P-xylene crystal separation method
A technology of para-xylene and crystallization separation, applied in the direction of crystallization separation, crystallization purification/separation, solution crystallization, etc., can solve the problems of raw material liquid disturbance, unfavorable crystal growth, affecting crystallization efficiency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
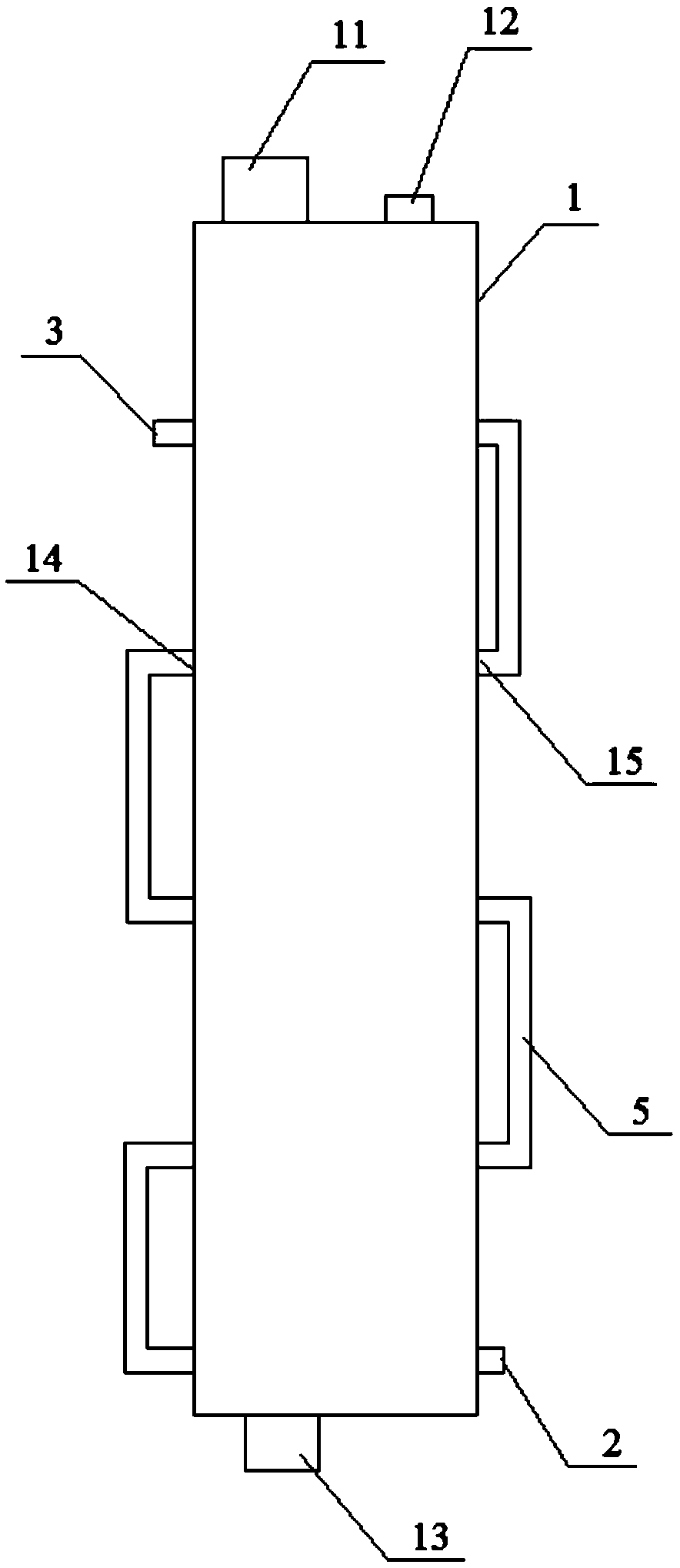
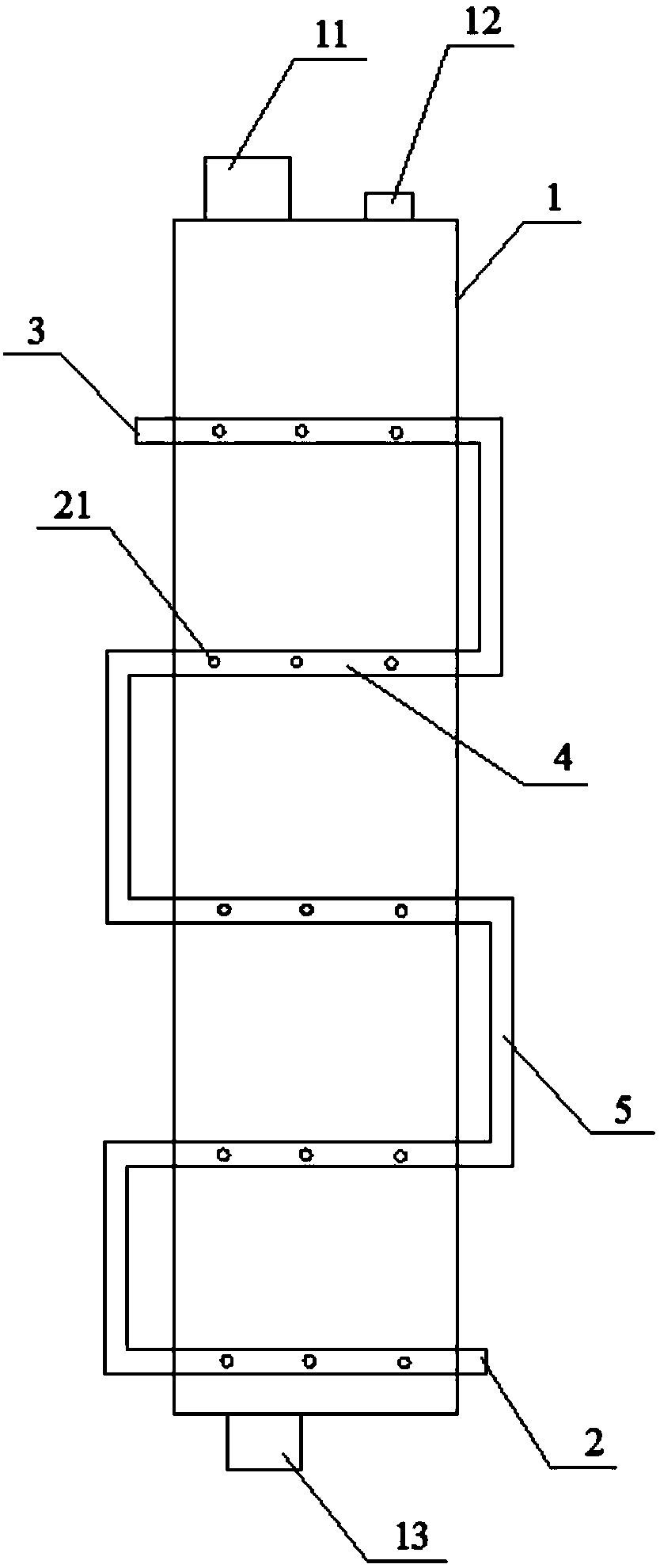
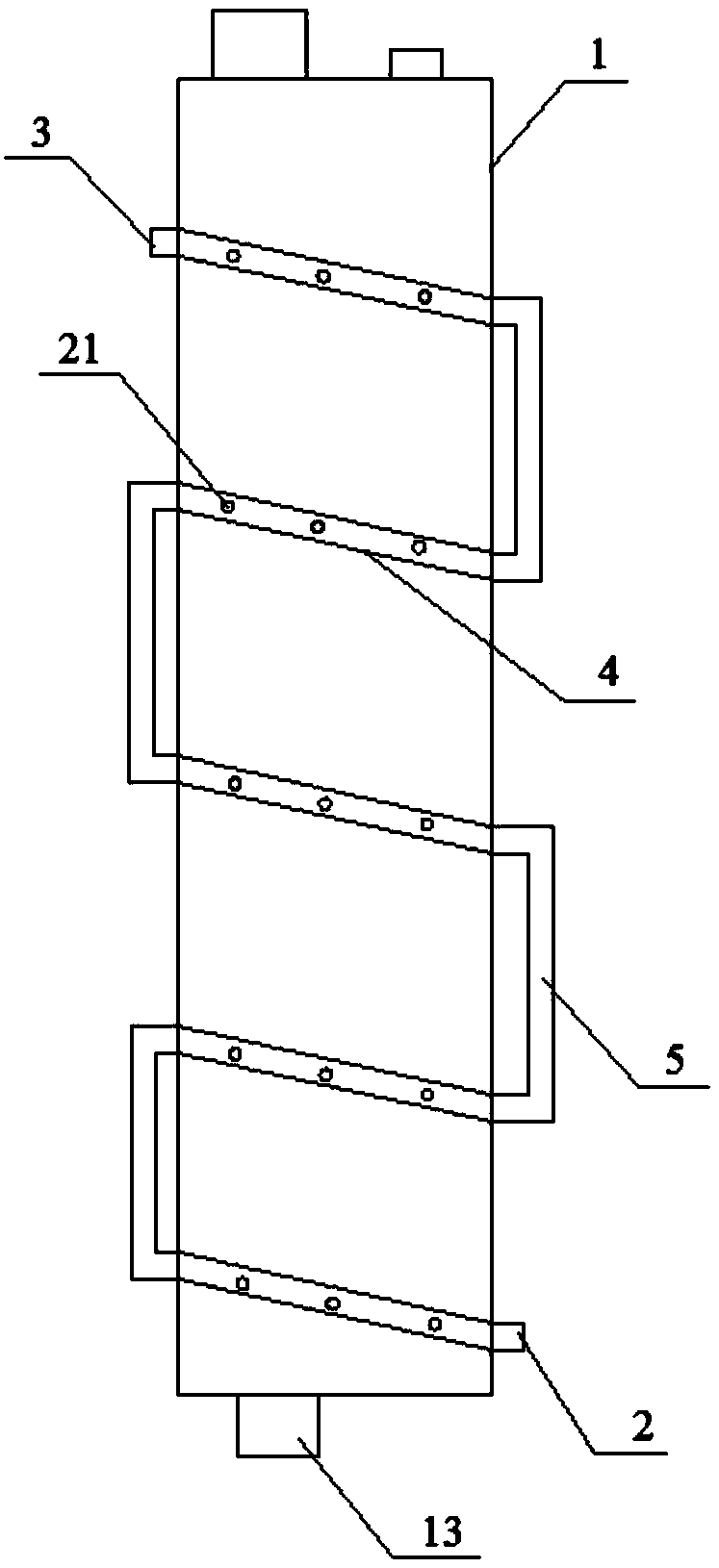
[0026] A method for crystallization and separation of p-xylene, the device structure for crystallization and separation of p-xylene is as follows Figure 1-2 ,and Figure 4 Shown, as follows: comprise crystallization tank 1 and condensing tube, the upper end of crystallization tank 1 is provided with feed port 11 and exhaust port 12, and the lower end of crystallization tank 1 is provided with discharge port 13, and crystallization tank 1 has the second left and right relative One side wall and the second side wall, a row of first through holes 14 is provided longitudinally along the first side wall, and a row of second through holes 15 is provided longitudinally along the second side wall, and the first through holes 14 and the second The two piercing holes 15 form a pair of perforations according to the order from top to bottom. There are several pairs of perforations in total. The condensation pipes pass through the pairs of perforations in turn to form a liquid passage, an...
Embodiment 2
[0032] A method for crystallization and separation of p-xylene, the structure of the device for crystallization and separation of p-xylene is basically the same as that of Example 1, the difference is that in Example 2, the positions of the first through hole 14 and the second through hole 15 are One by one, the line between the pair of perforations formed by two is inclined by 70 degrees with respect to the vertical axis of the crystallization tank 1 . The hole diameter of the liquid flow microhole 41 is 2mm. The structure of the device for crystallization and separation of p-xylene in embodiment 2 is as figure 1 and Figure 3-4 shown.
[0033] The crystallization and separation operation is basically the same as in Example 1, except that in Example 2, the inert cooling liquid is liquid carbon dioxide. The main components in the mixed xylene liquid raw material are C8 aromatic hydrocarbons m-xylene, o-xylene and C10 aromatic hydrocarbons, and the mass fraction of p-xylene ...
Embodiment 3
[0036]A method for crystallization and separation of p-xylene, the structure of the device for crystallization and separation of p-xylene is the same as in Example 1.
[0037] The crystallization and separation operation is basically the same as in Example 1, except that in Example 2, the inert cooling liquid is liquid carbon dioxide. The main components in the mixed xylene liquid raw material are C8 aromatic hydrocarbon m-xylene, ortho-xylene and C10 aromatic hydrocarbon, and the mass fraction of p-xylene in the mixed xylene liquid raw material is 5%.
[0038] In Example 3, the temperature of the liquid carbon dioxide is controlled to be about -10°C. When the crystal content in the crystallization tank 1 reaches 4.5% of the raw material quality, the material is discharged and the crystal is recovered. The purity of p-xylene in the finally measured crystal is 99.8% %; The total recovery rate of final p-xylene is 94.3%.
[0039] It should be noted that, in order to avoid exces...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com