Optical receiving device
A light-receiving device and technology of the device, applied in the field of optical communication, can solve the problems of difficult coupling of the optical path of the photosensitive surface of the PD chip, and achieve the effect of solving the reduction of the photosensitive surface
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
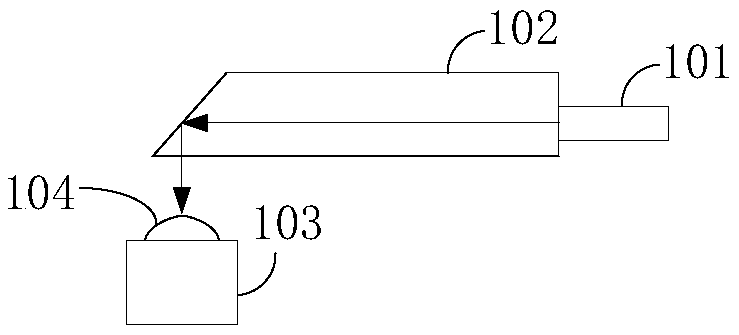
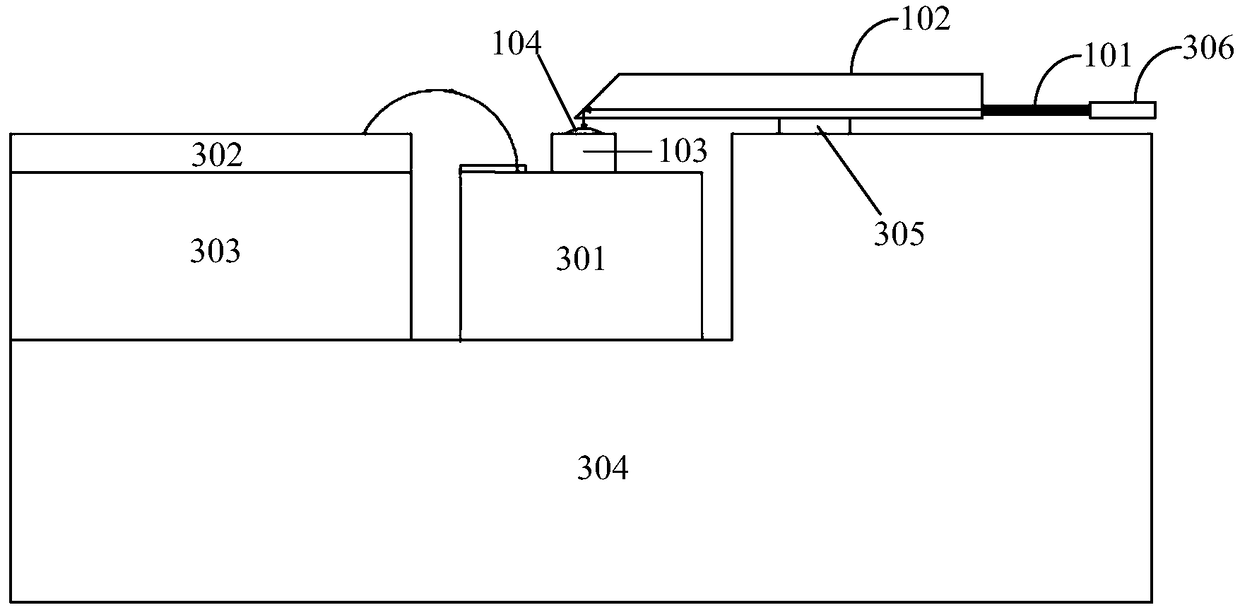
[0048] Figure 4 It is a structural schematic diagram of a light receiving device according to an embodiment of the present invention, refer to Figure 4 , an optical receiving device, including a pin 306 , an input optical fiber 101 , a waveguide chip 102 , a PD chip 103 and a transimpedance amplifier 302 . Wherein, the pin 306 is coupled to the input port of the input optical fiber 101, and the coupling port of the input optical fiber 101 is coupled to the input end face of the waveguide chip 102. Four PD chips 103 are arranged below the output end face of the waveguide chip 102, and each PD chip 103 A lens 104 is etched above the photosensitive surface for converging the optical signal emitted from the output end surface of the waveguide chip 102 and irradiating it onto the photosensitive surface of the PD chip 103 . The PD chip 103 is connected to the transimpedance amplifier 302 through gold wire bonding.
[0049] Wherein, the PD chip 103 is connected through a flip-chi...
example 2
[0055] refer to image 3 , the optical signal enters the input optical fiber 101 through the ferrule, and is transmitted in the waveguide through the waveguide chip 102 until it reaches the waveguide surface of the waveguide chip 102. Since the output end surface of the waveguide chip 102 is polished to an angle of 42° with the waveguide surface, the light passes through After total reflection, it is incident on the lens 104 of the PD chip 103 directly below. After being converged by the lens 104, it is irradiated on the photosensitive surface. The optical signal irradiated on the photosensitive surface of the PD chip 103 is converted into an electrical signal by the transimpedance amplifier 302 at the rear end and amplified. . The PD chip 103 and the transimpedance amplifier 302 are cascaded with gold wire bonding metal. Since different wire lengths will introduce different parasitic inductances and capacitances, especially in high-speed devices, the receiver bandwidth will b...
example 3
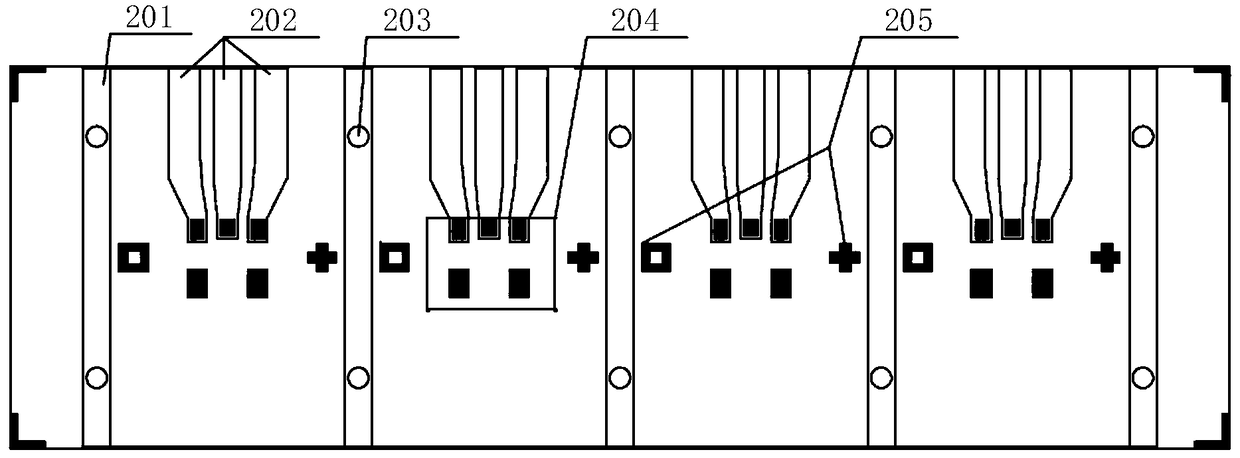
[0057] refer to figure 2 , the PD transition block 301 is provided with a ground isolation region 201 , a signal line 202 , a through hole 203 , a solder area 204 and a marking point 205 .
[0058] The back of the PD chip 103 used in this example has a deeply etched lens 104, which functions to expand the receiving area of the active region and reduce the difficulty of coupling. However, compared with the conventional front-incidence PD chip 103 , the mounting process of the back-incidence PD chip 103 is more complicated. In this example, a flip-chip mounting process is developed for the back-incidence PD chip 103. In order to ensure the feasibility of the process, a special aluminum nitride transition block, namely the PD transition block 301, is used in the design. Five gold-tin solder regions 204 are preset on the PD transition block 301 , which correspond to the gold-plated region at the bottom of the PD chip 103 . When welding, heat and pressure technology is used to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com