Method for deep treatment of tail water of sewage treatment plant by using constructed wetlands
A sewage treatment plant and artificial wetland technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of high investment and operating costs, large-scale use of chemicals, secondary pollution of chemicals, etc., to facilitate later management and maintenance, high water purification efficiency, and reduce equipment replacement Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
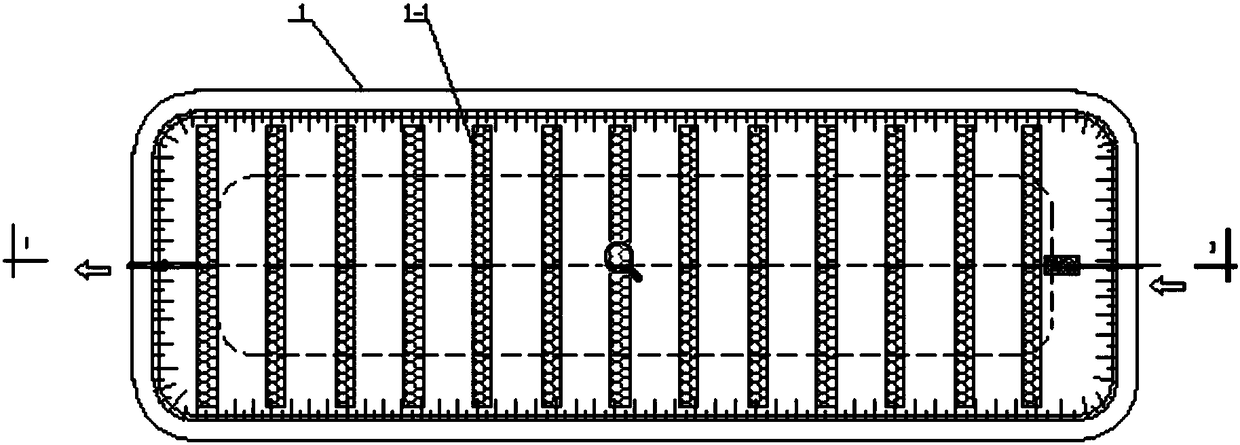
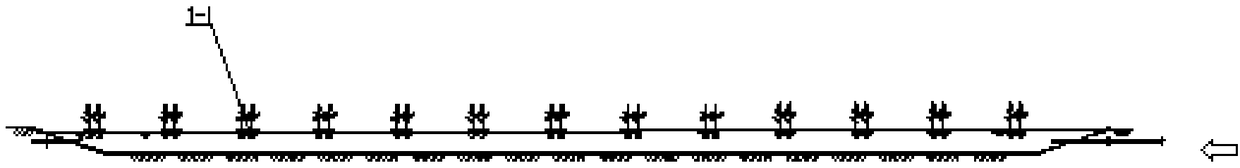
[0037] like Figure 1 to Figure 11 Shown, a kind of method of the present invention adopts artificial wetland advanced treatment sewage treatment plant tail water, comprises the following steps:
[0038] (1) The sewage to be treated is lifted by the lifting pump house 6 and then enters the sedimentation tank 1 for pretreatment, where the particulate matter settles. The sedimentation tank 1 is provided with an ecological floating bed 1-1; wetland plants capable of absorbing pollutants are planted on the ecological floating bed; a large number of microorganisms are attached to the root system surface of the wetland plants; the water depth of the sedimentation tank 1 is not less than 4m.
[0039] (2) The sewage enters the surface flow artificial wetland 2 from the sedimentation tank 1, and the pollutants in the sewage are further degraded. Pollutants in the sewage are further absorbed by plants and degraded by aerobic microorganisms; the water depth of the surface flow construc...
Embodiment 2
[0045]The difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is that a method for advanced treatment of tail water of a sewage treatment plant using a constructed wetland according to the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0046] In step (1), a large number of microorganisms are attached to the surface of the root system of the wetland plants; the water depth of the sedimentation tank 1 is not less than 4.5m. In step (3), the particle size of the packed gravel is 10 cm. In step (5), the natural ecological wetland 5 is provided with a second deep swamp 5-1 and a second shallow swamp 5-2. The water depth of the second deep swamp 5-1 is 1.5 mm.
Embodiment 3
[0048] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is:
[0049] A kind of method of the present invention adopts artificial wetland advanced treatment sewage treatment plant tail water, comprises the following steps: in step (1), the root system surface of described wetland plant adheres a large amount of microorganisms; The water depth of described sedimentation tank 1 is not less than 5m. In step (3), the particle size of the packed gravel is 15 cm. In step (5), the natural ecological wetland 5 is provided with a second deep swamp 5-1 and a second shallow swamp 5-2. The water depth of the second deep swamp 5-1 is 2.2m.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com