Rapid dewaxing method for nucleic acid extraction of FFPE sample
A sample and nucleic acid technology, which is applied in the field of rapid dewaxing of nucleic acid extraction from FFPE samples, can solve the problems of toxicity, time-consuming, and personal safety hazards of laboratory personnel in dewaxing reagents, so as to reduce the length of heating steps and simplify dewaxing and lysis steps. , the effect of simplifying the complexity of the operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
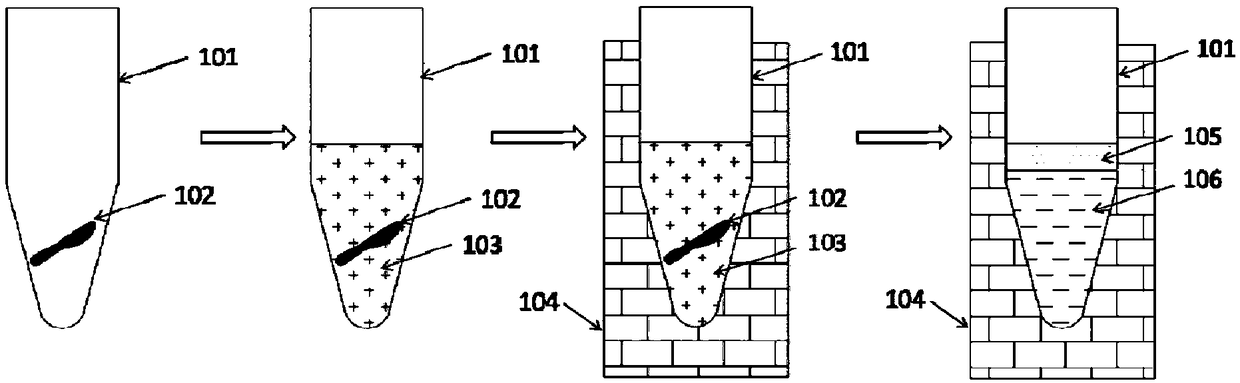
[0037] Add 200 μL of aqueous phase reagent (10 mM EDTA, 30 mM Tris-HCl, 3M guanidine isothiocyanate, 1% TritonX-100), 20 μL of proteinase K (5 mg / mL) and 50 μL of oil phase reagent (silicone oil) into the FFPE tissue sample In the 1.5mL centrifuge tube 101 of 102, briefly centrifuge after shaking and mixing to obtain the mixed solution 103.
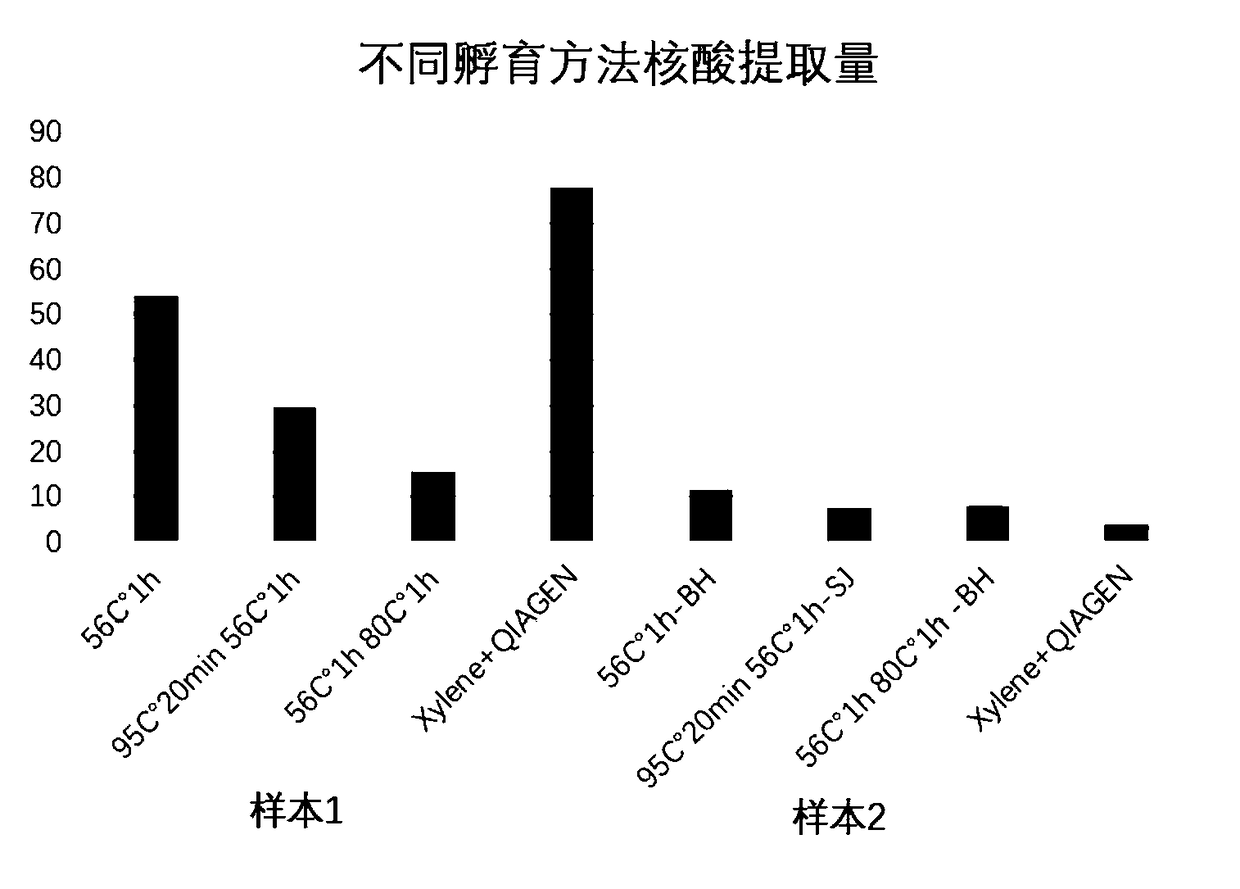
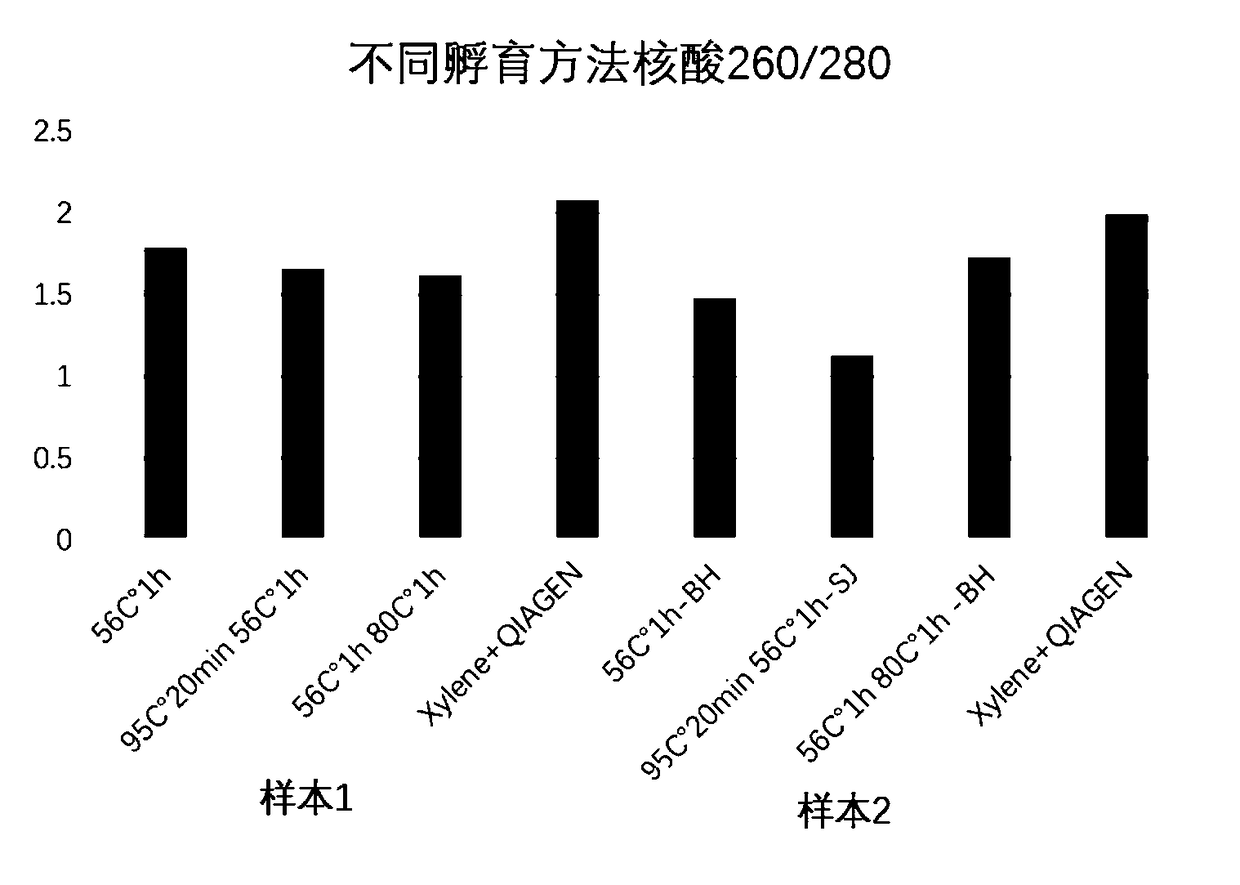
[0038] Put it into the heating device 104 that has been heated to 56°C, and incubate at 56°C for 1 hour. At this time, it can be observed that the mixed solution 103 in the tube is layered, the upper layer is the oil phase layer 105, and the lower layer is the water phase layer 106. After the incubation, take out the lower aqueous phase solution 106 with a pipette gun under heating conditions, or completely remove the lower aqueous phase solution 106 into a new centrifuge tube after cooling to room temperature.
[0039] If necessary, 2 μL RNase A can also be added to the aqueous phase solution, and left at room temperature for 5 minutes t...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Add 150 μL of aqueous phase reagent (1 mM EDTA, 50 mM PBS, 4M guanidine hydrochloride, 1% SDS), 20 μL of proteinase K (20 mg / mL) and 150 μL of paraffin oil into the 1.5 mL centrifuge tube 101 containing FFPE tissue sample 102, shake After mixing, centrifuge briefly to obtain a mixture 103.
[0043] Put the centrifuge tube into the heating device 104 that has been heated to 52°C, and incubate at 52°C for 3 hours. At this time, it can be observed that the mixed solution 103 in the tube is separated, the upper layer is the oil phase layer 105, and the lower layer is the water phase Layer 106. If necessary, the centrifuge tube 101 can be taken out, and the centrifuge tube 101 can be put in after the heating device 104 is heated to 80° C., and incubated for 1 hour. After the incubation, take out the lower aqueous phase solution 106 with a pipette gun under heating conditions, or completely remove the lower aqueous phase solution 106 into a new centrifuge tube after cooling ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Add 300 μL of aqueous phase reagent (10 mM EDTA, 50 mM Tris-HCl, 1% SDS), 20 μL of proteinase K (20 mg / mL) and 150 μL of xylene into the 1.5 mL centrifuge tube 101 containing FFPE tissue sample 102, shake and mix briefly Centrifuge to obtain the mixed solution 103.
[0047] Put the centrifuge tube into the heating device 104 that has been heated to 56°C, and incubate at 56°C for 2 hours. At this time, it can be observed that the mixed solution 103 in the tube is separated, the upper layer is the oil phase layer 105, and the lower layer is the water phase Layer 106. If necessary, the centrifuge tube 101 can be taken out, and the centrifuge tube 101 can be put in after the heating device 104 is heated to 90° C., and incubated for 30 minutes. After the incubation, take out the lower aqueous phase solution 106 with a pipette gun under heating conditions, or completely remove the lower aqueous phase solution 106 into a new centrifuge tube after cooling to room temperature. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com