Polypeptide for treating osteoporosis, preparation method and applications thereof
A technology of osteoporosis and polypeptide, applied in the field of bioengineering, to achieve good bone targeting effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
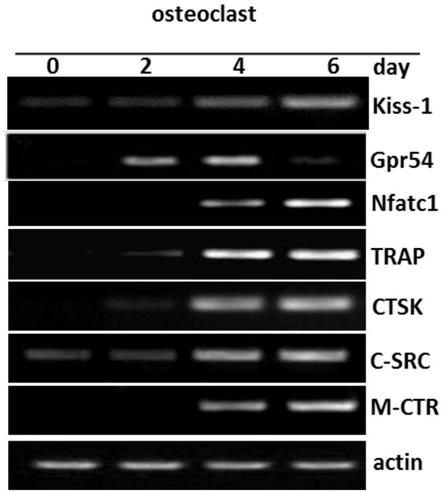
[0053] This example clarifies the expression of kiss1 and Gpr54 in osteoclast differentiation.
[0054] Principle: Bone marrow monocytes can differentiate into osteoclasts in one week under the continuous stimulation of cytokines M-CSF and RANKL. The genes involved in the regulation of osteoclasts should be highly expressed during the process of osteoclast differentiation. Therefore, we first detected the expression of Kiss1 and Gpr54 during osteoclast differentiation.
[0055] Methods: In this example, RANKL was used to induce the differentiation of mouse primary bone marrow mononuclear cells BMMs into osteoclasts, and the cellular RNAs of different induction days were collected, and then the expression levels of Kiss1 and Gpr54 mRNAs were detected during the osteoclast differentiation process.
[0056] Results and evaluation:
[0057] The result is as figure 1 As shown, the results show that Kiss1 and Gpr54 are up-regulated during osteoclast differentiation. This suggests...
Embodiment 2
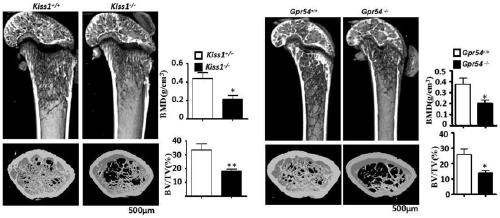
[0059] This example confirms the role of kiss1 and its receptor Gpr54 in positively regulating bone mass, and concludes that knockout of Gpr54 or Kiss1 gene leads to osteoporosis.
[0060] Principle: The mouse kiss1 and its receptor Gpr54 gene are edited on the genome to lose their function, and kiss1 and Gpr54 knockout mice are obtained respectively. Bone parameter changes were analyzed by micro-CT 3D imaging technology.
[0061] Methods: The femurs of 8-week wild-type (WT) and Gpr54 knockout (KO) mice were removed, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 hours, detected by micro-CT, and analyzed by 100 3D images under the growth plate.
[0062] RESULTS AND EVALUATION: The micro-CT scan imaging results showed that the Gpr54 knockout mice had significantly decreased bone mass, trabecular bone loss, and osteoporosis symptoms. The result is as figure 2 As shown, statistical results showed that compared with WT mice, Gpr54 knockout mice decreased nearly 50% in bone mineral density...
Embodiment 3
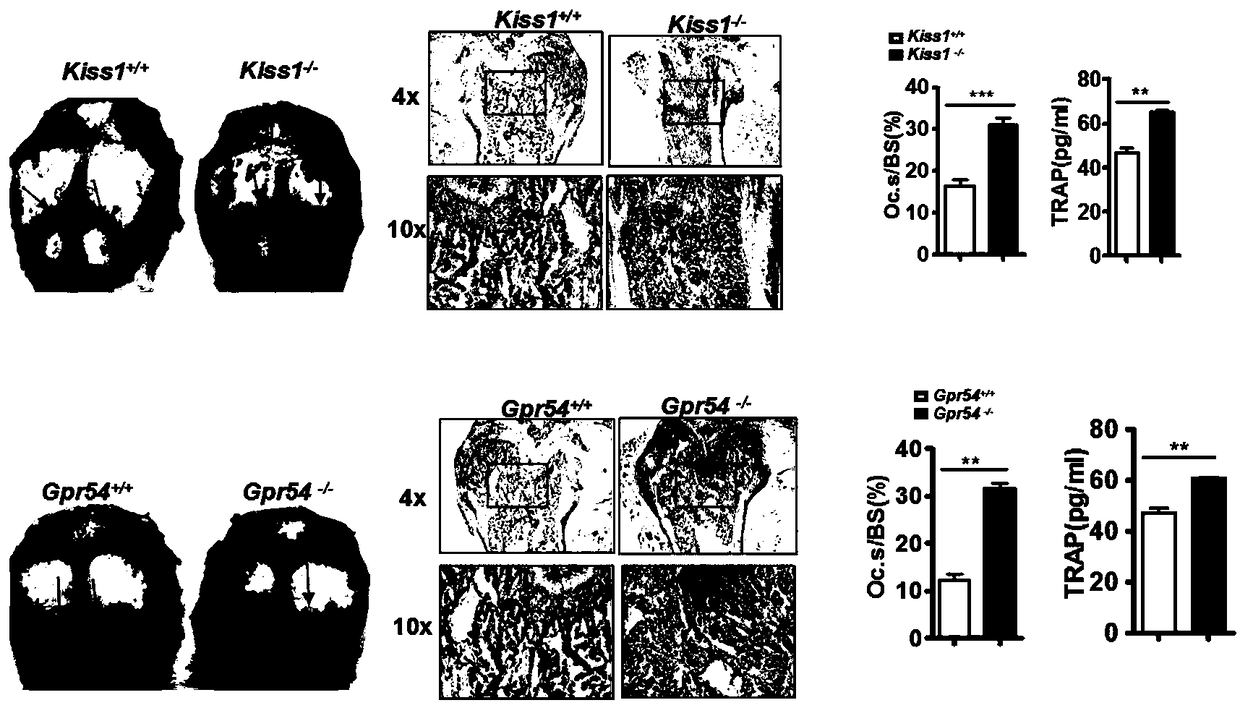
[0064] This example confirms that kiss1 and its receptor Gpr54 positively regulate osteoclast differentiation (in vivo / in vitro), and concludes that knockout of Gpr54 or Kiss1 leads to osteoclast activation (in vivo), and knockout of Gpr54 or Kiss1 leads to osteoclasts activation (in vitro).
[0065] Principle: Bone marrow mononuclear cells will differentiate into osteoclast precursor cells under the stimulation of cytokine M-CSF. At the same time, under the continuous stimulation of cytokine M-CSF and RANKL, the intercellular Contact with each other to fuse to form multinucleated cells, and then continue to differentiate to form mature osteoclasts with a sealing ring structure, expressing specific tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) to participate in the degradation of bone mineralization. Mature osteoclasts can adhere to the bone matrix and degrade bone by secreting protease, resulting in osteoporosis.
[0066] method:
[0067] In vivo osteoclast activity detection:...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com