Execution method for logarithmic loading instruction
An execution method and data loading technology, which is applied in the direction of machine execution devices, electrical digital data processing, program control design, etc., can solve the problems of increasing design complexity and implementation cost, increasing the complexity of related logic design, etc., to reduce design complexity The effect of reducing the number of destination register channels and simple data bypass logic
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
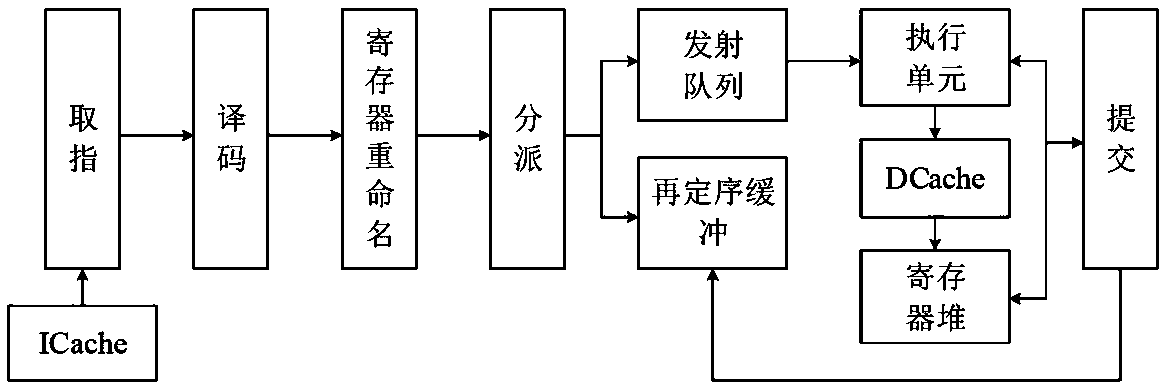
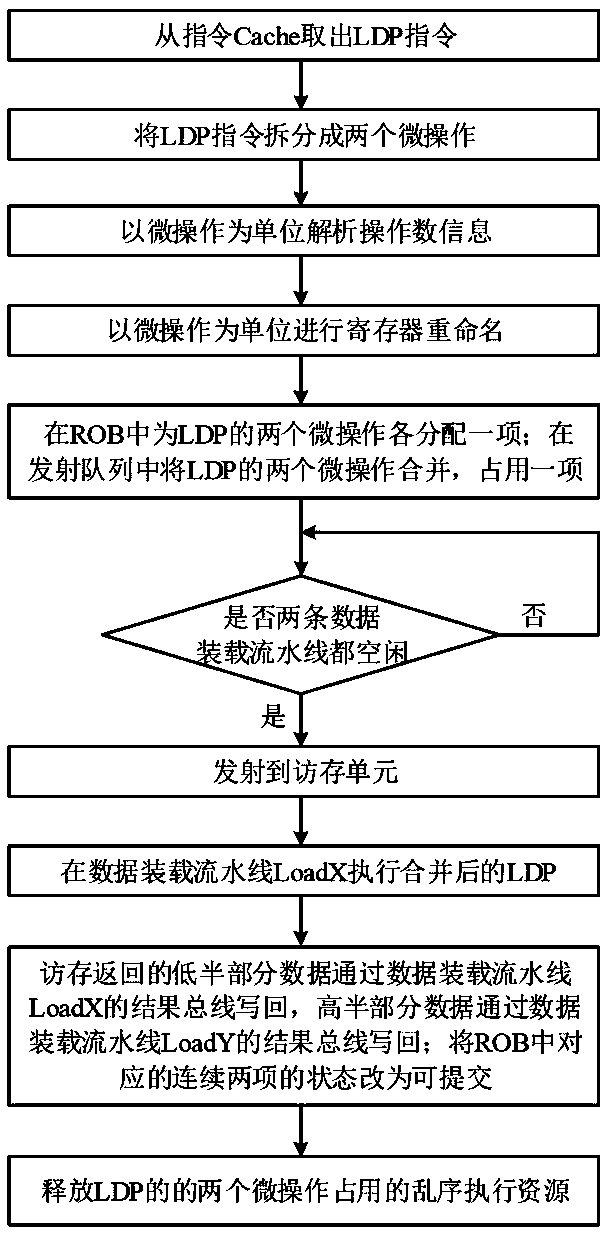
[0040] Such as figure 2 As shown, the implementation steps of the execution method of the logarithmic load instruction in this embodiment include:
[0041] 1) Fetch instruction: fetch a logarithmic load instruction LDP from the instruction buffer;
[0042] 2) Decoding: Split the pairwise load instruction LDP into two micro-operations, each with a destination register; decode in units of micro-operations, and the number of destination registers for each micro-operation does not exceed 1 ;
[0043] 3) Register renaming: rename the registers of the two split micro-operations in units of micro-operations;
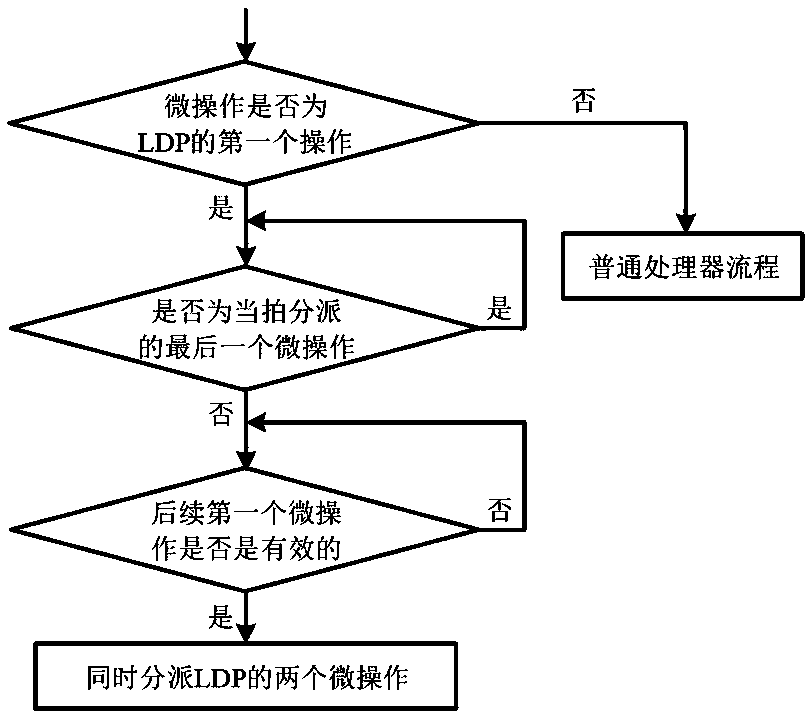
[0044] 4) Dispatch: assign one item to each of the two split micro-operations in the reordering buffer ROB, and merge the two split micro-operations in the launch queue to obtain a merged one that only occupies one item. Logarithmic load instruction LDP;
[0045] 5) Launch: Determine whether the source operand of the merged logarithm load instruction LDP is ready and there...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com