Method for predicting thermal mechanical fatigue life of metal material based on low cycle fatigue
A thermo-mechanical fatigue and low-cycle fatigue technology, applied in computer-aided design, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large experimental volume, low accuracy, high time, labor, and money costs, and achieve a clear physical meaning. , good applicability, good universal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
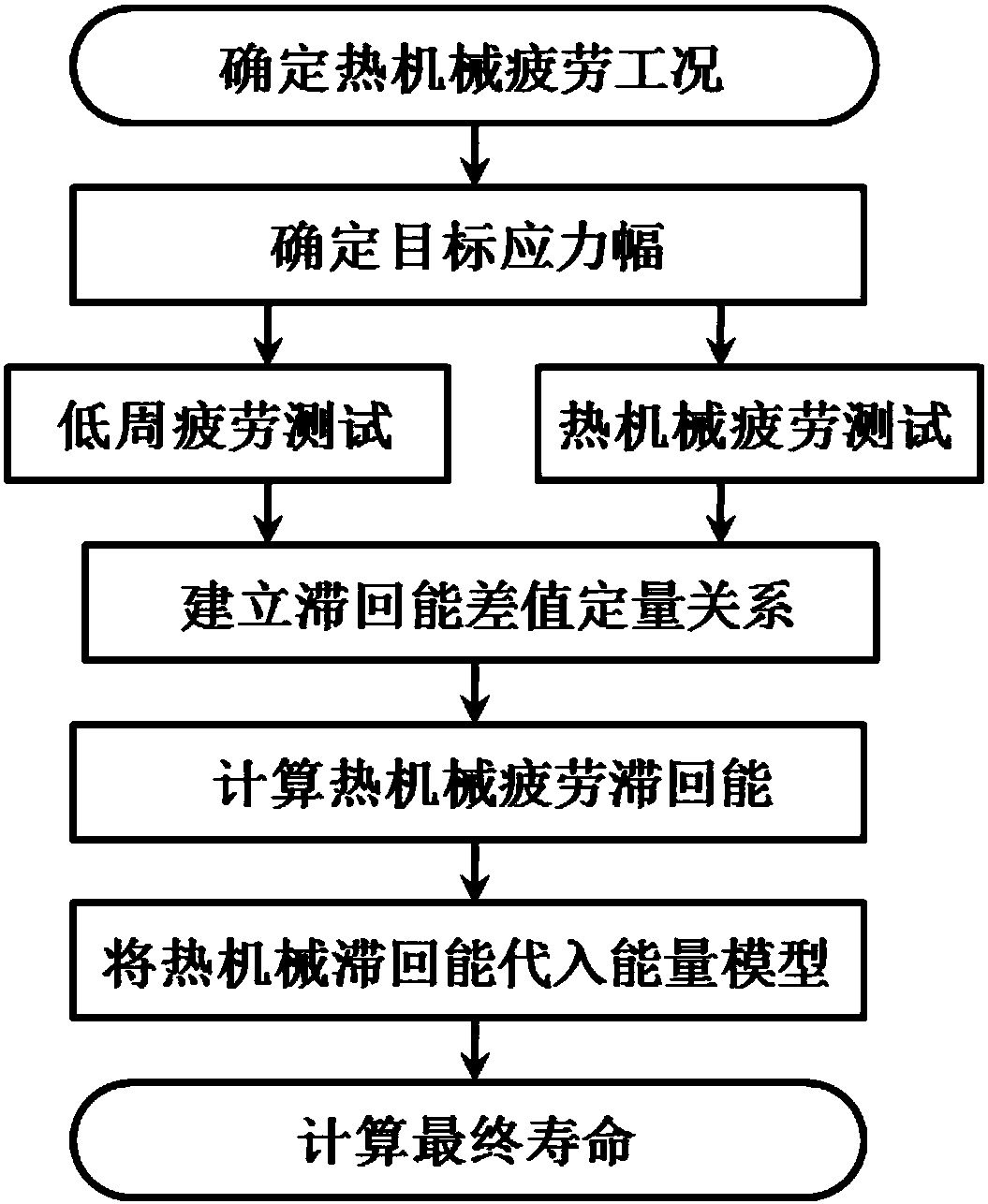
[0034] This embodiment is to predict the life of cast iron materials under the reverse potential thermomechanical fatigue condition. The prediction process is as follows figure 1 As shown, the specific process is as follows:
[0035] First, the cast iron material is taken from the diesel engine cylinder head. According to the working conditions, it is determined that the required predicted thermomechanical fatigue temperature load is 125-400°C and 125-500°C, and the mechanical strain condition is ±0.1%-±0.4%.
[0036] Second, in this embodiment, for the working condition of 125-400°C, the target strain amplitude is ±0.15%, ±0.2%, ±0.3%; for the working condition of 125-500°C, the target strain amplitude Values are ±0.15%, ±0.2%, ±0.3%. Here, multiple strain amplitudes are selected as the target strain amplitudes, the purpose of which is to compare with the experimental results.
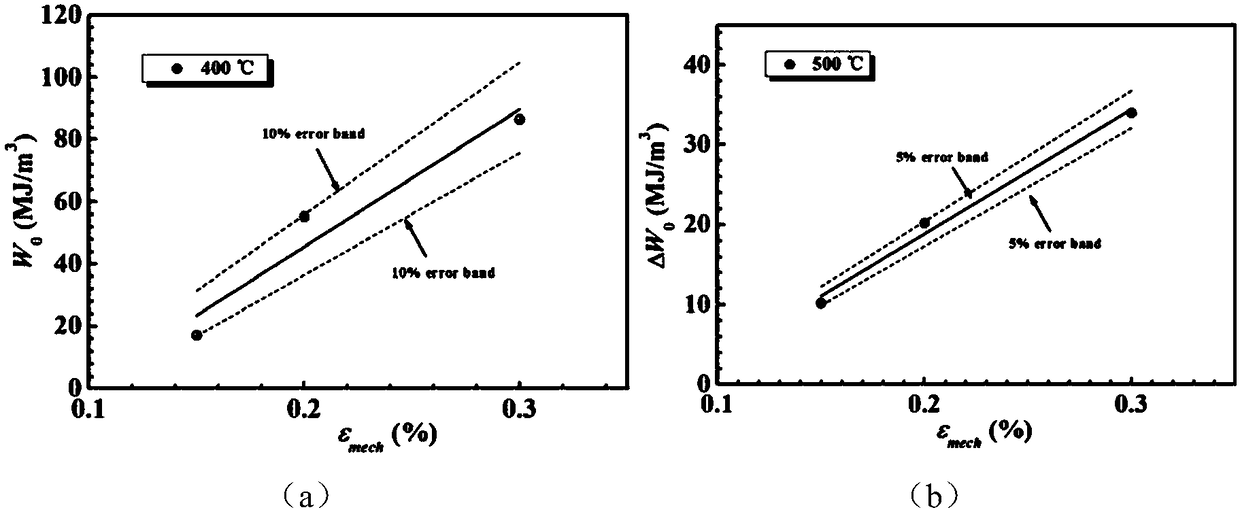
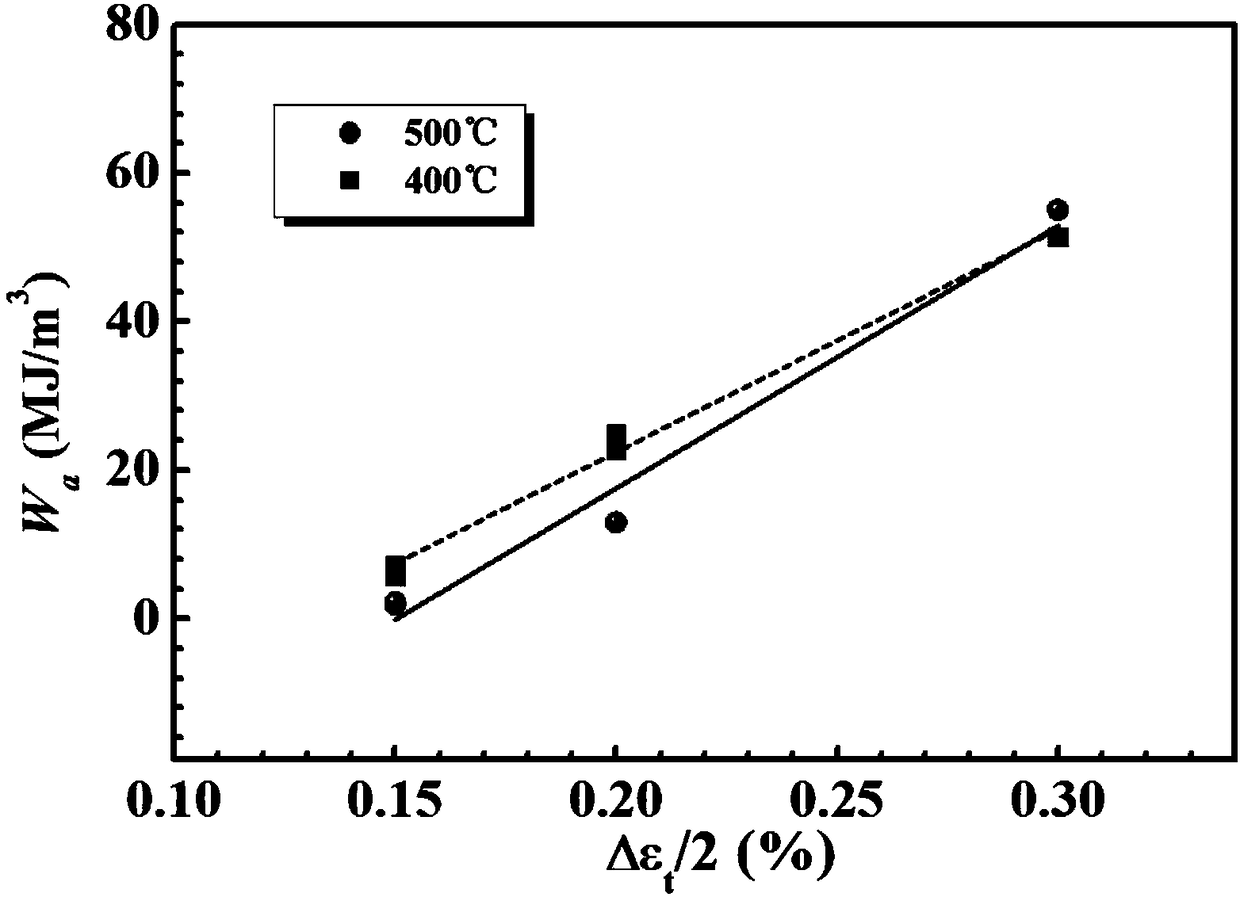
[0037]Third, the low cycle fatigue test, the test conditions are: three tests at 400°C, with m...
Embodiment 2
[0053] This embodiment is to predict the life of the cast aluminum material under the condition of thermomechanical fatigue in the same direction.
[0054] First, the cast aluminum material is taken from the diesel engine piston. According to the working conditions, it is determined that the required predicted thermomechanical fatigue temperature load is 125-350°C, and the mechanical strain condition is ±0.1%-±0.4%.
[0055] Second, in this embodiment, for the temperature load of 125 to 350°C working conditions, the target strain amplitudes are ±0.25%, ±0.35%, ±0.3%, ±0.45%; multiple strain amplitudes are selected here , as the target strain amplitude, the purpose of which is to compare with the experimental results.
[0056] Third, the low cycle fatigue test, the test conditions are: four tests at 350°C, the mechanical strains are ±0.25%, ±0.35%, ±0.3%, ±0.45% respectively; calculate the median life hysteresis loop area of each test data .
[0057] Fourth, thermomechanica...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com