A library robot positioning and navigation method
A technology of robot positioning and navigation method, which is applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, instrument, vehicle position/route/height control, etc., and can solve problems such as complex travel route, increased cost, and positioning failure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
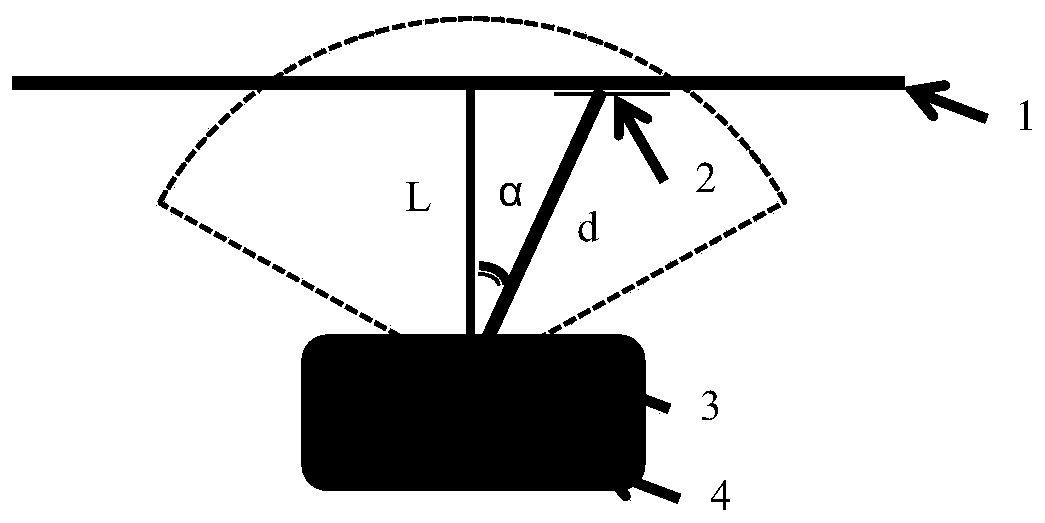
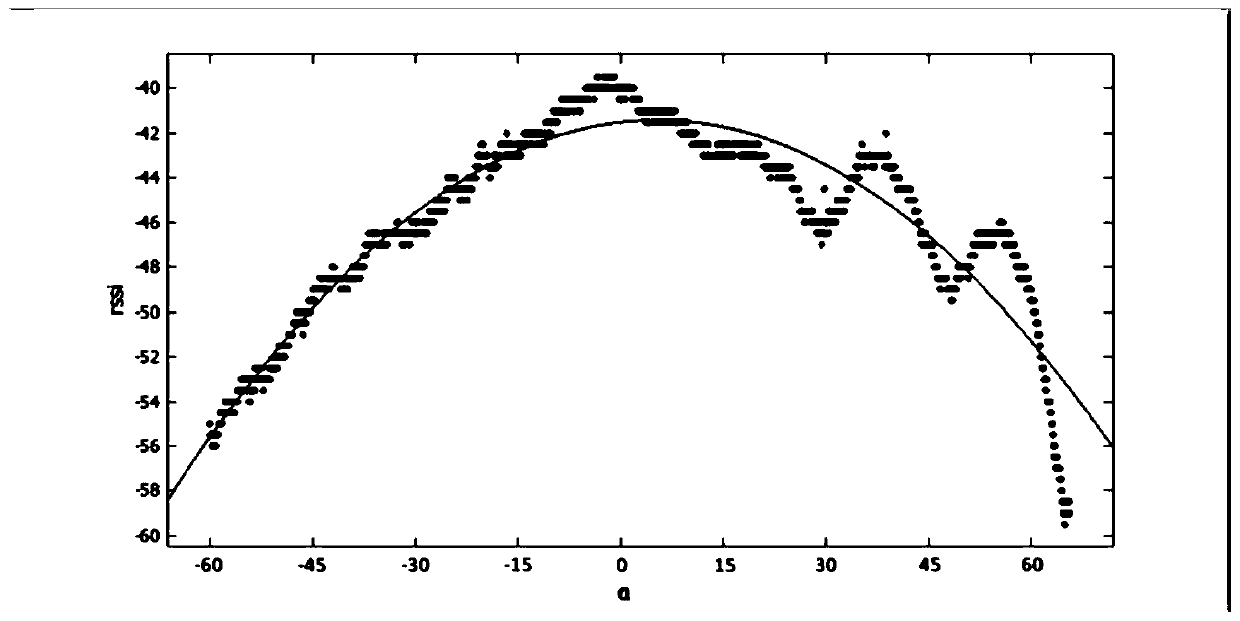
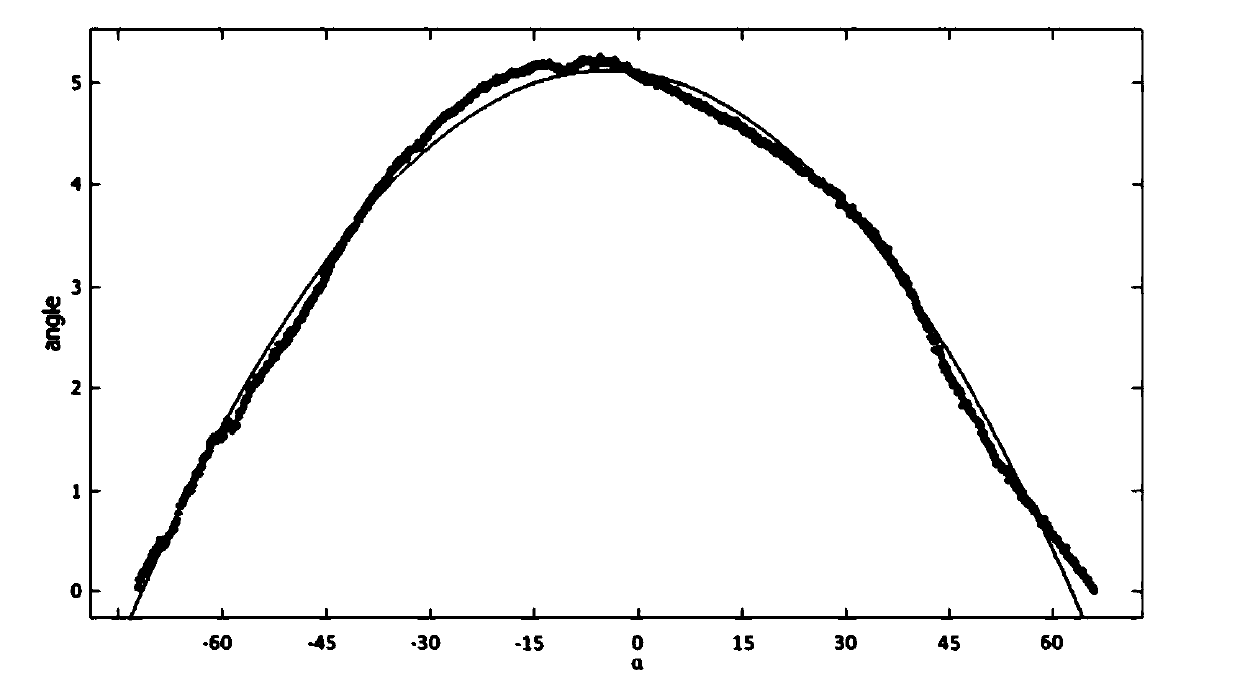
[0085] RFID technology is mainly composed of three parts: antenna, reader and RFID tag. There are three types of RFID tags in terms of starting energy. The most important one is passive RFID tags. RFID tags do not have energy themselves, and only transmit data by reflecting radio frequency signals emitted from the antenna. The reflected signal can be described by a variety of physical properties, RSSI value and phase angle are two of them. According to the formula, the relationship between the distance and the RSSI value is as follows:
[0086] d=10^((abs(RSSI)-A) / (10*n)).....(6)
[0087] Among them, d is the straight-line distance between the antenna center point and the RFID tag, RSSI is the received signal strength (negative value), A is the RSSI value when the distance between the transmitting antenna and the RFID tag is 1 meter, n is the environmental attenuation factor, and the above formula is converted Available:
[0088] RSSI=-log(10*n*d+A)......(7)
[0089] In th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com