Microwave hyperthermia monitoring method based on ultrasonic echo decorrelation imaging technology
A technology of microwave hyperthermia and ultrasonic echo, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve the problems of high cost, unsuitable for long-term monitoring, real-time performance and low imaging resolution, and achieve the effect of reducing tissue cavitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
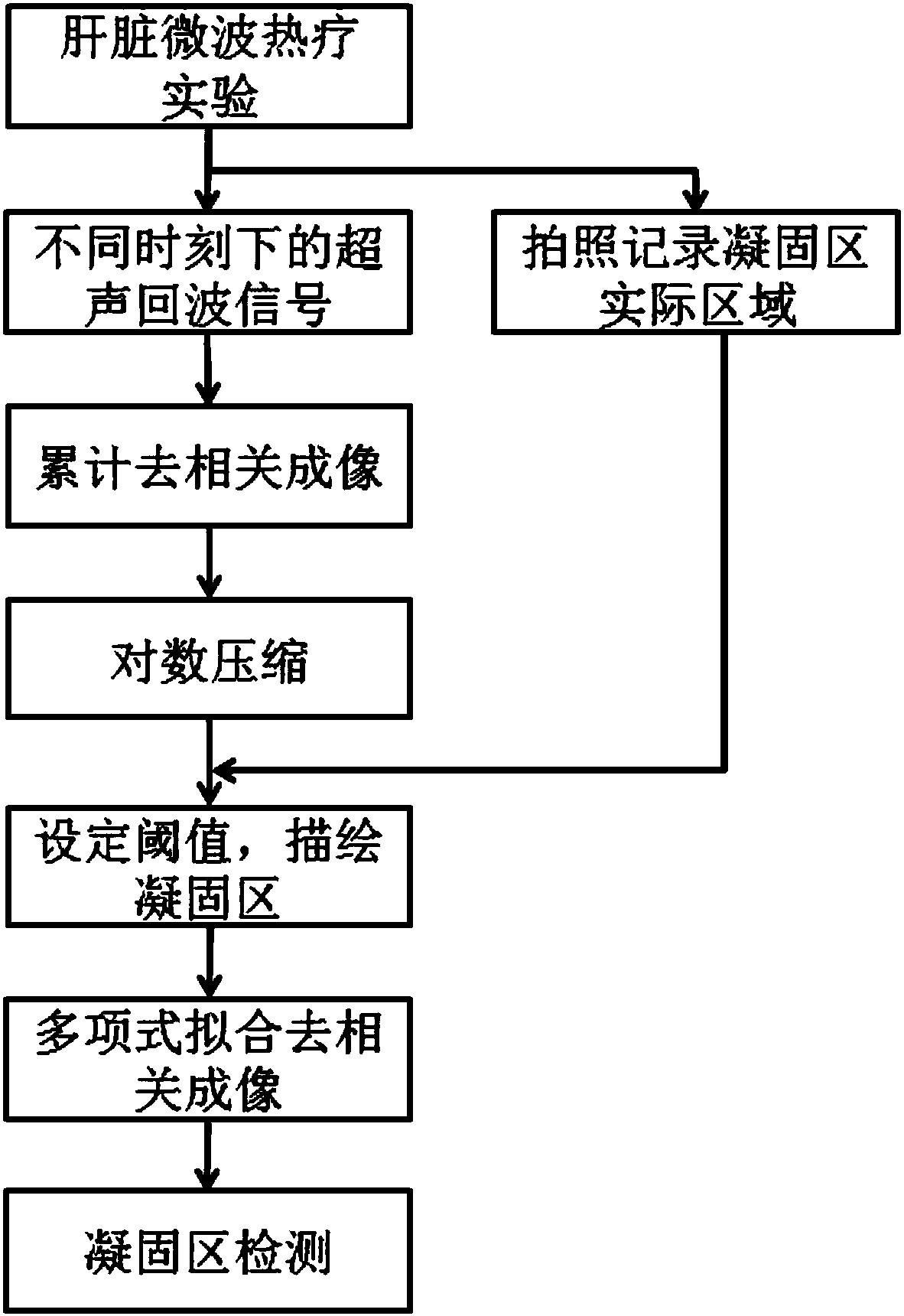
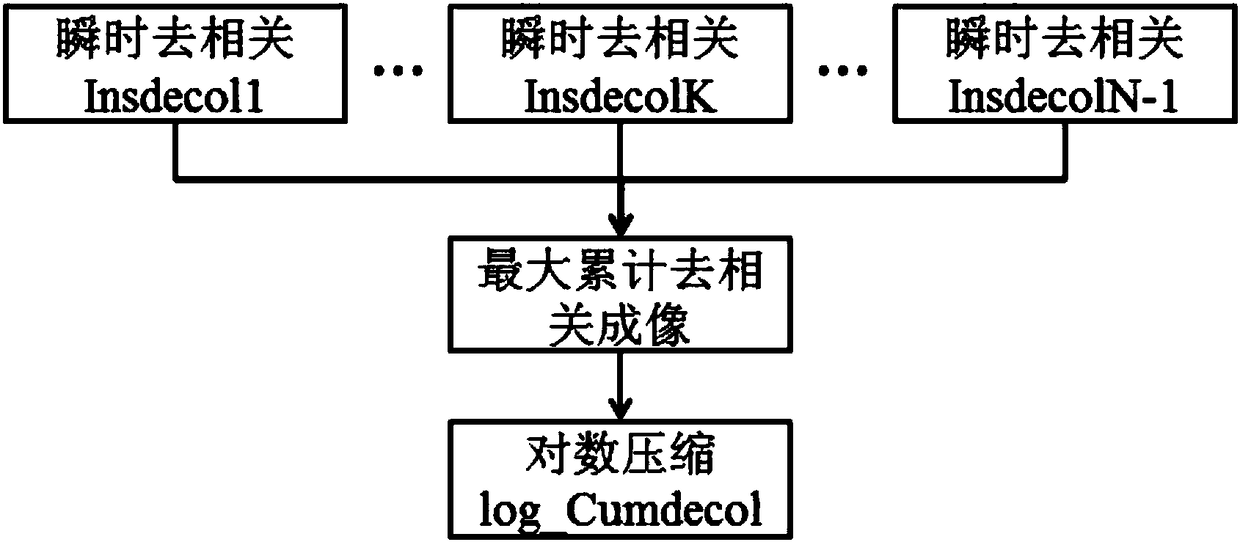
[0027] Such as figure 1 Shown is a flow chart of the method of the present invention, which mainly includes maximum accumulative decorrelation imaging based on ultrasonic echo signals and coagulation zone delineation based on accumulative decorrelation images.
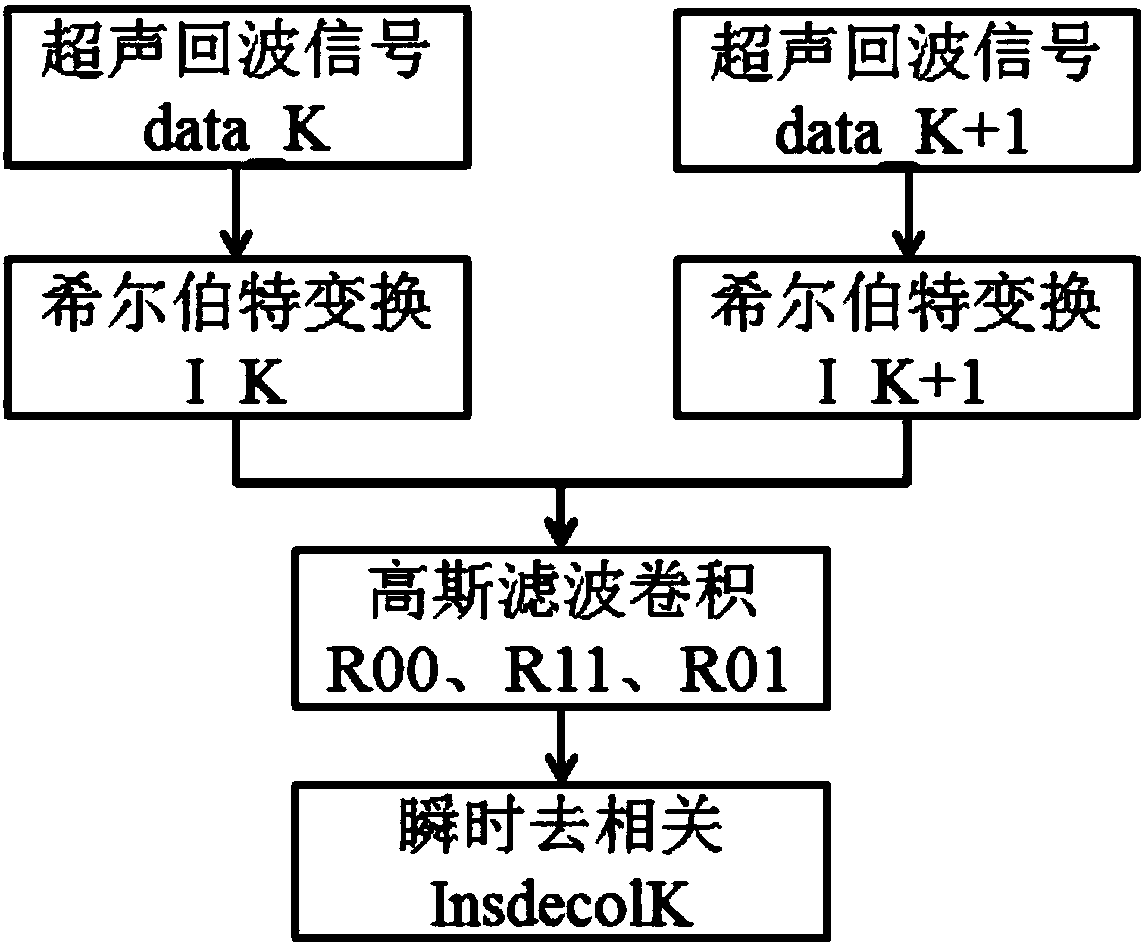
[0028] Such as figure 2 As shown, the ultrasonic echo transient decorrelation imaging specifically includes:
[0029] Step 1. Continuously collect ultrasonic echo signals data_1, data_2...data_N at different moments of microwave hyperthermia;
[0030] Step 2. Perform Hilbert transform on two adjacent frames of ultrasound data data_K and data_K+1 to obtain complex analysis signals I_K and I_K+1;
[0031] Step 3. Perform Gaussian convolution filtering on I_K.*conj(I_K+1), abs(I_K).^2 and abs(I_K+1).^2 respectively to obtain R01, R00 and R11;
[0032] Step 4. According to the formula 2*(R00.*R11-abs(R01).^2). / (R00.*R11+mean(mean(R00.*R11))) calculate the instantaneous mean value of two adjacent frames of ultrasound da...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com