Manufacturing method of LED array device
A technology of LED array and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of identification devices, instruments, electrical components, etc., and can solve the problems of slow transfer speed, low efficiency, and difficulty in mass production of micro-LED displays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
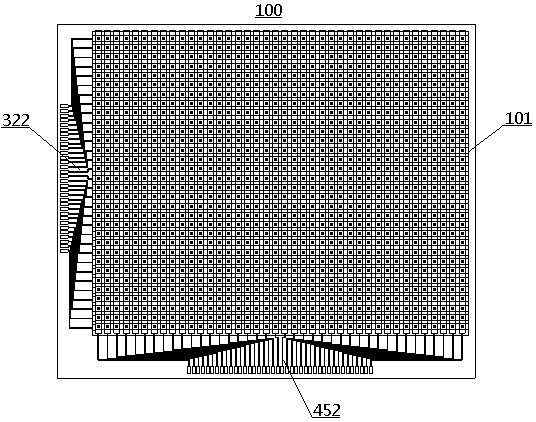
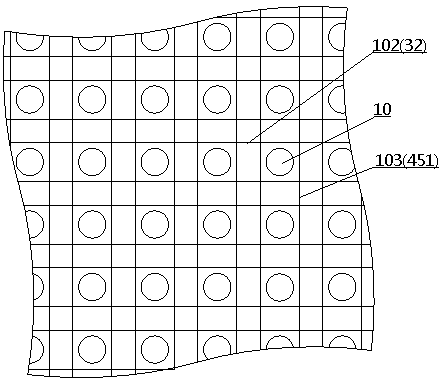
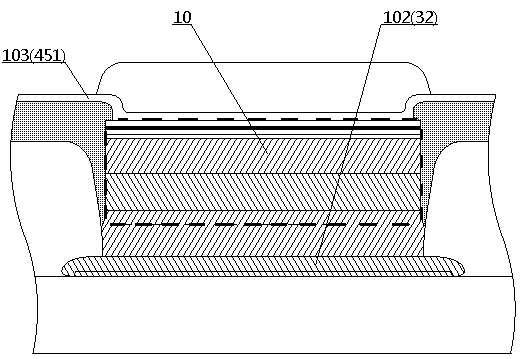
[0098] Embodiment 1 provides the manufacturing method of LED display 100, such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, display 100 is a passively driven monochrome LED display having a pixel area of 1.61 inches and a resolution of 40×32. The main body of the display 100 is an LED array 101, which includes 40×32 LED devices 10 arranged in a square matrix, and the pitch of the LED devices 10 is 0.8mm. The LED array 101 is driven by intersecting row electrodes 102 and column electrodes 103, and each pixel has image 3 The cross-sectional structure shown.
[0099] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the LED device 10 is a GaN-based blue light vertical circular LED device with a standard diameter of 0.3mm, and its film layers are the first bonding layer 11, the soft magnetic metal layer (the first magnetic part) from the inside to the outside. ) 12, non-magnetic metal layer 13, first electrode 14 and semiconductor layer 15. Among them, the first bonding layer 11 is a 5 μm thick tin metal layer, t...
Embodiment 2
[0123] Such as Figure 32 As shown in —34, what the second embodiment will make is an active matrix driven color LED display 200, which has a pixel area of 26 inches and a resolution of 1920×1080, and each pixel 201 further includes a red (R) , green (G), blue (B), and white (W) sub-pixels 202 in four primary colors. The main body of the display 200 is an LED array 203, which includes a total of 8,294,400 LED devices 10 arranged in a square matrix of 1920×1080×4, and the pitch of the LED devices 10 is 150 μm.
[0124] The LED device 10 of the second embodiment is basically the same as that of the first embodiment (refer to Figure 4 ), the difference is that the diameter of the LED device in Embodiment 2 is 100 μm, the thickness of the soft magnetic metal layer and the copper metal layer are both 20 μm, and the first bonding layer is changed to an indium metal layer with a thickness of 3 μm. The LED device is suspended in DI water to form a dispersion liquid with a dispers...
Embodiment 3
[0135] Such as Figure 54 As shown, the display 300 to be produced in the third embodiment is basically the same as that in the second embodiment, the difference is that each pixel 301 includes a red sub-pixel (R sub-pixel) 3021, a blue sub-pixel 3022 (B sub-pixel ) and two green sub-pixels 3023 (G sub-pixels). In order to save the setting step of the colored layer, the third embodiment uses LED devices of three colors, which are red LED 101 (GaAs LED), blue LED 102 (GaN LED) and green LED 103 (GaP LED). The diameters of the LED devices are 100 μm, 162 μm and 50 μm respectively, and their structures and manufacturing steps (epitaxy substrates used and process parameters may be different) are the same as those of the LED devices used in Example 2, and they are made into DI aqueous dispersions 1911, 1911, and 1911 respectively. 1912 and 1913.
[0136] The design and fabrication steps of the motherboard, base layer and driving circuit layer of the third embodiment are basically...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com