Mitochondria sequence splicing and copy number measuring method based on high-throughput sequencing
A technology of sequence splicing and mitochondria, applied in the field of genomics, can solve the problems of high sample quality requirements, troublesome design, complicated operation, etc., and achieve the effects of low sample quality requirements, low unit cost, and simple experiments.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The mitochondrial DNA sequencing and assembly of three cases of Eriocheir sinensis included the following steps:
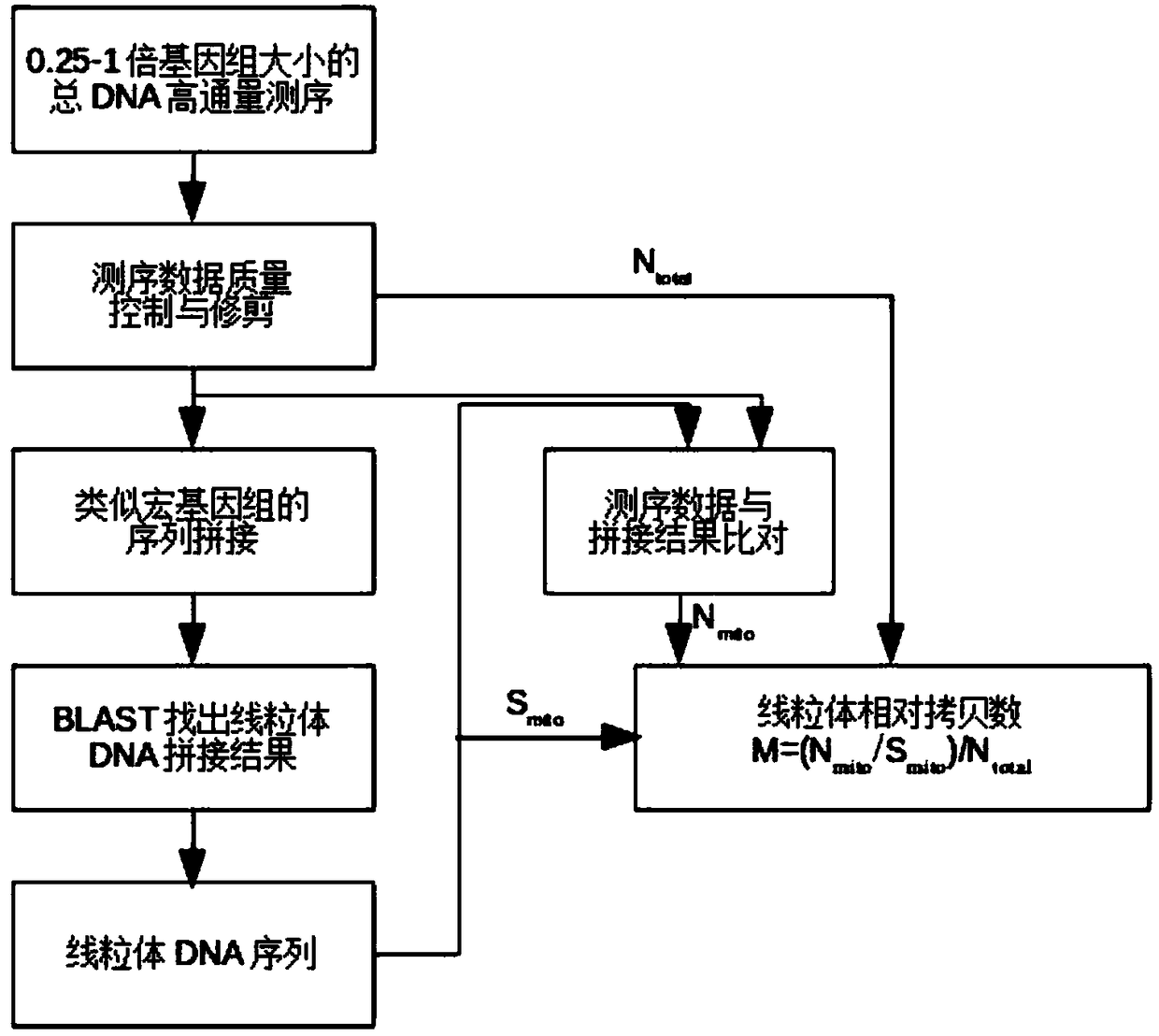
[0037] 1. The total DNA of the muscle tissue of 3 Chinese mitten crabs was ultrasonically interrupted to 500-700bp and used DNA library construction kits construct high-throughput sequencing libraries.
[0038] 2. Construct and use high-throughput sequencing library NextSeq500 high-throughput sequencer performs sequencing, and the sequencing volume of each sample is 2G. And use bcl2fastq software to convert the sequencing results into fastq format.
[0039] 3. Use Trimmomatic software to control the quality of the sequencing data. The specific key parameters are: LEADING:5TRAILING:5SLIDINGWINDOW:4:15MINLEN:30 to obtain high-quality sequencing data.
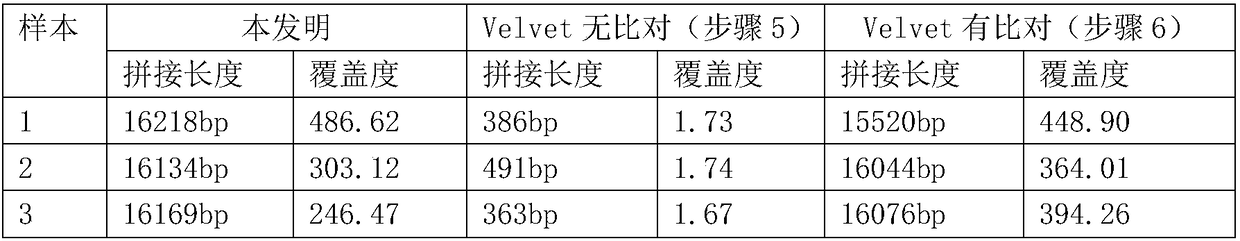
[0040] 4. Use SPAdes software to splice the above-mentioned high-quality sequencing data. The specific key parameters are: --meta-k 55 (see Table 1).
[0041] 5. The control group used velvet software to splice the ab...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The effect of different sequencing amounts and the proportion of mitochondrial DNA sequences on the splicing effect is as follows:
[0049] 1. Simulate data with different sequencing amounts and mitochondrial DNA sequence ratios. Using the high-quality sequencing data of the sample in Example 1, randomly select 1 / 3, 1 / 6, and 1 / 12 of the data, and use the data without mitochondrial DNA to merge with the aforementioned randomly selected data until the total amount of data reaches 2G, 1G and 0.5G.
[0050] 2. Use SPAdes software to splice the simulated data, and the splicing process refers to step 4 in the above embodiment 1.
[0051] 3. Find the spliced mitochondrial DNA sequence in the splicing result, and the method is the same as step 7 in Example 1.
[0052] The stitching results of the simulation results are as follows:
[0053] sample
[0054] The results show that even if the mitochondrial DNA content in the data is reduced to 1 / 12 of the original data, longer splicin...
Embodiment 3
[0056] To calculate the mitochondrial copy number in the sequencing data, the steps are as follows:
[0057] 1. Sequencing and splicing data are the data and splicing results used in Example 1. Use Reseqtools software to view the total number of bases in high-quality data, denoted as N total .
[0058] 2 Calculate the total length of mitochondrial DNA after splicing and mark it as S mito .
[0059] 3 Use bowtie2 software to compare high-quality data to the sequence of mitochondrial splicing results and generate sam data files. Use the flagstat function of samtools to calculate the above sam file to obtain the total base number of reads that can be compared to the mitochondrial DNA sequence, denoted as N mito .
[0060] 4 Calculate the normalized copy number of the sample M = (N mito / S mito ) / N total . The results are as follows:
[0061] sample
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com