3D-Printing photo-curable slurry and preparation method thereof
A 3D printing and light-curing technology, applied in the field of 3D printing, can solve the problems of black light-curing system, such as hard curing and curing thickness, and achieve the effect of improving the ability of curing reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
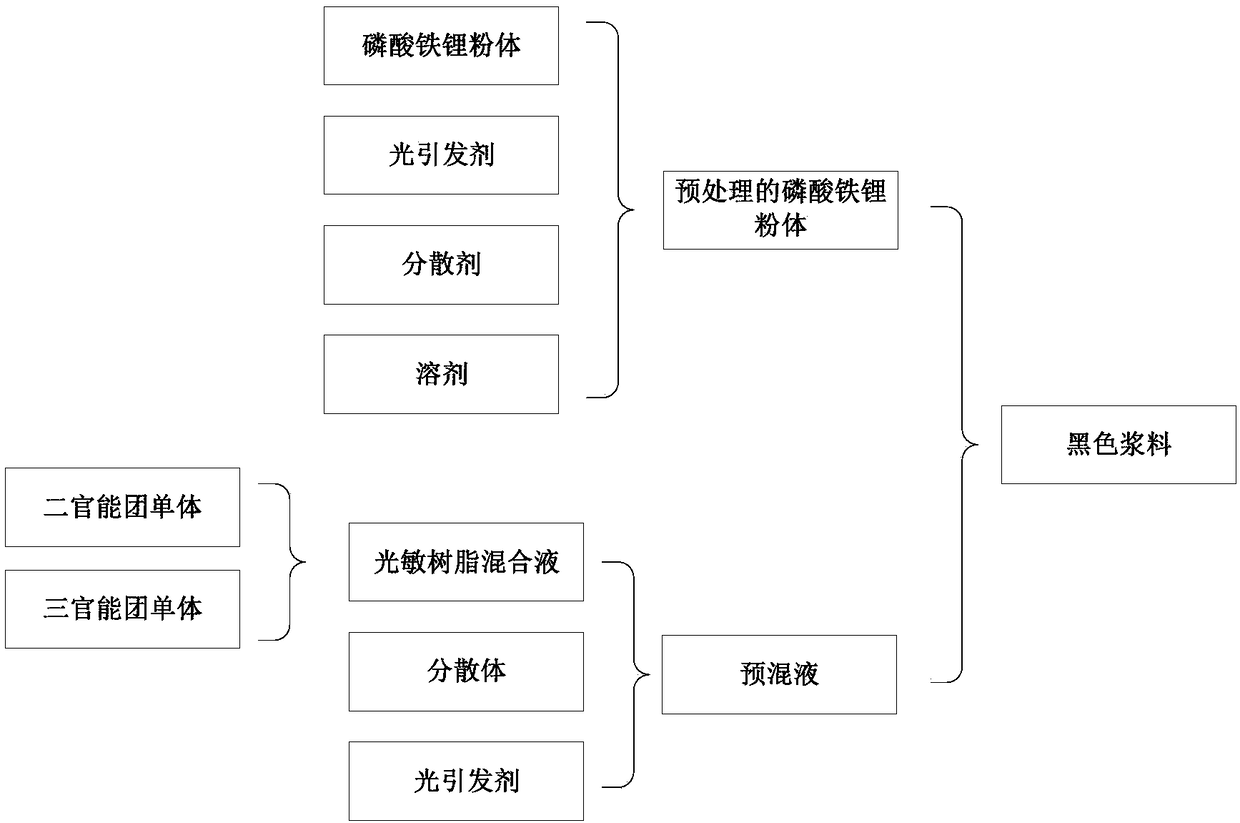
[0020] The preparation method of the 3D printing light-cured slurry provided in this embodiment, its process flow chart is as follows figure 1 shown, including:
[0021] S1. Material pretreatment: The black material, photoinitiator, dispersant, and solvent are fully mixed and then dried to obtain the pretreated material.
[0022] The black material in this embodiment mainly adopts the lithium iron phosphate powder that is used to form the electrode material, preferably the particle size of the lithium iron phosphate powder is 10-15 μ m, and the specific surface area (BET) is 8-15 m 2 / g, purity>99%.
[0023] Photoinitiator selects commercial photoinitiator 389 (2-dimethylamino-2-benzyl-1-(4-piperidine phenyl)-1-butanone), photoinitiator 184 (1-hydroxycyclohexylbenzene methyl ketone), photoinitiator EMK (4,4-bis(diethoxy)benzophenone), photoinitiator TPO (2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl-diphenylphosphine oxide) , photoinitiator 819 (phenylbis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phosphine oxide),...
Embodiment 1
[0038] Weigh 120g of lithium iron phosphate powder into a 1L corundum ball mill jar, pour about 120g of absolute ethanol, and add 3.6g of photoinitiator TPO and 1.2g of dispersant RQT-FS. Then start ball milling, the rotating speed is set at 170r / min, ball milling 3h. After completion, filter and dry to collect the pretreated lithium iron phosphate powder for use.
[0039] Pour 120 g of HDDA and 36 g of TMPTA into the beaker, and ultrasonically stir for 20 min to obtain a photosensitive resin mixture, which is ready for use.
[0040] Add 120g of photosensitive resin mixed solution, 2.4g of photoinitiator TPO and 2.4g of dispersant RQT-FS into the beaker, ultrasonicate for 30min, after forming a uniform and stable solution, transfer it to a 1L corundum ball mill jar. Then 120 g of pretreated lithium iron phosphate powder was weighed and added thereto, and ball milled at 170 r / min for 20 h. A black slurry was collected upon completion. The black paste is directly used for 3D pr...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Weigh 120g of lithium iron phosphate powder into a 1L corundum ball mill jar, pour about 120g of absolute ethanol, and add 1.2g of photoinitiator 389 and 3g of dispersant BYK111. Then start ball milling, the rotating speed is set at 250r / min, ball milling 4h. After completion, filter and dry to collect the pretreated lithium iron phosphate powder for use.
[0043] Pour 120g of DEGDMA and 60g of PET3A into the beaker, and ultrasonically stir for 20min to obtain a photosensitive resin mixture, which is ready for use.
[0044] Add 120g of photosensitive resin mixture, 1.2g of photoinitiator 389, and 1.2g of dispersant BYK111 into the beaker, and ultrasonicate for 20min. After forming a uniform and stable solution, transfer it to a 1L corundum ball mill jar. Then 21.6g of pretreated lithium iron phosphate powder was weighed and added thereto, and ball milled at 150r / min for 25h. A black slurry was collected upon completion. The black paste is directly used for 3D printin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com