Method for rapid identification of proliferation phenotype in cell line after esophagus cancer functional gene knockout
A technology of functional genes and identification methods, which can be applied to other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, genetic engineering, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of delaying the research progress and breadth of esophageal cancer functional genes, consuming a lot of time and labor costs , Time-consuming analysis of phenotypes, etc., to save manpower and time costs, high-throughput molecular screening, and time-saving effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
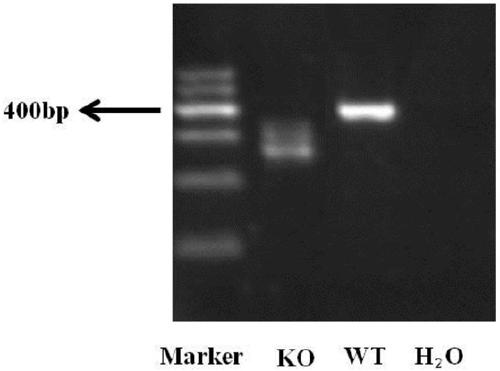
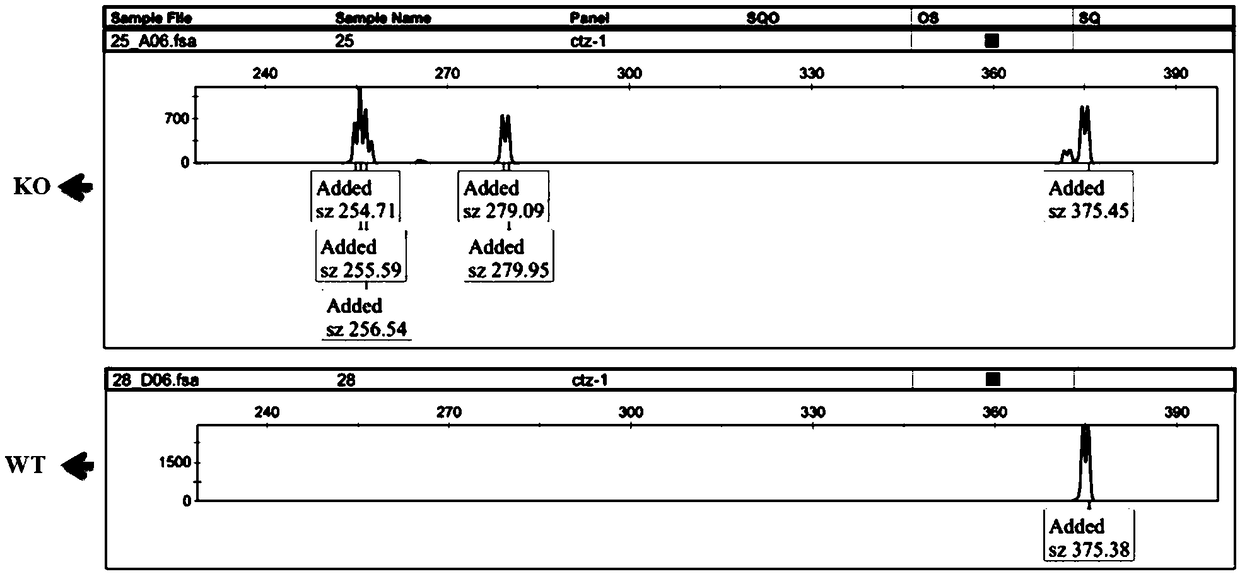
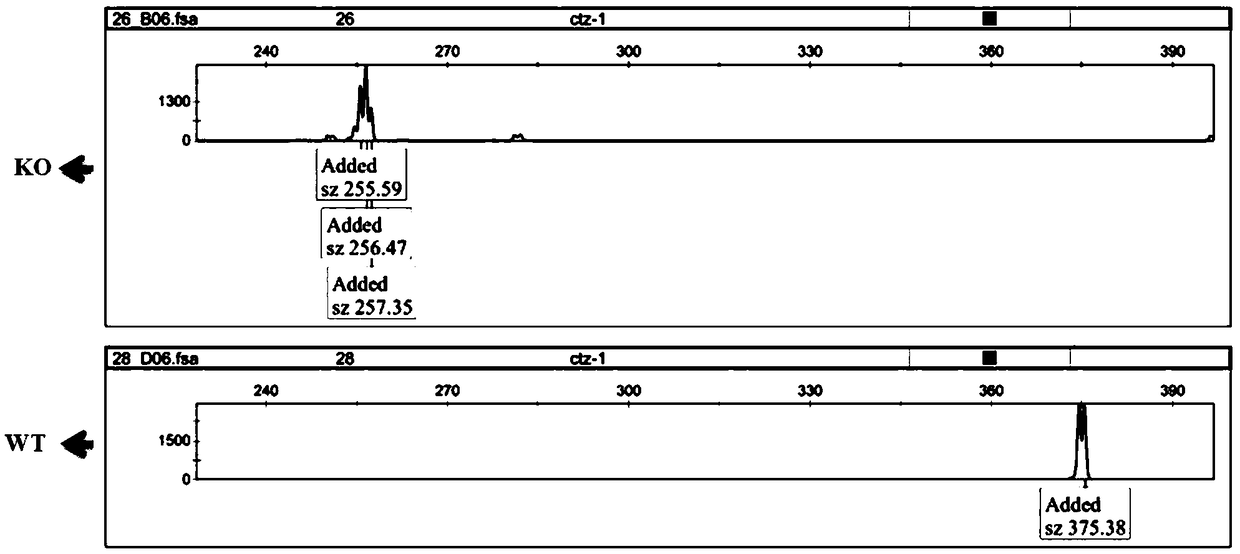
[0043]The inventive idea of the rapid identification method for the proliferation phenotype of esophageal cancer after functional gene knockout in the cell line of the present invention is: use CRISPR-Cas9 technology to knock out the candidate functional genes of esophageal cancer, and use flow cytometry technology to sort the genes after gene knockout. Select the fluorescent positive cell population into a 96-well cell culture plate, and the number of cells per well is 200 (200-300 is acceptable), so that the cells will soon fill up a well. At this time, the cells are collected, and the DNA is extracted for fragment analysis. According to the peak map analysis of fragment analysis, it can be known that after CRISPR-Cas9 targets the functional gene, clones with different gene deletions or mutations can be obtained. At this time, the peak pattern remains, and the cells sorted into another well of the 96-well plate are expanded to a 6-well plate, and the cells are collected aga...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com