Ground wave over-the-horizon radar power range assessment method based on equivalent noise coefficient
A ground wave beyond-the-horizon and equivalent noise technology, which is applied to radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of complex calculations and the inability to evaluate the range of power, etc., to solve complex calculations, avoid repeated calculations, and reduce the amount of calculations Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0035] Specific implementation mode one: the ground-wave over-the-horizon radar power range evaluation method based on the equivalent noise figure comprises the following steps:
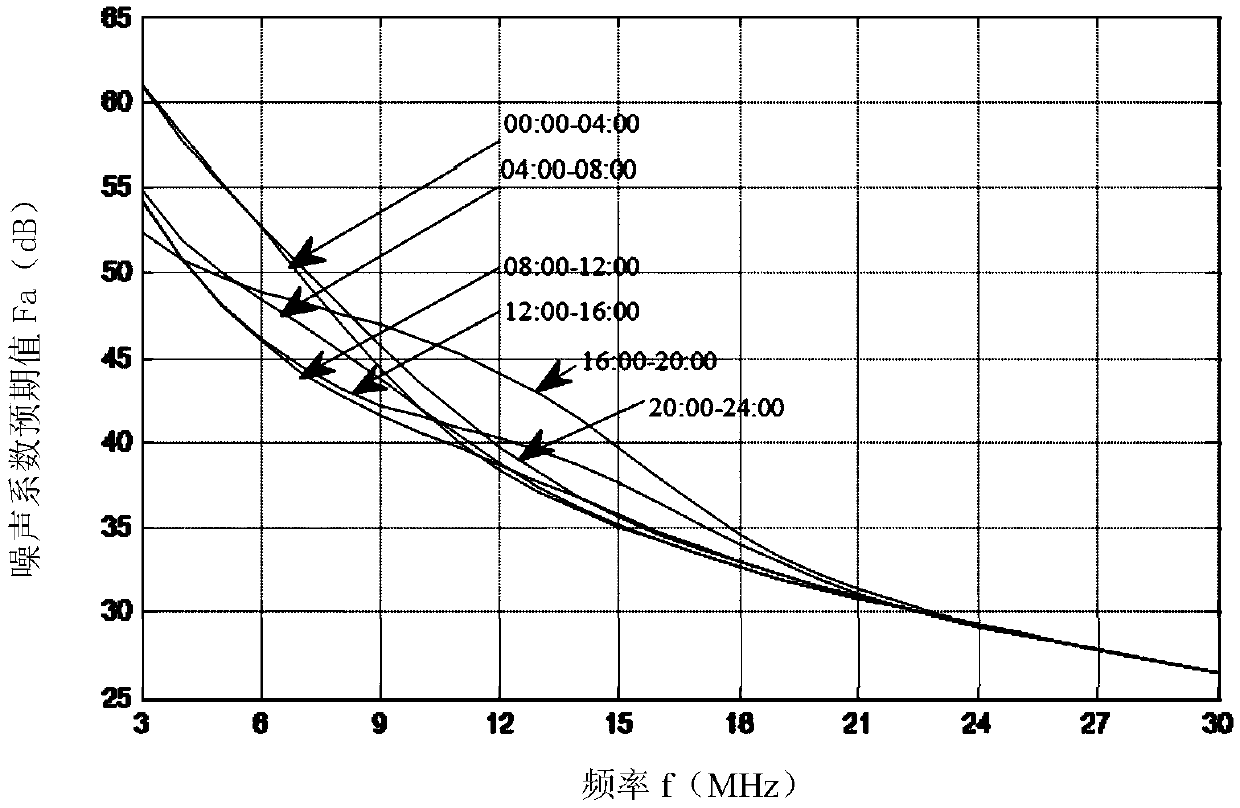
[0036] Step 1: The detection background of the ground wave over-the-horizon radar includes two parts: noise and clutter, expressed as the environmental noise power P n (p,f,t) and clutter power P c The sum of (p, f, t), that is, the detection background base power P nc (p, f, t); when noise and clutter exist at the same time, the radar equation is expressed in the form of signal-to-noise ratio SCNR;
[0037] Said p is the erection site of the radar, f is the operating frequency of the radar, and t is the operating time of the radar;
[0038] Step 2: According to the radar equation expressed in the form of signal-to-noise-noise ratio (SCNR) obtained in step 1, consider radar system parameters, time, location and other factors, and set the radar system signal-to-noise ratio detection threshold SCNR 0 ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0053] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the detection background base of the ground wave over-the-horizon radar in the step one includes noise and clutter two parts, expressed as the environmental noise power P n (p,f,t) and clutter power P c The sum of (p, f, t), that is, the detection background base power P nc (p, f, t); when noise and clutter exist at the same time, the specific process of expressing the radar equation in the form of signal-to-noise ratio SCNR is:
[0054] Detect background base power P nc (p,f,t) is expressed as:
[0055] P nc (p,f,t)=P n (p,f,t)+P c (p,f,t)
[0056] When noise and clutter exist at the same time, the radar equation is expressed in the form of signal-to-noise ratio SCNR:
[0057]
[0058] Where SCNR is the signal-to-noise ratio of the target echo at a distance R, P t is the peak transmit power, γ is the duty cycle of the transmit signal, G t is the transmit antenna ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
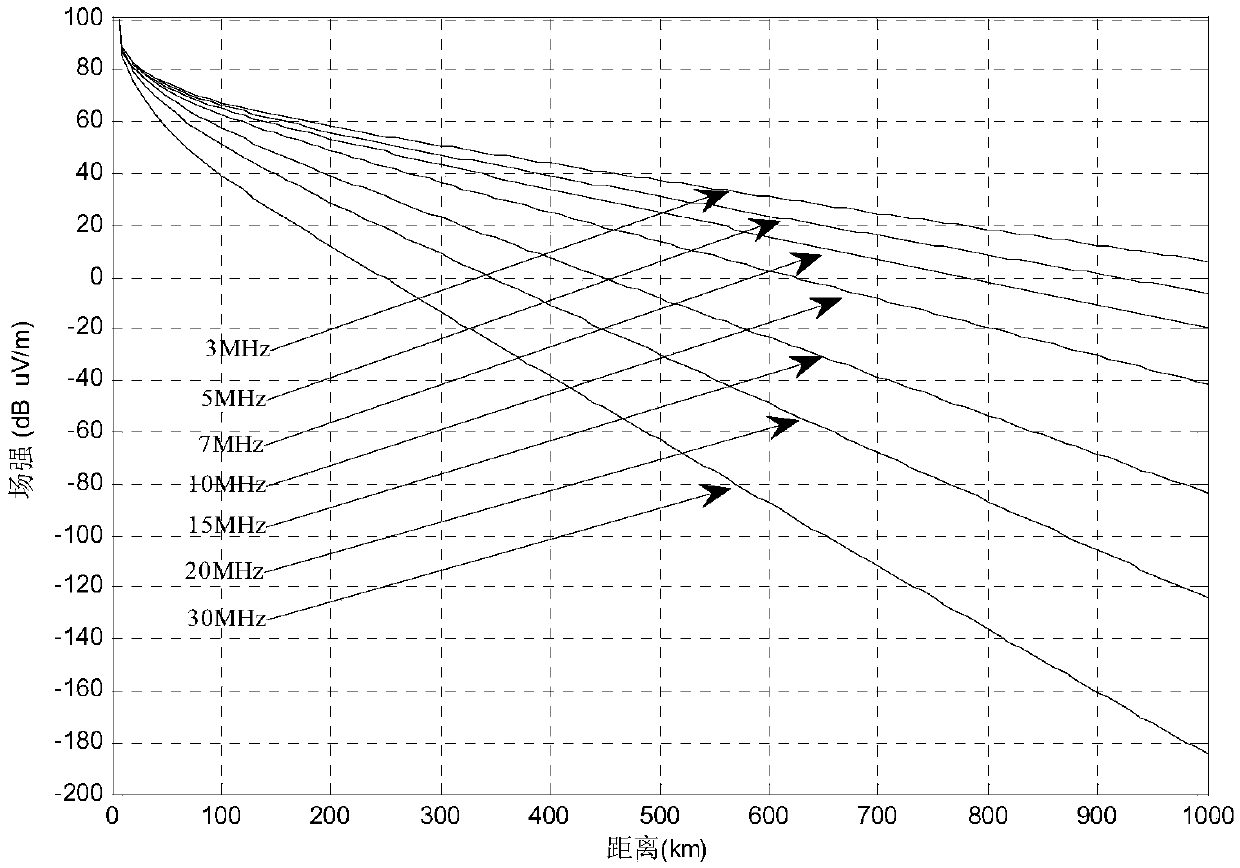
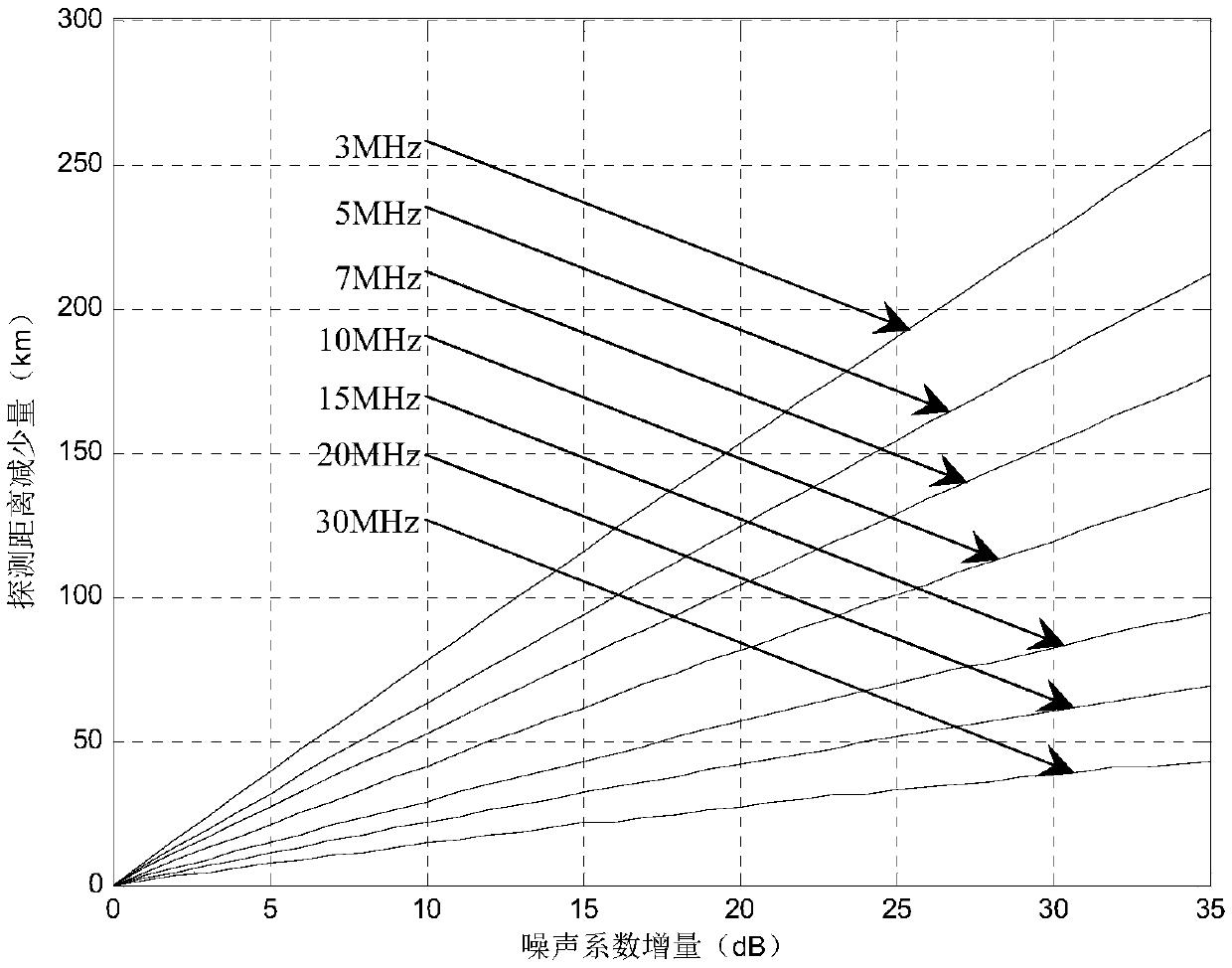
[0061] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is: in the said step two, according to the radar equation expressed in the form of signal-to-noise-to-noise ratio (SCNR) obtained in step one, the radar system signal-to-noise-noise ratio detection is set Threshold SCNR 0 , the expression of the ground wave field strength E(R) is:
[0062]
[0063] where SCNR 0 is the SNR detection threshold corresponding to the maximum detection distance (minimum SNR).
[0064] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com