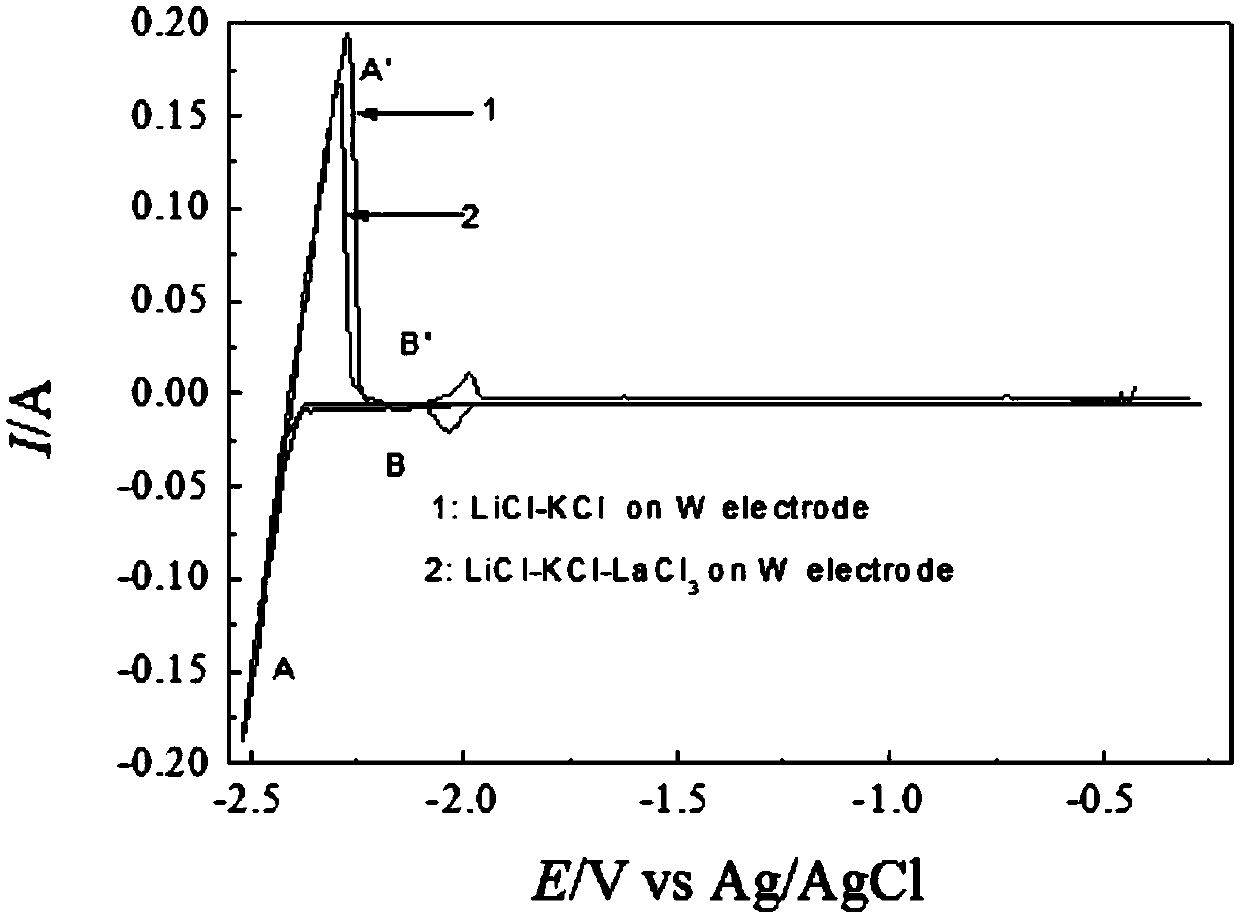
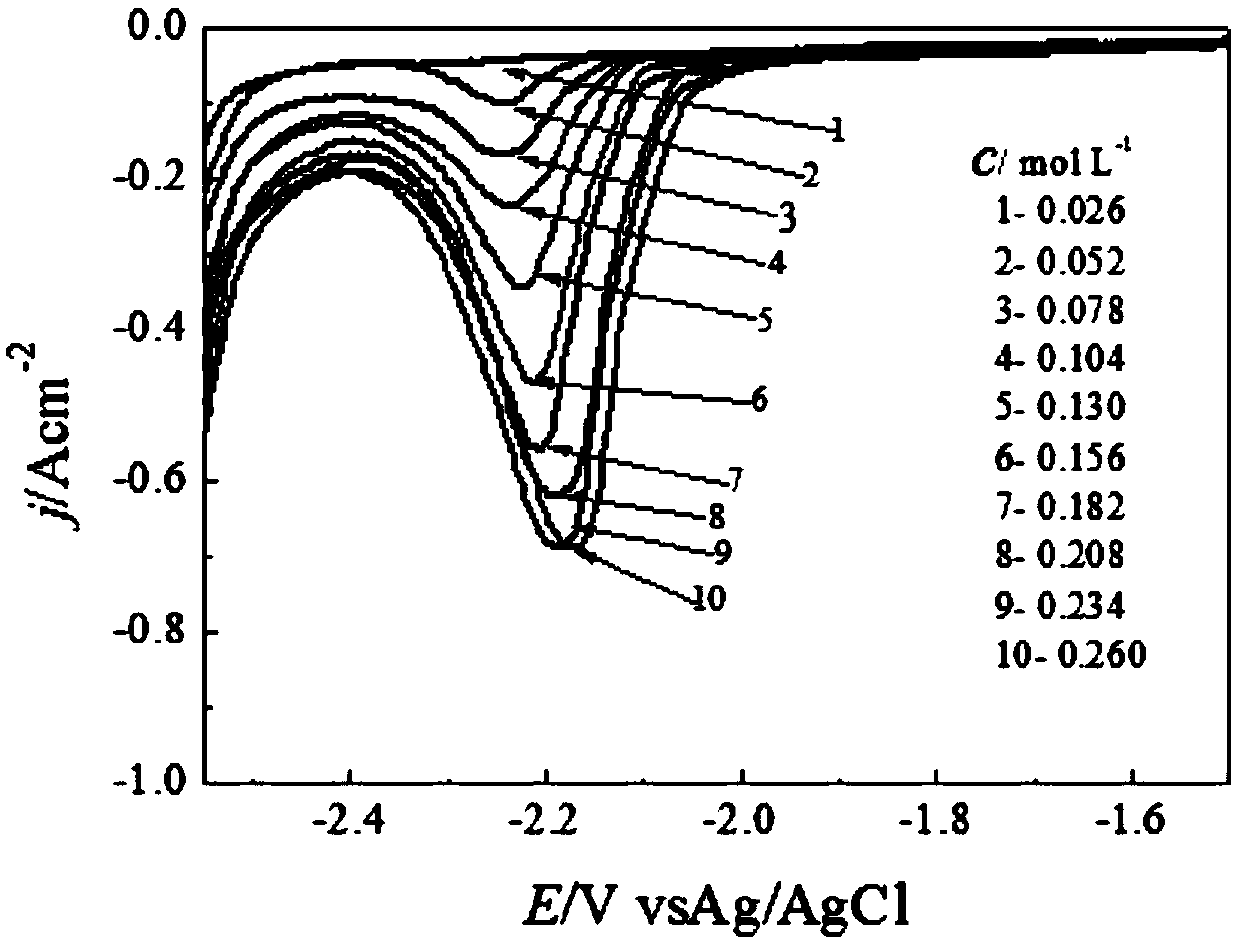
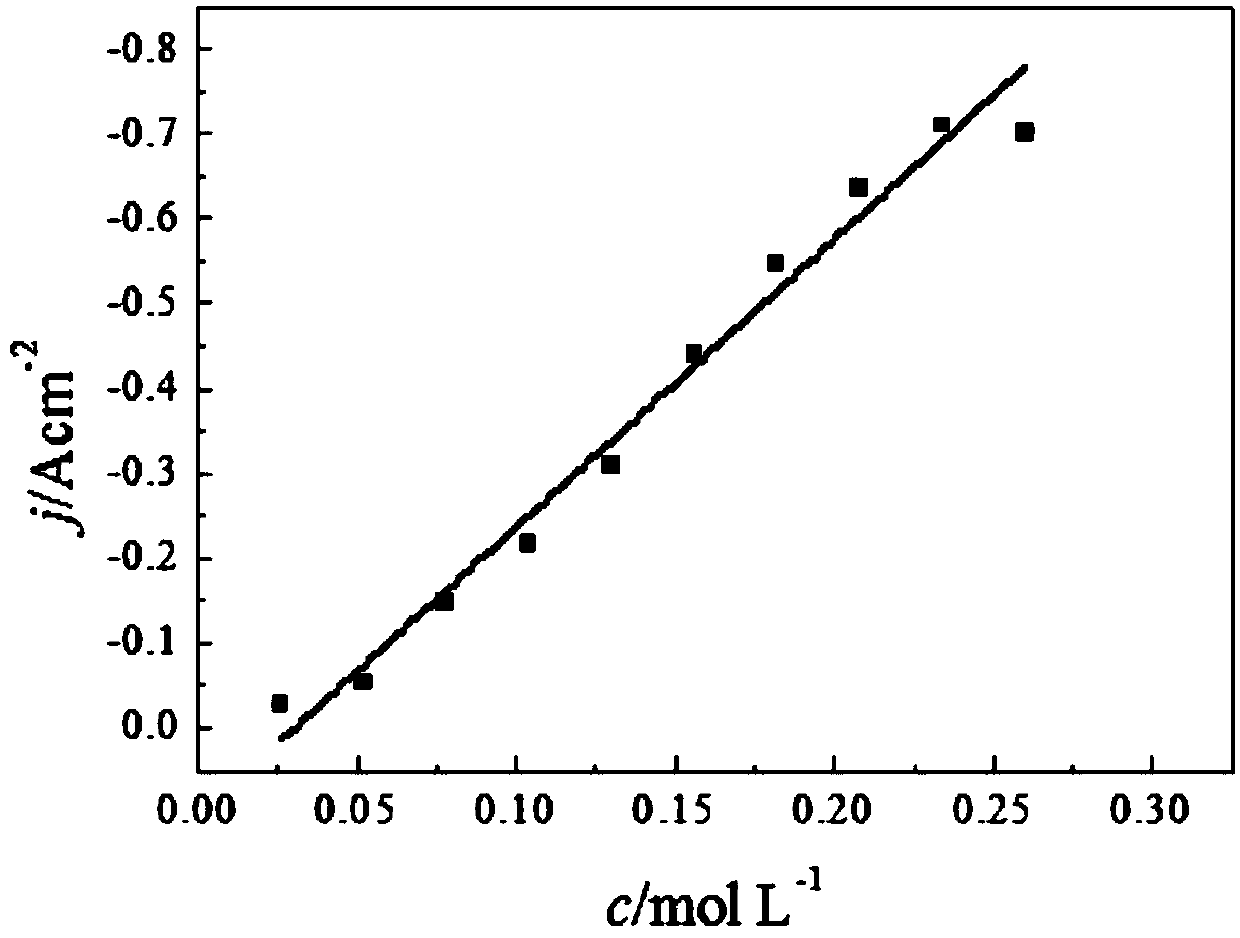
Method for online monitoring metal ion concentration in anodic dissolution process in real time
A technology of metal ion concentration and anode dissolution, which is applied in the field of real-time online monitoring of metal ion concentration in the process of anode dissolution, molten salt electrolytic refining, and spent fuel dry reprocessing. It can solve the problems of long test time and reduce radiation and other hazards. , good accuracy and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: At 450°C, LiCl-KCl (mass ratio of 45:38wt.%) was used as the electrolyte system, and Bi-RE (9.7wt.%)-Li (2.4wt.%) alloy was used as the working electrode (electrode Area 1.53cm 2), the spectrally pure graphite rod is the auxiliary electrode, Ag / AgCl is the reference electrode, and the anodic dissolution is performed at the potential of -0.5V (Vs Ag / AgCl), and the anode dissolution is temporarily stopped every 10 minutes, and the working electrode is replaced by a tungsten electrode The other electrodes remain unchanged, and the square wave voltammetry is used for online testing to obtain the current intensities of different anode dissolution times. According to the curve, it can be seen that RE was detected in the first 70 minutes 3+ After 80 minutes, the reduction signals of Bi-Li and Bi-RE alloys were detected. Compared with the standard concentration working curve, the dissolved ion concentration range was 0.14-3.55wt%.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: At 500°C, with LiCl-KCl (mass ratio of 45:38wt.%) as the electrolyte system, with Bi-RE (9.7wt.%)-Li (2.4wt.%) alloy as the working electrode (electrode Area 1.53cm 2 ), the spectrally pure graphite rod is the auxiliary electrode, Ag / AgCl is the reference electrode, and the anodic dissolution is performed at the potential of -1.0V (Vs Ag / AgCl), and the anode dissolution is temporarily stopped every 10min, and the working electrode is replaced with a tungsten electrode. The other electrodes remain unchanged, and the square wave voltammetry is used for online testing to obtain the current intensities of different anode dissolution times. According to the curve, only RE was detected in the first 50 minutes 3+ The reduction signal of the Bi-Li alloy was detected at 60 minutes, and the reduction signal of the Bi-RE alloy was detected after 110 minutes. Compared with the standard concentration working curve, the dissolved ion concentration range was 0.138-3.8wt%. ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3: At 600°C, with LiCl-KCl (mass ratio of 45:38wt.%) as the electrolyte system, with Bi-RE (9.7wt.%)-Li (2.4wt.%) alloy as the working electrode (electrode Area 1.53cm 2 ), the spectrally pure graphite rod is the auxiliary electrode, Ag / AgCl is the reference electrode, and the anodic dissolution is performed at the potential of -1.3V (Vs Ag / AgCl), and the anode dissolution is temporarily stopped every 10min, and the working electrode is replaced by a W electrode. The other electrodes remain unchanged, and square wave voltammetry is used for online testing to obtain current intensities at different anode dissolution times. According to the curve, only RE was detected in the first 40min 3+ The reduction signal of the Bi-Li alloy was detected at 50 minutes, and the reduction signal of the Bi-RE alloy was not detected. Compared with the standard concentration working curve, the dissolved ion concentration range was 0.135-4.1wt%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com