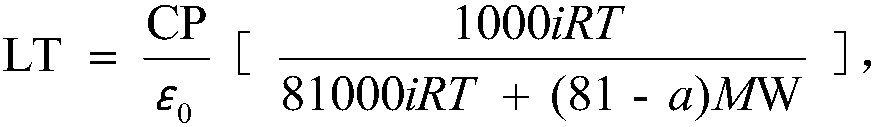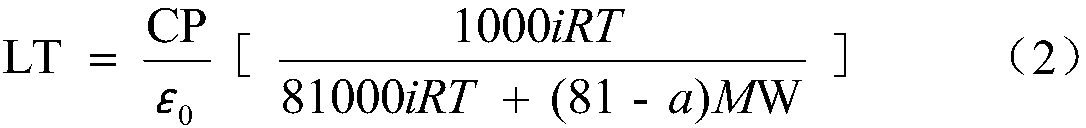Method for quantitatively detecting water retaining capability of plant leaf
A technology for plant leaves and water retention capacity, applied in the direction of applying stable tension/pressure to test the strength of materials, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of complex measurement process, long time, lack of quantitative technology, etc., and achieve accurate and reliable results. high sex effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Take the fresh branches of the mulberry tree with leaves, and wrap the base of the plant branches with a damp cloth to slow down the water dissipation; quickly return to the laboratory, clean up the dust on the surface of the mulberry leaves, and pick the more consistent growth on the fresh branches. Put 10 leaves in a container filled with water and soak for 30 minutes; after soaking for 30 minutes, the leaves become saturated with water, take out 10 leaves after soaking, and quickly and gently absorb the water on the surface of all leaves with a paper towel , put it on a dry and ventilated desktop to let it dry and lose water. After the leaves dry and lose water at 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 hours, take out one piece of the above-mentioned dried and water-losing leaves respectively, and measure them with a texture analyzer The maximum compressive internal force F of the left half of the main vein of the dehydrated leaf max (See Table 1); Measure the blade water potential W ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Taking mulberry as an example, all steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0068] Table 4 The maximum compressive internal force F of mulberry leaves at different dehydration moments max , leaf water potential W and physiological capacitance CP
[0069]
[0070] Table 5 Ultimate stress σ of mulberry leaves at different dehydration moments max , blade tension LT and blade stiffness LCS
[0071]
[0072]
[0073] Table 6 Average leaf stiffness LCS, relative leaf stiffness RLCS and cumulative relative leaf stiffness TRLCS of mulberry trees at different dehydration moments
[0074]
[0075] Therefore, the leaf water retention capacity of mulberry is 5.33.
[0076] Implementation effect of the present invention is as follows:
[0077] It can be seen from Tables 3 and 6 that the water retention capacity of the leaves of the mulberry tree (9.16) is greater than that of the mulberry tree (5.33), indicating that the drought resistance of the mulberry tree is higher...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com