Magnetic components with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy maintaining high coercivity after high temperature annealing
An anisotropic, magnetic storage element technology, applied to the components of electromagnetic equipment, material selection, magnetic field controlled resistors, etc., can solve problems such as high Hc and thermal stability, hard mask material diffusion, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
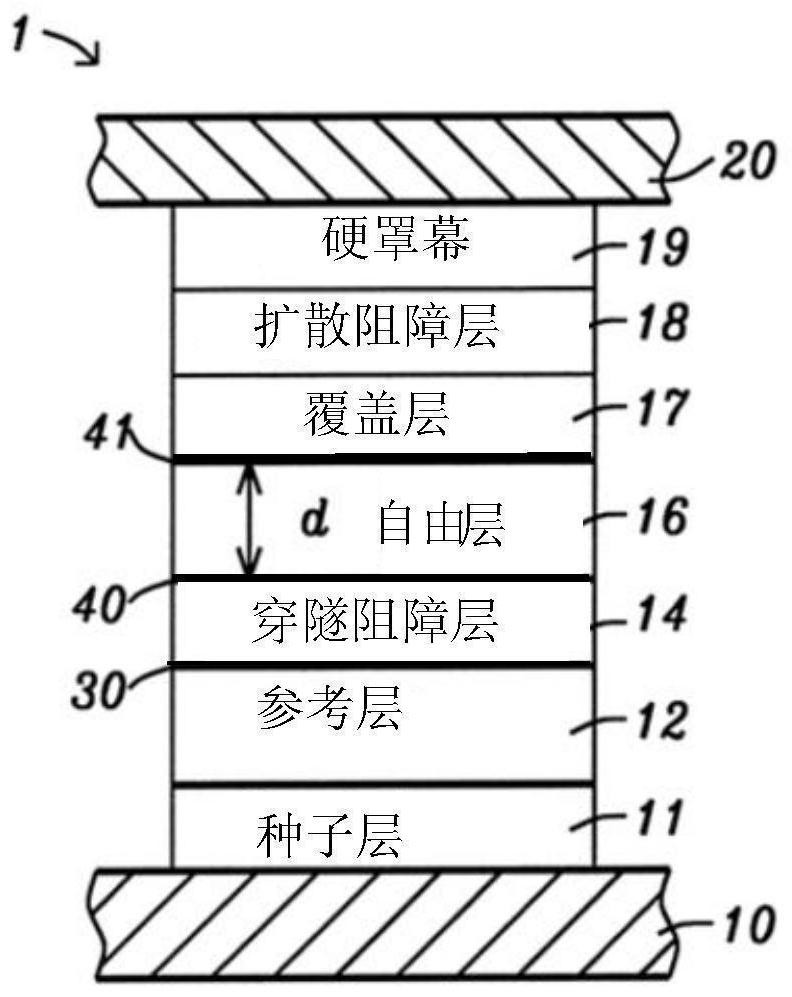
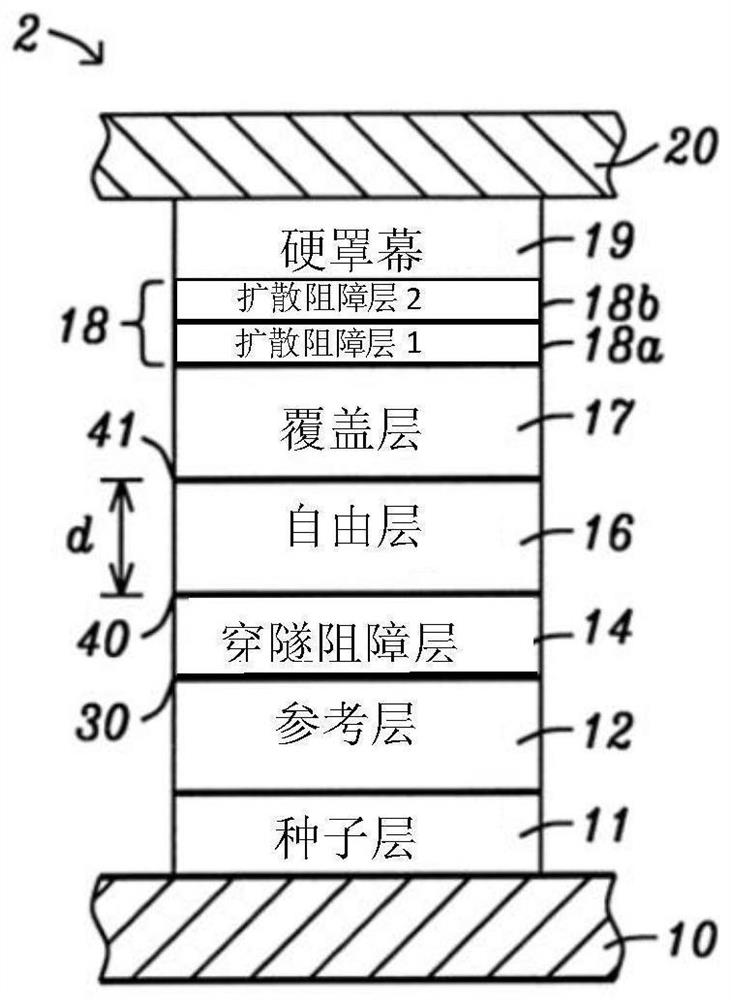
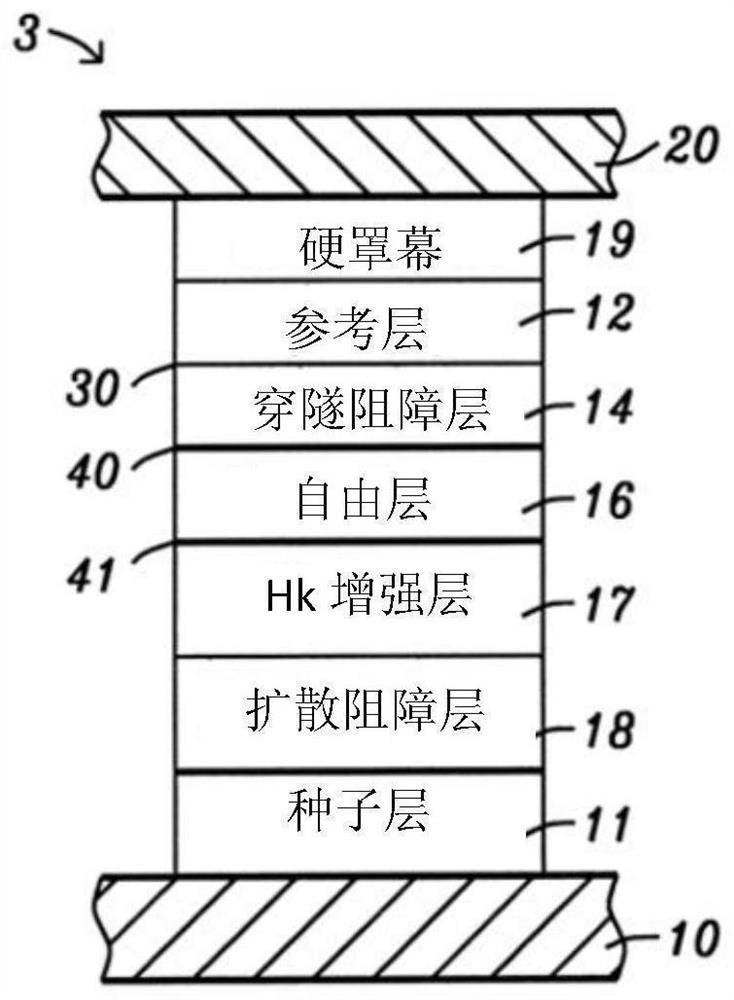
[0035] The present invention is an MTJ assembly in which the free layer has a thermal stability of at least 400°C due to the fact that the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in the free layer is established through the interface with the two metal oxide layers, and in which The diffusion barrier prevents the non-magnetic metal from diffusing from the hard mask or bottom electrode into the adjacent metal oxide layer, thereby maintaining the PMA and Hc in the free layer. If processed at high temperatures, MTJ components can be used in magnetic memory devices such as MRAM and STT-MRAM, in spintronic devices such as MAMR and STO, and as TMR sensors between top and bottom shields in read heads. As understood by those skilled in the art, an MTJ can have a bottom spin valve, top spin valve, or dual spin valve configuration. Although multiple MTJ assemblies are typically formed on a substrate, only one MTJ assembly is shown in the exemplary embodiment for simplicity of illustrati...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com