Method for preparing starch-protein complex having digestion resistance and high nutrition
A high-nutrition, anti-digestion technology, applied in the field of starch-protein complex preparation, can solve the problems of cumbersome process and poor anti-digestion effect of starch, so as to achieve rich sources of raw materials, promote short-range ordered structure, and control postprandial blood sugar effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
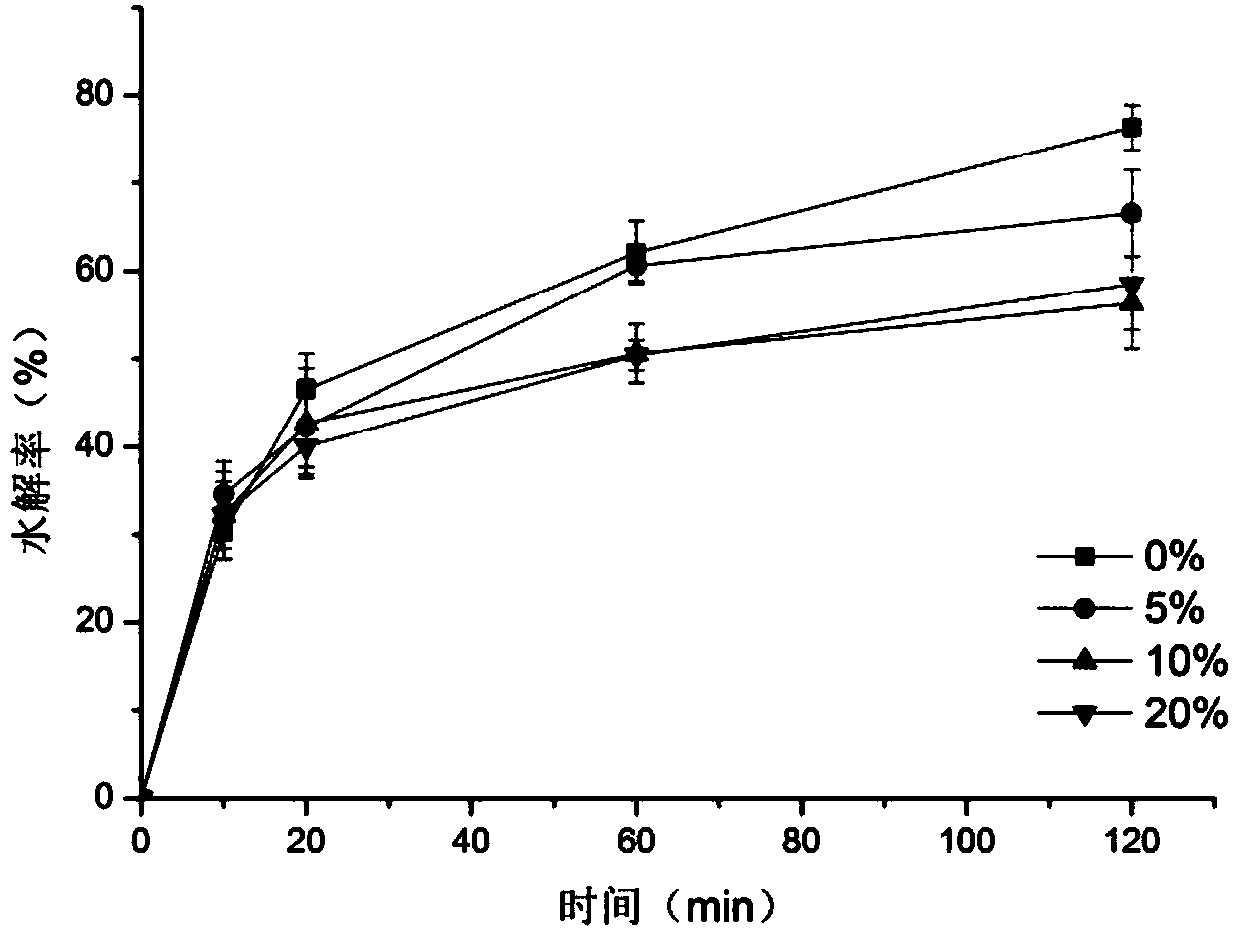
[0030] Accurately weigh 5g of corn starch into a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 0g, 0.25g, 0.5g, and 1g of whey protein powder (WPI) respectively, mix well, add deionized water at a ratio of 1:3 to the powder mass, and add a rotor. In a water bath at 95°C for 30 min. After the sample was taken out, it was allowed to cool naturally, and after standing for 5 days at 4 / 25°C with a time interval of 24h, the sample was dried at a low temperature of 35°C and passed through a 200-mesh sieve. The nutrient fragments of the complex were determined by double-enzyme method in vitro, and the resistant starch increased significantly with the increase of the protein ratio, and the content of resistant starch in the 10% WPI group was as high as 43.70%.
[0031] The starch-protein complex of this example was tested for starch digestibility by Englyst in vitro dual-enzyme method, as shown in Table 1.
[0032] Table 1 Contents of fast-digesting, slow-digesting and resistant starch in starch-protein ...
Embodiment 2
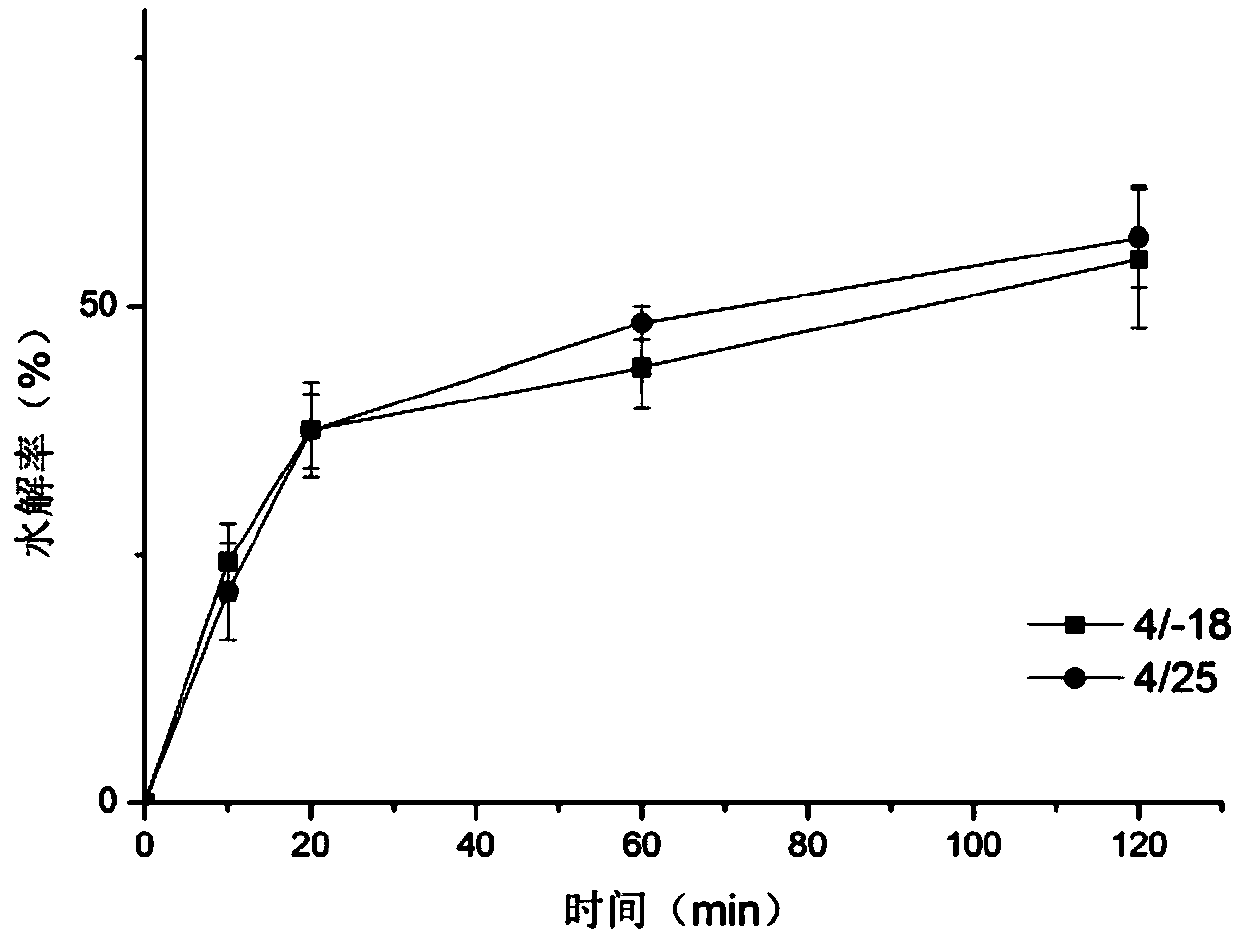
[0035] Accurately weigh 5g of cornstarch into a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 0.5g of whey protein powder, mix well, add deionized water at a ratio of 1:3 to the powder mass, add a rotor, and treat in a water bath at 95°C for 30 minutes. After the sample was taken out, it was allowed to cool naturally, and then placed at 4 / -18°C and 4 / 25°C for 5 days at an interval of 24 hours, then dried at a low temperature of 35°C and passed through a 200-mesh sieve.
[0036] The starch-protein complex of this example was measured by Englyst in vitro dual-enzyme method for starch digestibility, as shown in Table 2.
[0037] Table 2 Contents of fast-digesting, slow-digesting and resistant starch in starch-protein complexes prepared at different temperature changes
[0038]
Embodiment 3
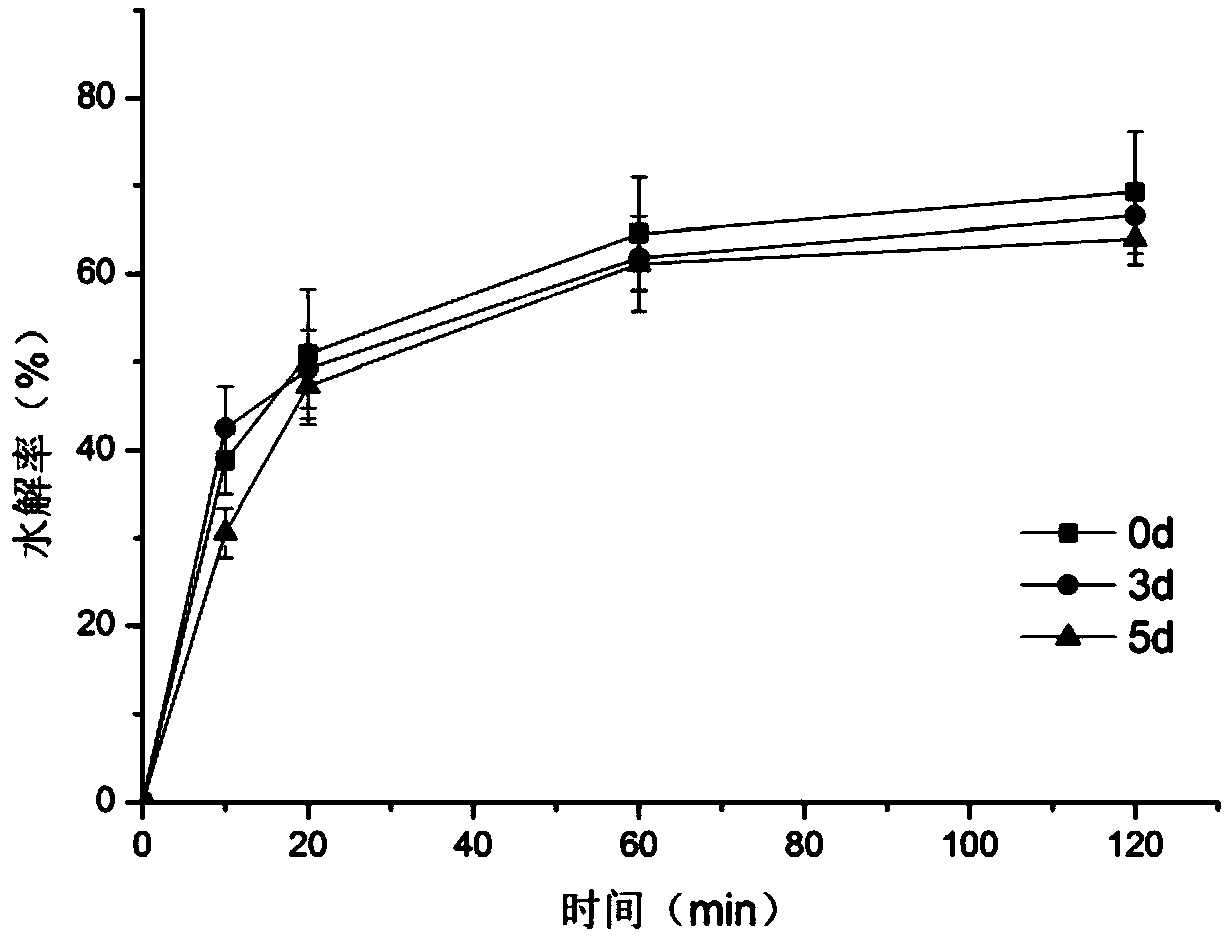
[0040] Accurately weigh 5g of cornstarch into a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 0.5g of whey protein powder, mix well, add deionized water at a ratio of 1:3 to the powder mass, add a rotor, and treat in a water bath at 95°C for 30 minutes. After taking out the sample, let it cool naturally, and place it at 4 / 25°C for 24h for 0d, 3d, and 5d, then dry the sample at a low temperature of 35°C and pass through a 200-mesh sieve. The digestibility of starch was determined by Englyst in vitro dual-enzyme method, and the digestion resistance of starch was significantly improved with the increase of temperature changing time.
[0041] The starch-protein complex of this example was measured by the Englyst in vitro dual-enzyme method for starch digestibility, as shown in Table 3.
[0042] Table 3 Contents of fast-digesting, slow-digesting and resistant starch in starch-protein complexes prepared at different temperature changes
[0043]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com