A docking method between a robot and an object and its robot
A technology for robots and objects, applied in the field of robots, can solve the problems of magnetic strip wear, low precision, repeated docking, etc., and achieve the effect of fast efficiency and high precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
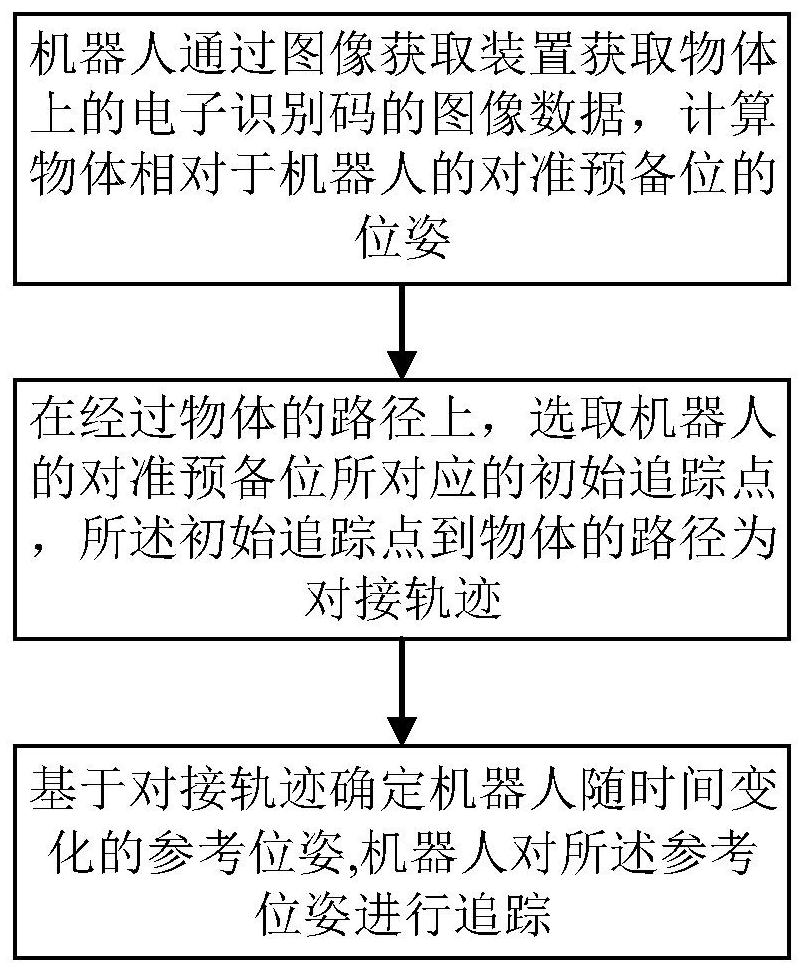
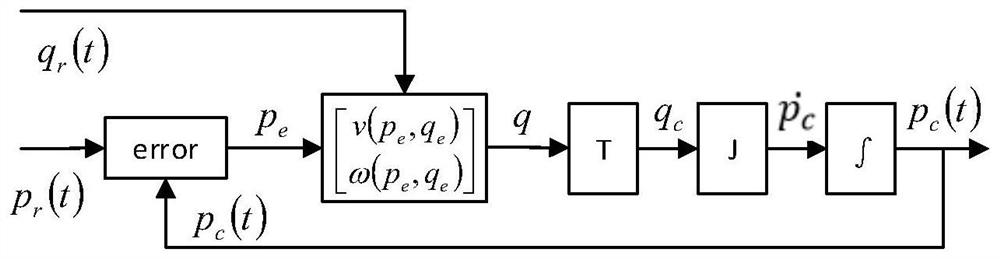
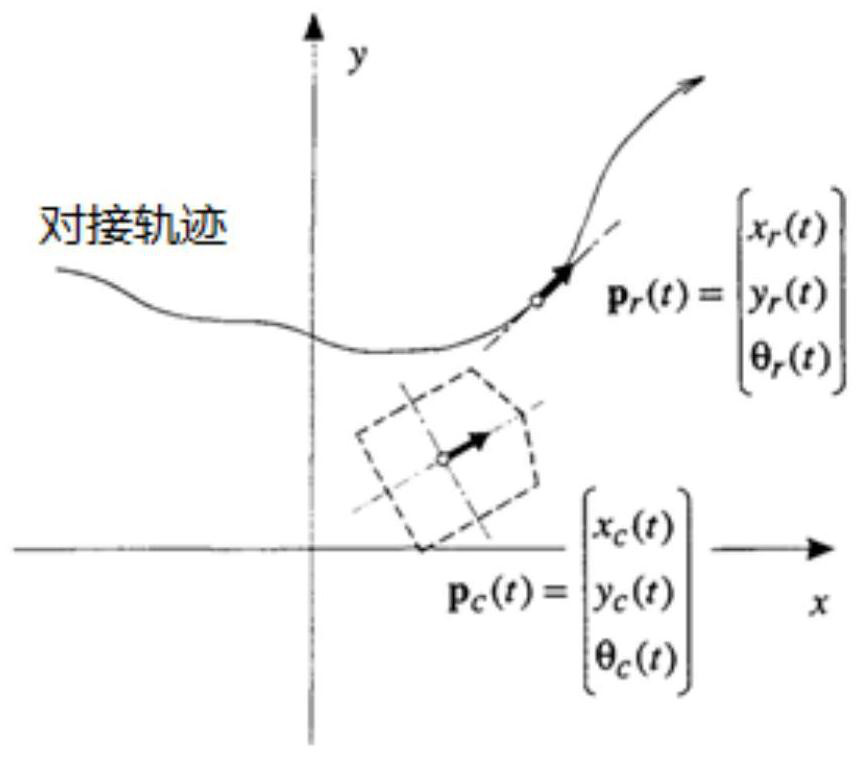
[0063] Such as figure 1 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention proposes a docking method between a robot and an object. The robot is provided with an image acquisition device, and the object is provided with an electronic identification code. The robot is set (for example, moved) to the alignment preparation position relative to the object, so that the image acquisition device on the robot can acquire the electronic identification code on the object. In the prior art, various methods can be used to position the robot to the alignment preparation position. The embodiment of the present invention uses the laser radar-based particle filter positioning algorithm for real-time positioning of the robot and the global path planning based on the A* algorithm (A-Star algorithm is the most effective direct search method for solving the shortest path in a static road network), Navigation based on local path planning of DWA algorithm (Dynamic Window Approach). Those skilled i...
Embodiment 2
[0086] In this embodiment, the forklift robot is docked with a container as an example to further describe the above method. Such as Figure 4 As shown, a vision-based docking method between a forklift robot and a cargo box, wherein the forklift robot is provided with an image acquisition device, and the cargo box is provided with an electronic identification code. The robot is set (for example, moved) to the alignment preparation position relative to the cargo box, so that the image acquisition device on the robot can acquire the electronic identification code on the cargo box.
[0087] Figure 4 The image acquisition device of the robot in the middle is facing the electronic identification code on the cargo box, and those skilled in the art can understand that the method in the embodiment of the present invention is not limited to this facing method, and can also be applied to Figure 5 As shown, the image acquisition device on the robot is obliquely facing the electronic ...
Embodiment 3
[0120] As another application of the embodiment of the present invention, the same method as the method in embodiment 1 or 2 can be applied to the docking of the robot and its charging stand. Among them, the robot is equipped with an image acquisition device, and the charging base is equipped with an electronic identification code, such as Figure 7a , 7b shown. The robot is set (for example, moved) to the alignment preparation position relative to the charging base, so that the image acquisition device on the robot can acquire the electronic identification code on the charging base, such as Figure 7a shown. By performing the same method as in Embodiments 1 and 2, the precise docking of the robot and the charging plug can be realized, and the robot can be charged, such as Figure 7b shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com