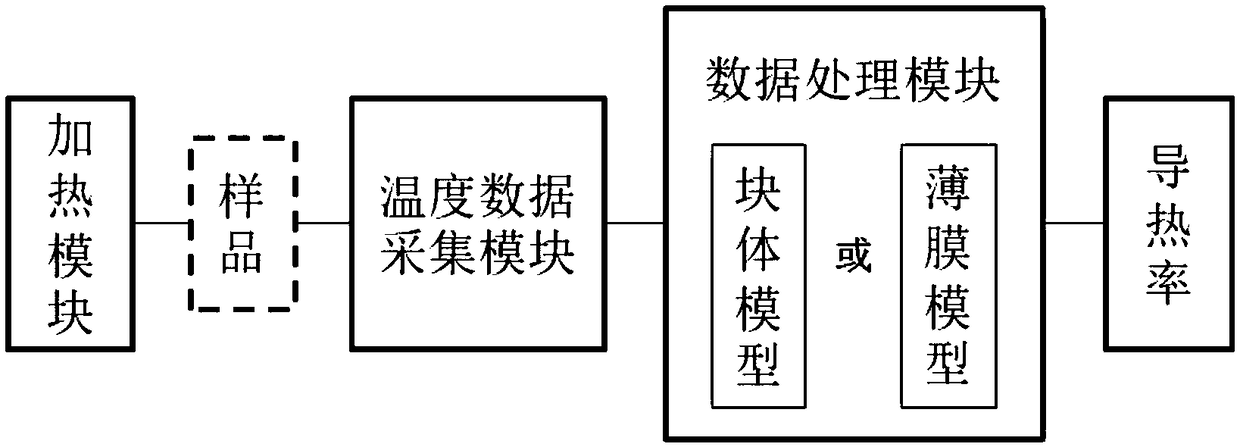
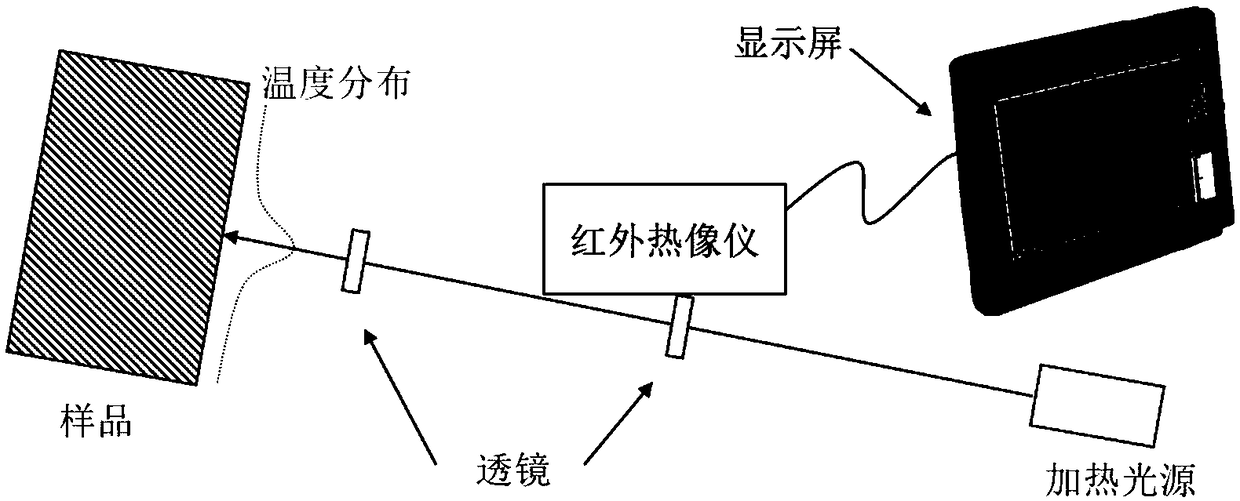
Nondestructive steady-state thermal conductivity measurement method
A measurement method and technology of thermal conductivity, which is applied in the field of non-destructive steady-state thermal conductivity measurement, can solve the problems of limited engineering field application, complex measurement device, and long time, and achieve the effects of shortened measurement time, wide measurement range, and low preparation requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] In this embodiment, the temperature field on the surface of the sample is characterized by measuring the temperature difference between any two points on the heated surface of the sample. Select two measured points with different spatial positions near the heating point, and measure the temperature difference between them, and obtain the temperature rise of the two measured points as:
[0062] T 1 –T 0 =Q·F 1 / κ
[0063] T 2 –T 0 =Q·F 2 / κ
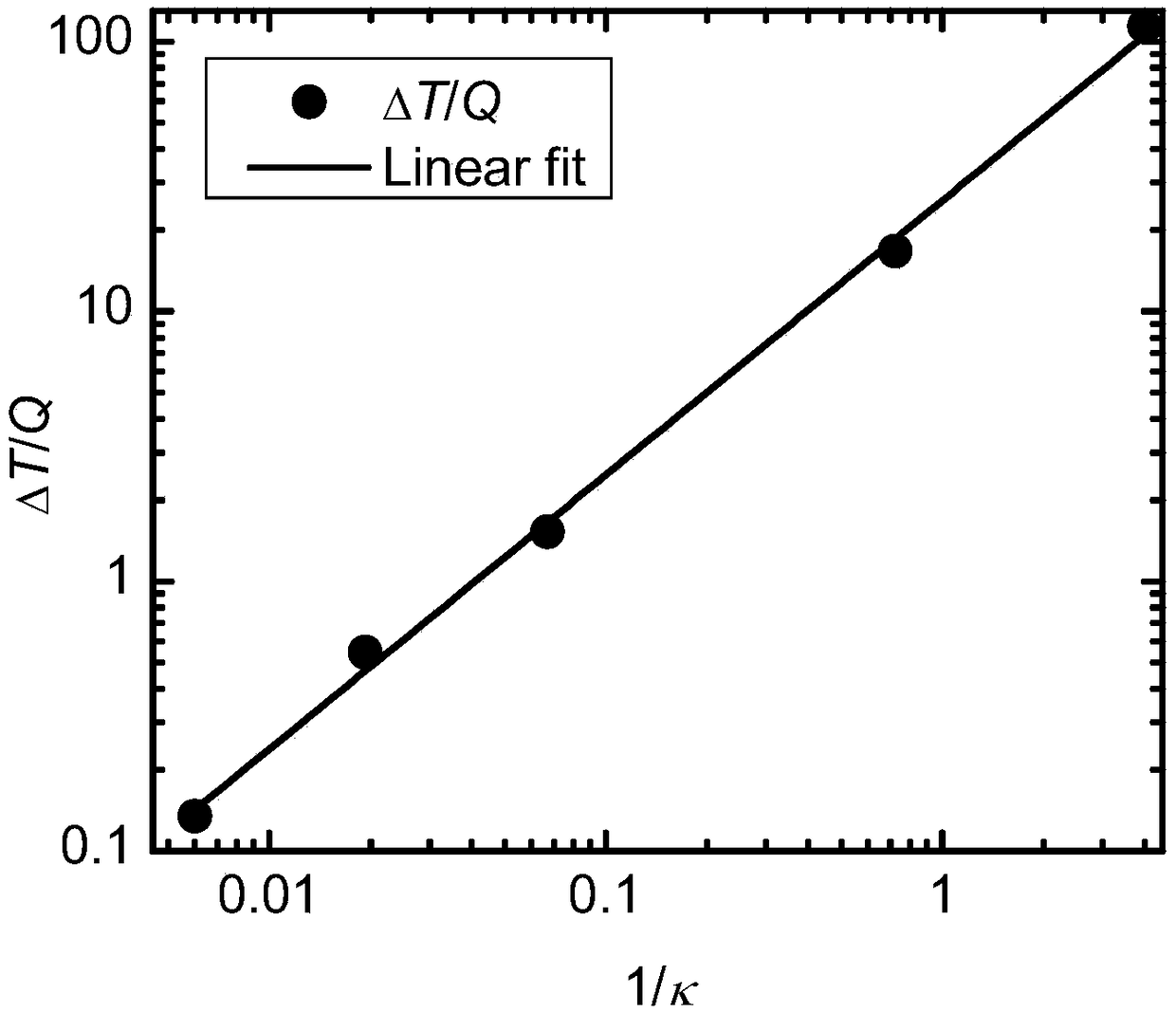
[0064] The temperature T of these two points 1 , T 2 It is obtained at the same time, not the temperature difference between a certain point before and after heating; and the spatial position of the two points is very close to the heating point, and the influence of the environment (convection effect, etc.) on the heating point and the measurement point can be ignored, effectively avoiding the environment during outdoor measurement influences. Sample thermal conductivity κ and temperature difference ΔT between two points ...
Embodiment 2
[0069] The method can be used to non-destructively detect the composition and distribution of heterogeneous materials. In this embodiment, the method and device are used to scan the variation of the thermal conductivity of the cement brick surface with the spatial position, such as Figure 4 As shown, it can be used to assist in characterizing the distribution of different components in cement bricks.
Embodiment 3
[0071] The method can be used to detect cracks in materials non-destructively. In this embodiment, there are cracks on the surface or shallow surface of the cement brick, and the cracks can be considered as filled with air, without heat absorption, so there is no obvious temperature rise, and the equivalent thermal conductivity of the cracks changes abruptly, as shown in Figure 5 As shown, the peak position in the figure represents the crack, and this method can be applied to the non-destructive detection of voids and cracks on the front surface of engineering materials.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com