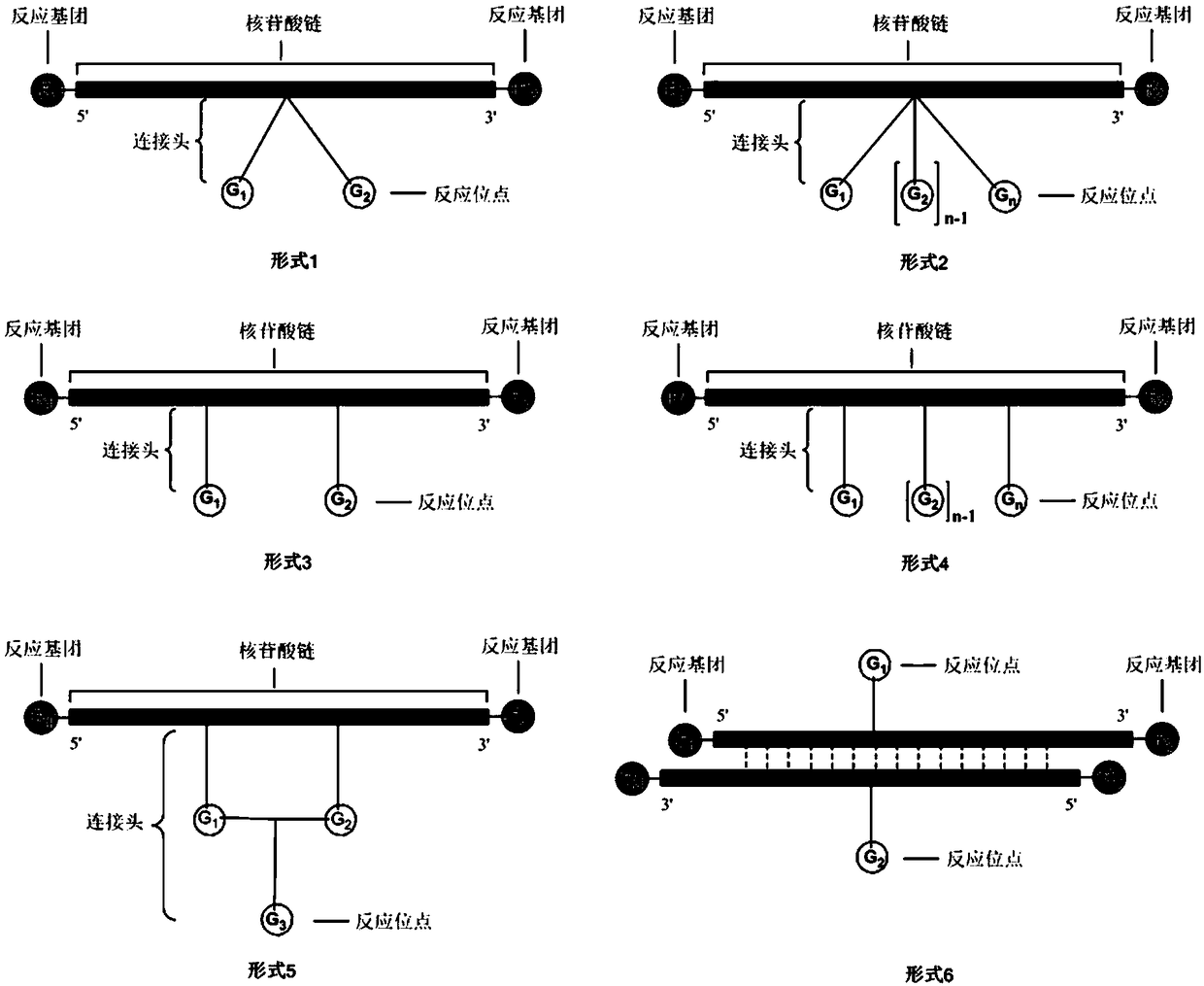
Method for preparing DNA coding compound library, initial head fragment compound and prepared DNA coding compound
A compound and fragment technology, applied in the field of combinatorial chemistry, can solve problems such as tedious coding transformation, heavy workload, and difficult screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Embodiment 1, the preparation of starting head fragment (SO-1)
[0075] A 5' phosphorylated nucleotide chain with the following sequence was synthesized as a starting head fragment and purified by HPLC by Suzhou Jinweizhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0076] 5'-PO 4 2- CTGCATA AGGCCT TAGTCTTdTTTdTTTGACTA AGGCCT TATGCAGCC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 01, MW: 14460.2, Figure 11)
[0077] dT has the following structure:
[0078]
[0079] The base was obtained by using the following monomer in a DNA synthesizer: Fmoc Amino-Modifier C6-dT-CEPhosphoramidite (MFCD08061991, CAS: 210534-16-0).
[0080] Part of the bases at both ends of the nucleotide chain is complementary pairing, which can form a large hairpin structure with a protruding base sequence CC and two cleavage sites ( AGGCCT ), the cleavage site for the nicking variant of the restriction endonuclease StuI. There are two bases in the middle of the hairpin ring, and there is a 6-carbon alkyl chain at the side chain C5 of t...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Embodiment 2, the preparation of the complete head fragment (SO-2) that has linker
[0083] The initial head fragment obtained in Example 1 was reacted with Fmoc-PEG5-NHS ester and Acid-PEG5-NHS ester to prepare the head fragment SO-2 with the following sequence.
[0084] 5'-PO 4 2- CTGCATA AGGCCT TAGTCTTdT(X)TTdT(Y)TTGACTA AGGCCT TATGCA GCC-3' (sequence number: 02, molecular weight: 15294.2)
[0085] X and Y represent any one of the following structures:
[0086]
[0087]
[0088]100 nmol of the starting head fragment (SO-1) was dissolved in 100 μl of sodium borate buffer solution (pH=9.5, 250 mM), 200 nmol of Fmoc-PEG5-NHS ester (MFCD28976702, CAS: 1402080- 11-8, molecular weight: 628.67, customized by Shanghai WuXi Kangde New Drug Development Co., Ltd.) was dissolved in 20uL dimethylacetamide (DMAc) and reacted in the solution of SO-1 at room temperature. Add 12 microliters of 5N sodium chloride solution and 360 microliters of cold ethanol to the reacti...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Example 3, Preparation of a DNA-encoded compound library with two pharmacophores in a 10×10 library
[0091] Step 1: Ligation of Initiating Primer to Complete Head Fragment SO-2 to Get Primed Head Fragment SO-2-P
[0092] In this exemplary DNA-encoded compound library, a fixed-coded nucleotide duplex (referred to as the initial primer, customized by Suzhou Jinweizhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd., HPLC purified) was connected to SO-2 for subsequent screening. General primer fragments for PCR of DNA-encoded compounds:
[0093] Starting primer upper chain: 5'-PO 4 2- -AAATCGATGACACAG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 03)
[0094] Starting primer lower strand: 5'-PO 4 2- -CATCGATTTGG-3' (sequence number: 04)
[0095] Mix 100 microliters of 100 nanomolar complete head fragment SO-2 aqueous solution with 110 microliters of a mixed aqueous solution of 110 nanomolar initial primer upper chain and 110 nanomolar initial primer lower chain, and then place in a PCR machine for 90 ℃ heating for 5 min...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com