Method of passivating cadmium pollution in rice field in situ by bottom ash of agriculture and forestry biomass direct-fired power generation plant
A cadmium pollution and biomass technology, applied in the field of soil cadmium pollution control, can solve the problems of not considering the positive effect of increasing soil available silicon content, reducing soil permeability, disadvantages, etc., and achieves obvious effect of soil cadmium passivation and effective soil The effect of increasing the silicon content and reducing the available cadmium content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Low dosage of restoration agent (1kg / m 2 ) in situ passivation repair of early rice
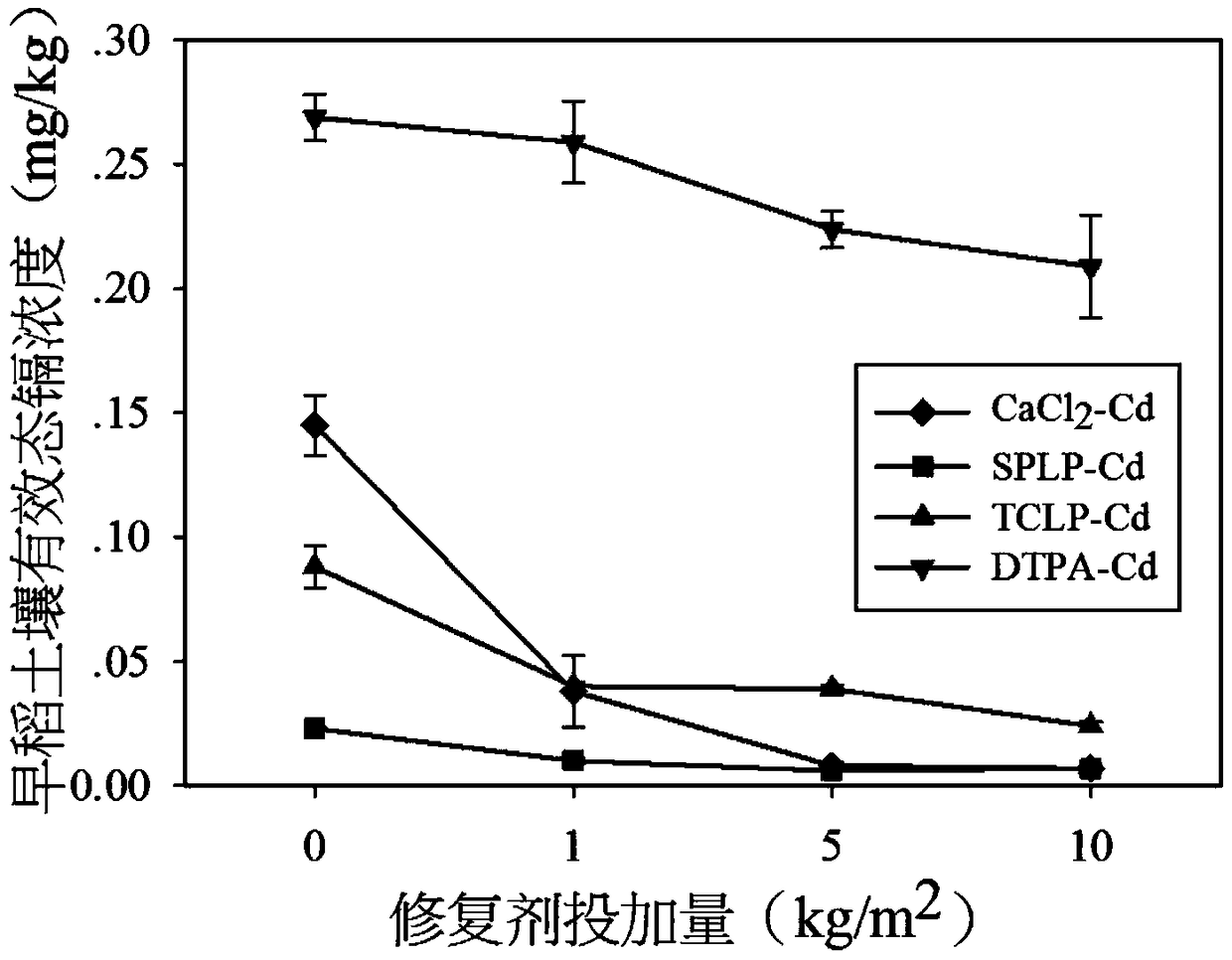
[0059] The test site is located in a cadmium-contaminated rice field in Xiangtan County, Hunan Province, and the farming system is a double-cropping rice field. The soil available state (DTPA leached state) cadmium content in the test plot is about 0.28 mg / kg, and the total cadmium content is 0.5-0.9 mg / kg. The variety of rice planted is Zhongjiazao 17, and the area of each experimental plot is 30m 2 , while doing three parallel control groups. The selected in-situ passivation restoration materials for heavy metal-contaminated soil are: 90% bottom ash from direct-fired power plants of agricultural and forestry biomass (with a particle size in the range of 70-500 μm), 5% animal charcoal, and 5% bentonite. Quantity (1kg / m 2 ) in-situ passivation remediation effect on cadmium-contaminated paddy soil. The restoration agent is evenly mixed with the soil tillage, and the soil and rice...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Medium dosage of restoration agent (5kg / m 2 ) in situ passivation repair of early rice
[0062] The test site is located in a cadmium-contaminated rice field in Xiangtan County, Hunan Province, and the farming system is a double-cropping rice field. The soil available state (DTPA leached state) cadmium content in the test plot is about 0.28 mg / kg, and the total cadmium content is 0.5-0.9 mg / kg. The variety of rice planted is Zhongjiazao 17, and the area of each experimental plot is 30m 2 , while doing three parallel control groups. The selected in-situ passivation repair materials for heavy metal contaminated soil are: 90% agricultural and forestry biomass direct-fired power plant bottom ash (particle size range of 70-500 μm), 5% animal charcoal, 5% bentonite, medium dosage of inspection and repair agent Quantity (5kg / m 2 ) in-situ passivation remediation effect on cadmium-contaminated paddy soil. The restoration agent is evenly mixed with the soil tillage, and t...
Embodiment 3
[0064] High dosage of restoration agent (10kg / m 2 ) in situ passivation repair of early rice
[0065] The test site is located in a cadmium-contaminated rice field in Xiangtan County, Hunan Province, and the farming system is a double-cropping rice field. The soil available state (DTPA leached state) cadmium content in the test plot is about 0.28 mg / kg, and the total cadmium content is 0.5-0.9 mg / kg. The variety of rice planted is Zhongjiazao 17, and the area of each experimental plot is 30m 2 , while doing three parallel control groups. The selected in-situ passivation repair materials for heavy metal-contaminated soil are: 90% bottom ash from direct-fired power plants of agricultural and forestry biomass (with a particle size in the range of 70-500 μm), 5% animal charcoal, and 5% bentonite. Quantity (10kg / m 2 ) in-situ passivation remediation effect on cadmium-contaminated paddy soil. The restoration agent is evenly mixed with the soil tillage, and the soil and rice s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
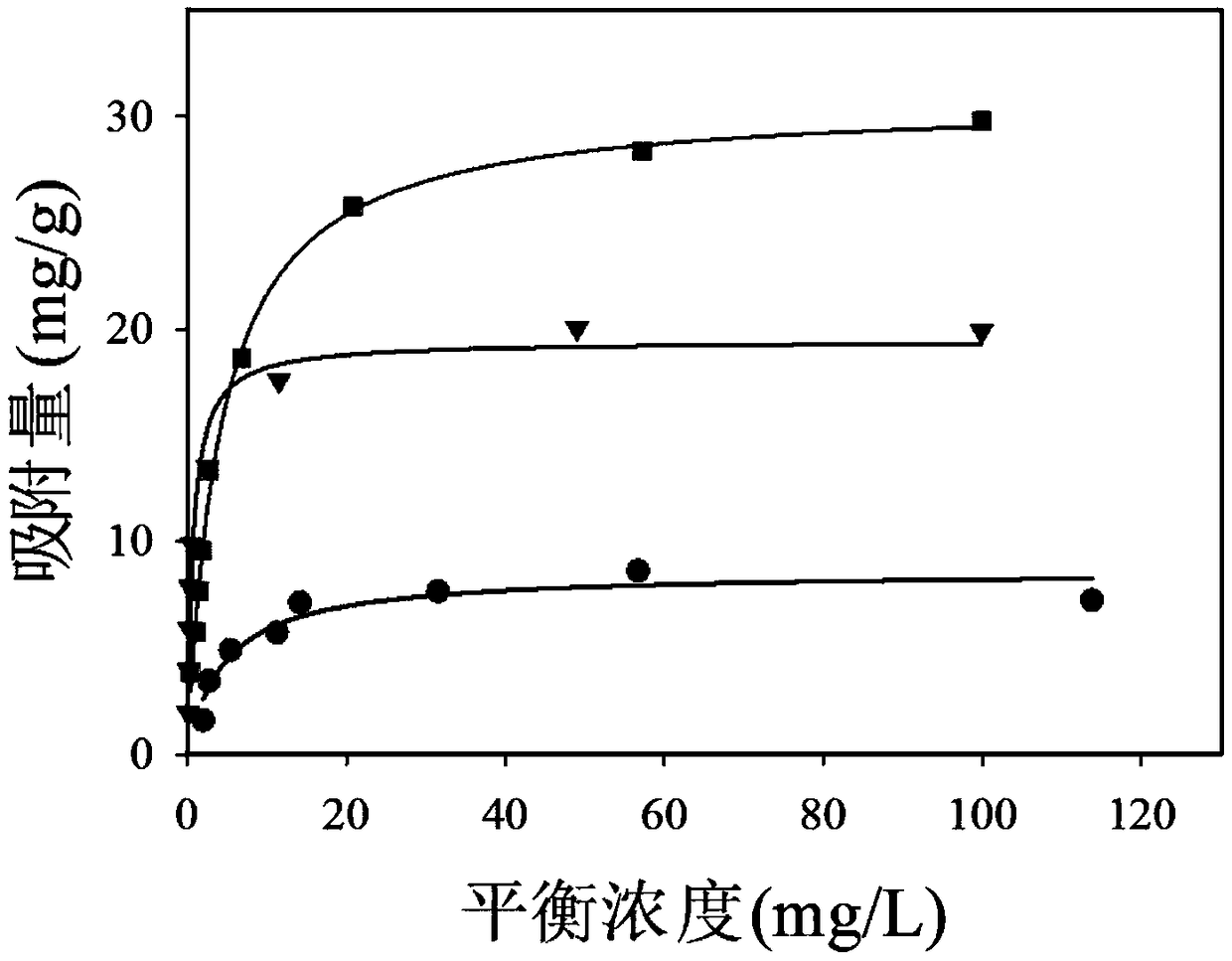
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com