Method for <60>Co-gamma radiation mutation breeding of new tulipa gesneriana variety with protective agent
A protective agent and tulip technology, which is applied in the field of cultivating new varieties of tulips by using radiation mutation breeding technology, can solve the problems that have not yet been seen in the application research of protective agents, and achieve the effects of increasing the mutation rate, expanding the mutant population, and reducing the short growth cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: The effect of protective agent treatment on the survival rate of tulips after gamma ray irradiation:
[0038] This experiment was carried out in the multi-span greenhouse of the School of Life Science and Engineering, Southwest University of Science and Technology. use 60 Co-γ irradiated healthy tulip bulbs, the radiation dose was 5Gy, 10Gy, 20Gy, 40Gy, 60Gy, 80Gy, 100Gy, and the radiation dose was 2.57Gy / min. Two controls were set up in the experiment, one was unirradiated and unwatered bulbs (CK 1 ), the second is the bulbs soaked in deionized water for 30 minutes (CK 2 ). According to 3 different melatonin concentrations for each radiation dose (see Table 1-1 for specific melatonin formulations), soak for 30 minutes respectively, dry and plant. The tulip planting time is January 20th, planted in a 10cm*10cm*30cm black nutrient pot, the soil formula is special soil for plant cultivation: fermented organic substrate: leaf humus: vermiculite = 2:1:1:1 ...
Embodiment 2
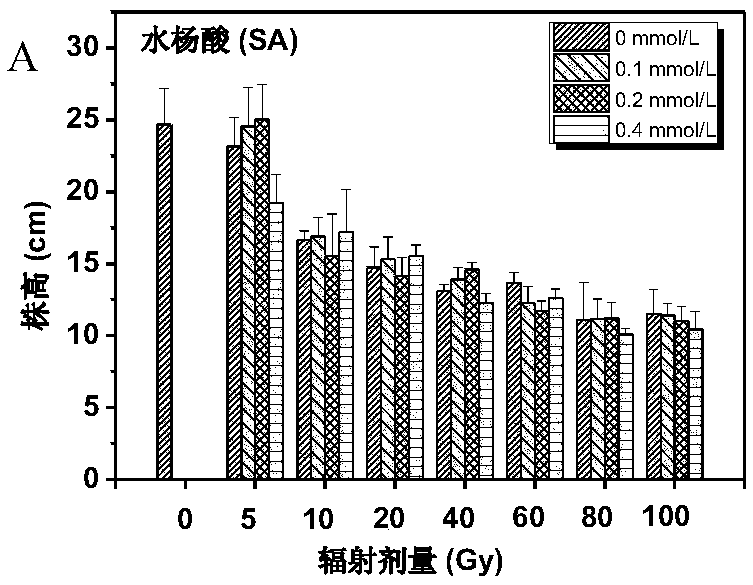
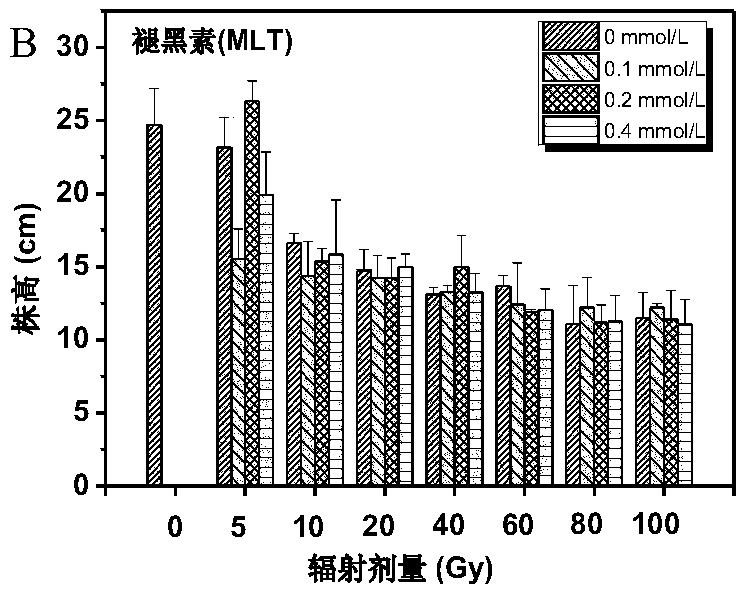
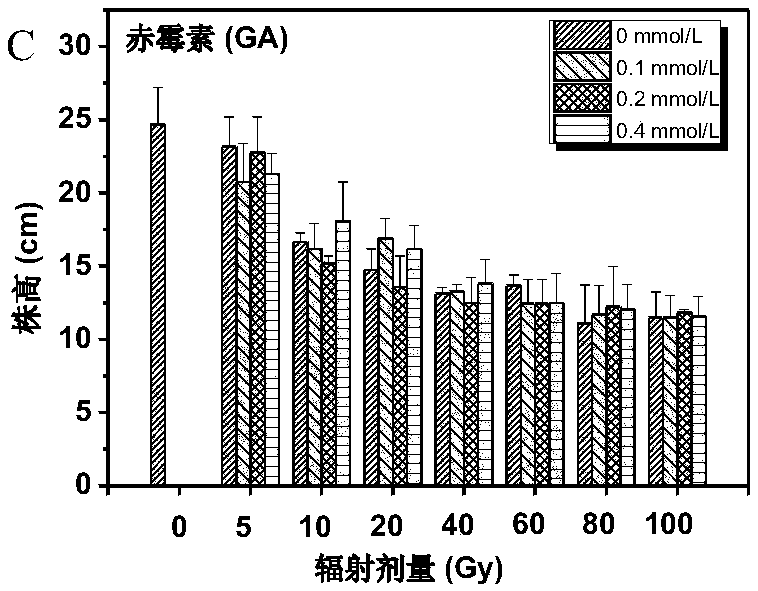
[0051] Embodiment 2: The effect of protective agent treatment on tulip vegetative growth after gamma ray irradiation:
[0052] This experiment was carried out in the multi-span greenhouse of the School of Life Science and Engineering, Southwest University of Science and Technology. use 60 Co-γ irradiated healthy tulip bulbs, the radiation dose was 5Gy, 10Gy, 20Gy, 40Gy, 60Gy, 80Gy, 100Gy, and the radiation dose was 2.57Gy / min. Two controls were set up in the experiment, one was unirradiated and unwatered bulbs (CK 1 ), the second is the bulbs soaked in deionized water for 30 minutes (CK 2 ). According to 3 different melatonin concentrations for each radiation dose (see Table 2-1 for the specific melatonin formula), soak for 30 minutes respectively, dry and plant. The tulip planting time is January 20th, planted in a 10cm*10cm*30cm black nutrient pot, the soil formula is special soil for plant cultivation: fermented organic substrate: leaf humus: vermiculite = 2:1:1:1 (mixe...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Embodiment 3: the effect of protective agent treatment on tulip reproductive growth after gamma ray irradiation:
[0063] This experiment was carried out in the multi-span greenhouse of the School of Life Science and Engineering, Southwest University of Science and Technology. use 60 Co-γ irradiated healthy tulip bulbs, the radiation dose was 5Gy, 10Gy, 20Gy, 40Gy, 60Gy, 80Gy, 100Gy, and the radiation dose was 2.57Gy / min. Two controls were set up in the experiment, one was unirradiated and unwatered bulbs (CK 1 ), the second is the bulbs soaked in deionized water for 30 minutes (CK 2 ). According to 3 different melatonin concentrations for each radiation dose (see Table 1-1 for specific melatonin formulations), soak for 30 minutes respectively, dry and plant. The tulip planting time is January 20th, planted in a 10cm*10cm*30cm black nutrient pot, the soil formula is special soil for plant cultivation: fermented organic substrate: leaf humus: vermiculite = 2:1:1:1 (m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com