Printing device and printing method
A technology for printing devices and driving devices, which is applied to printing devices, printing, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the number of production processes, degrading the performance of light-emitting devices, and weak product competitiveness, etc., and achieves reducing the number of process processes and eliminating solvents The effect of the difference in steam concentration and the shortening of the printing process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] The situation of printing a small amount of ink in the pixel pit of embodiment 1
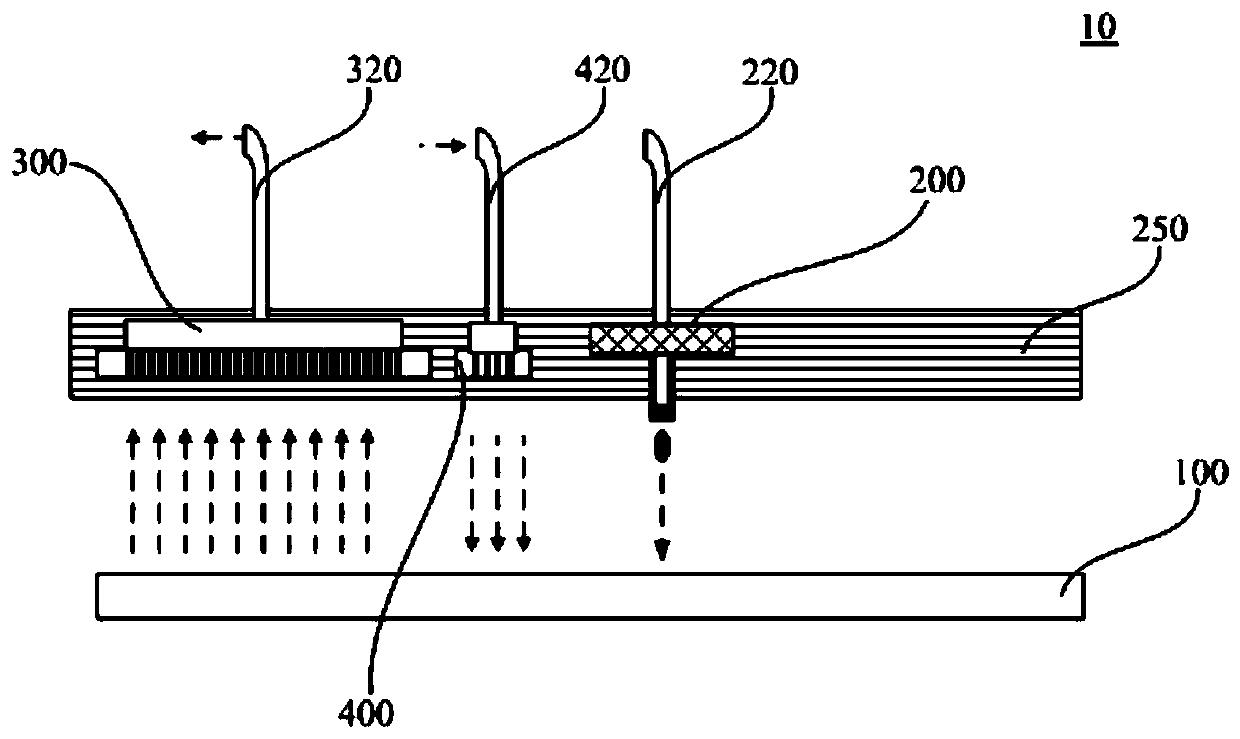
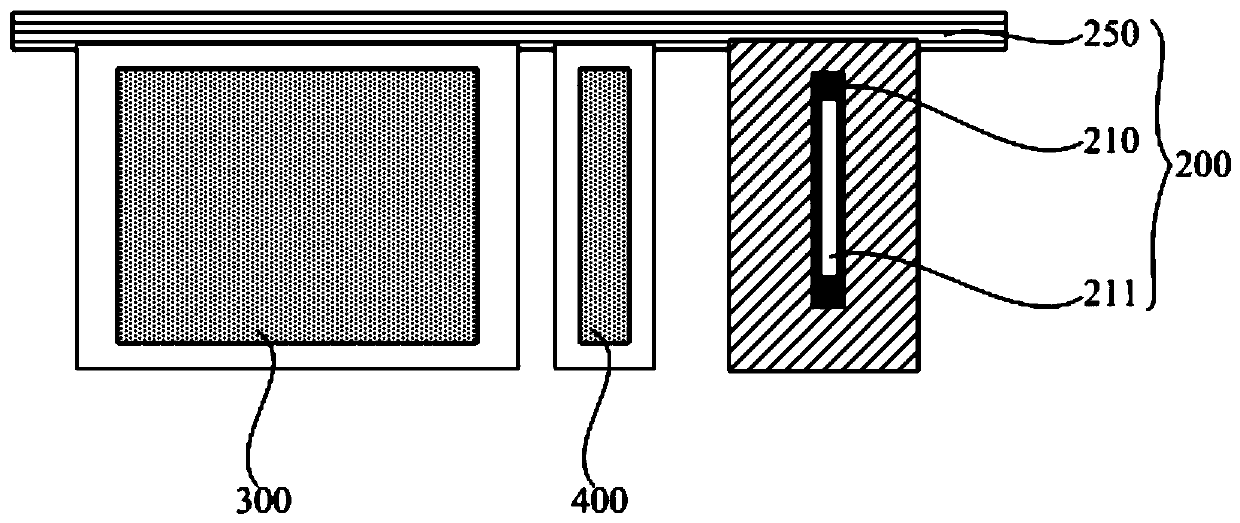
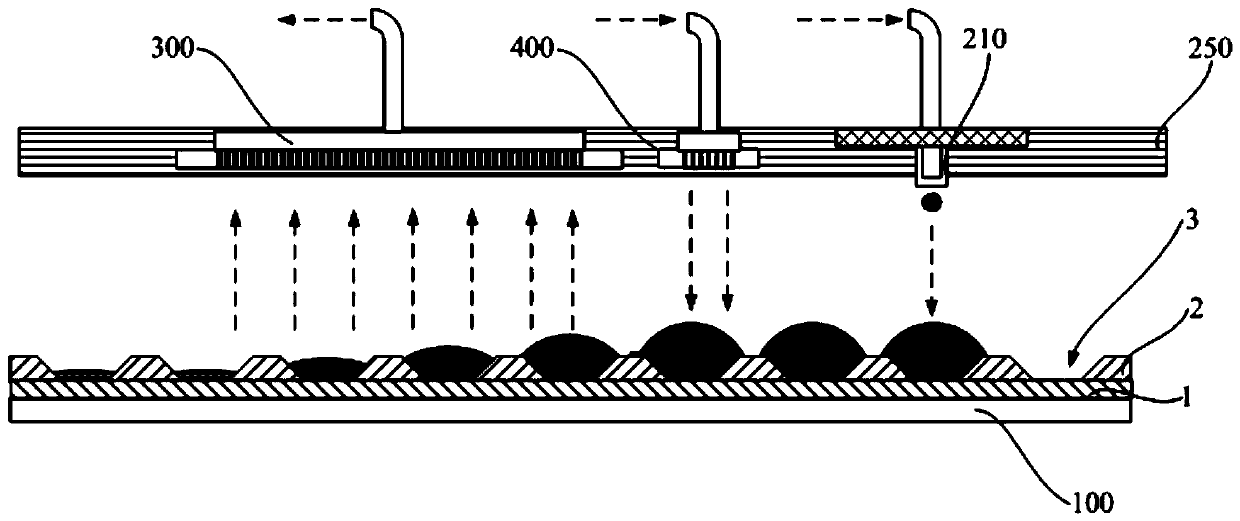
[0080] Please combine further image 3 , for a functional layer with a thin film thickness, such as a material with a film thickness of about 20 nm to 30 nm. Generally, in one sub-pixel, if the print head 210 prints at a speed of 10 pl per drop, only 5 to 8 drops of ink (less than 80 pl) are needed, and the liquid level is relatively thin at this time. After printing by the print head 210 , the ink falls into the pixel pit 3 surrounded by the pixel defining layer 2 to be distributed and spread, and then the vacuum drying mechanism 300 moves over this area to vacuum dry it.
[0081] At this time, since there is less ink, its surface area is larger and it is easy to volatilize, the lateral flow of ink in the pixel pit 3 is relatively small. As the vacuum drying mechanism 300 moves forward, the ink in the pixel pit 3 has been completely dried to form a film. After the printing is complete...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Embodiment 2 The situation where a large amount of ink is printed in the pixel pit
[0083] Please combine further Figure 4 , for a thicker functional layer, such as a material with a film thickness of about 40nm-80nm. Generally, in one sub-pixel, the print head 210 needs 10 to 18 drops of ink to print with 10 pl per drop, and the liquid level is relatively thick at this time. After printing by the nozzle, the ink falls into the pixel pit 3 surrounded by the pixel defining layer 2, and is distributed and spread. At this time, the thickness of the ink is e1 and the viscosity is η1, and the lateral flow rate of the ink at this time is Q1. Because the ink is thick, its lateral flow Q1 is very large, which easily leads to uneven ink film formation.
[0084] Because there is more ink, it is more difficult to volatilize. Then, when the vacuum drying mechanism 300 advances, most of the ink in the pixel pit 3 can be dried and formed into a film.
[0085] After the vacuum d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com