A pcanet image change detection method based on saliency analysis
An image change detection and salience technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of poor overall accuracy execution efficiency, the influence of scattering noise on classification results, and influence on sample selection, so as to achieve reliable training features, reduce influence, and improve detection speed. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
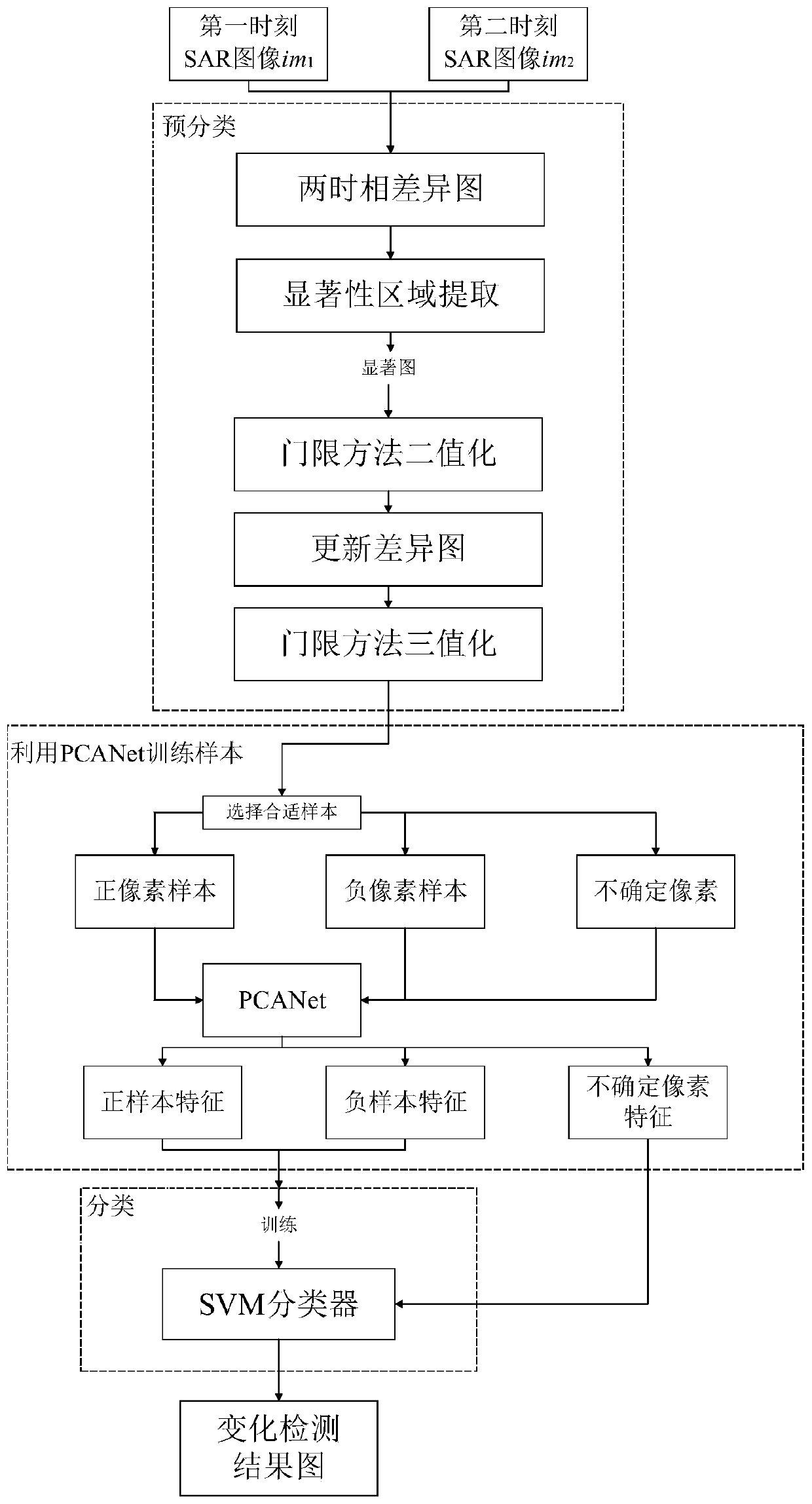
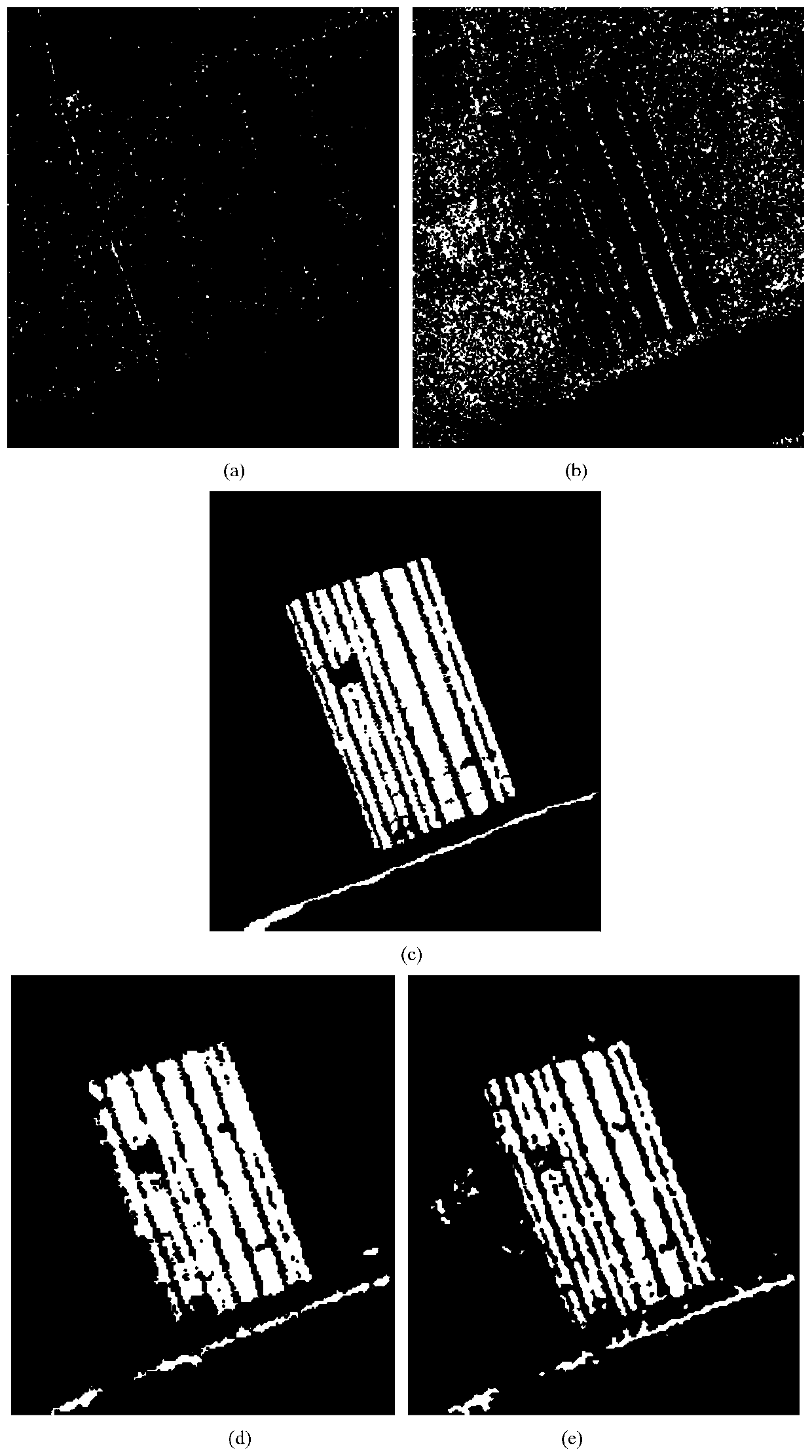
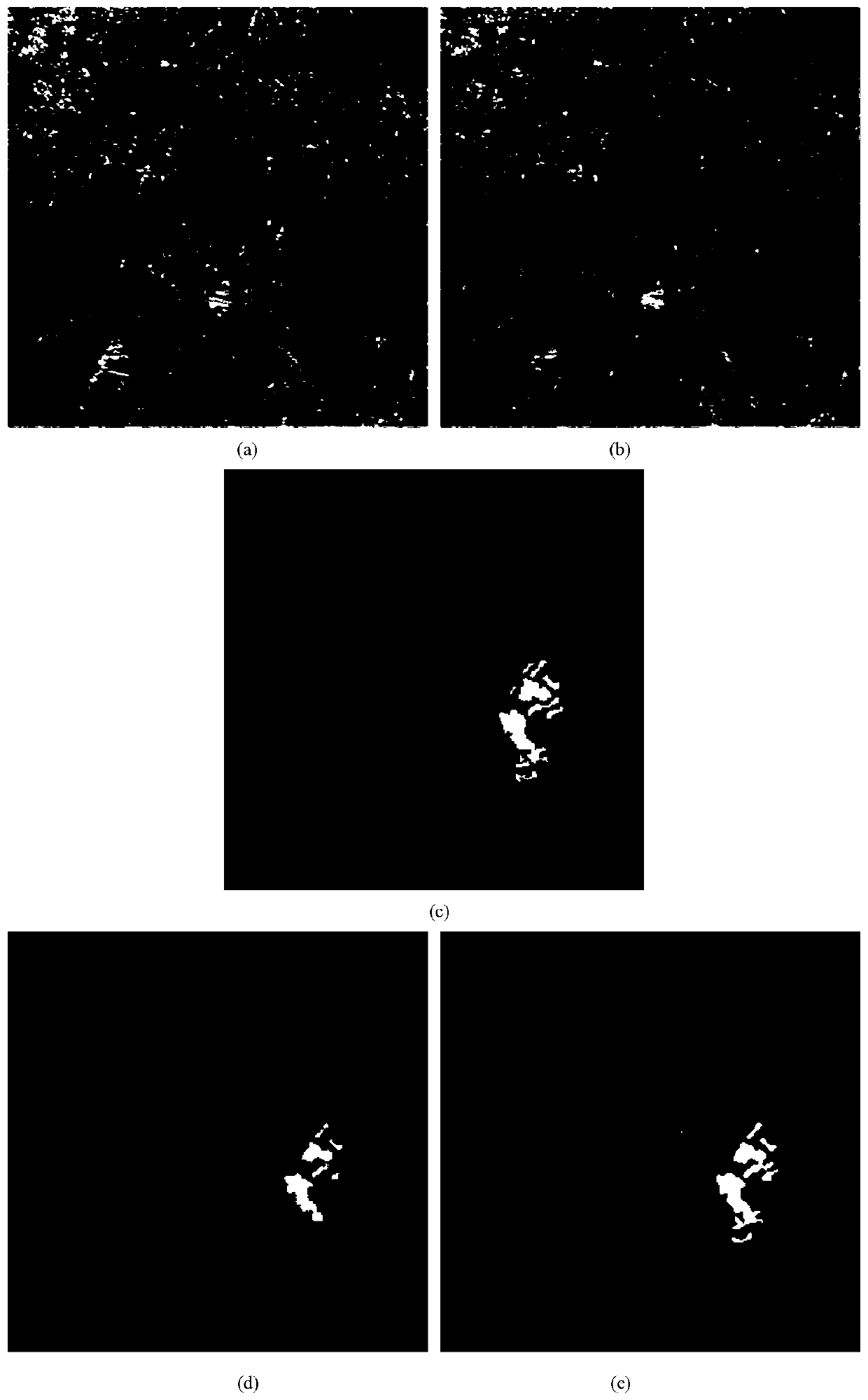
[0026] Change detection for SAR images, including SAR image transformation detection methods based on discriminant random fields and PCANet-based deep learning networks, but the above-mentioned change detection methods have poor overall accuracy and execution efficiency for SAR image change detection results And the classification results are seriously affected by scattering noise. The present invention studies the above problems, and proposes a PCANet image change detection method based on saliency analysis, which is used for SAR image change detection. In order to more accurately analyze the changes in the same area at different times, obtain reliable environmental change data, or detect military targets, as well as monitor and evaluate natural disasters, it is necessary to first obtain two sets of SAR images in the same area at different times. These two sets of SAR images are used for change detection with high accuracy and detection efficiency, and the determined changed ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The PCANet image change detection method based on significance analysis is the same as embodiment 1, described in step (2) according to four reference principles of significance region extraction method setting similarity measure value d(p i ,q k ) and get the significant value specifically is:
[0045]
[0046]
[0047] Among them, c=f is a constant parameter, and f can take any positive integer. In this example, f takes a value of 5, and d color (p i ,q k ) represents the sub-block p i and q k The color value Euclidean distance; k∈[1,K], K=m represents the distance between two samples, m can take any positive integer according to the needs of the sample, in this example, the value of m is 64; d position (p i ,q k ) represents the sub-block p i and q k The Euclidean distance of the location; d(p i ,q k ) means with p i The color distance of the kth sub-block with the highest similarity, if the Euclidean distance between the k-th sub-block and the co...
Embodiment 3
[0049] The PCANet image change detection method based on significance analysis is the same as embodiment 1-2, the optimized significant value result described in step (3) for:
[0050]
[0051] Among them, will as the point of interest; is the Euclidean position distance between pixel i and the nearest point of interest, and its value is normalized to [0,1]; R={r 1 ,r 2 ,...,r m} represents the set of block sizes around the computed pixel i.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com