A multi-photon entanglement light source
A multi-photon, entangled light technology, applied in optics, optical components, structures/shapes of optical resonators, etc., can solve problems such as loss of quantum information, errors in quantum logic operations, loss of qubits, etc., to improve the signal-to-noise of quantum detection ratio, the effect of solving the quantum decoherence problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
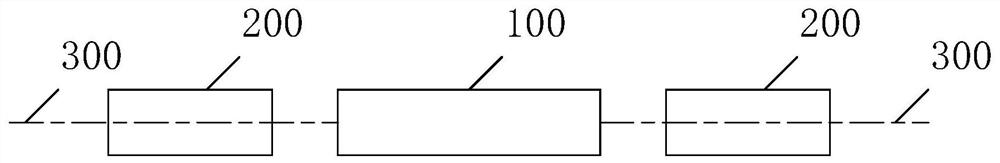
[0049] see figure 1 , is a schematic structural diagram of a multi-photon entangled light source provided in this embodiment. The multi-photon entangled light source is used to output macro-scale multi-photon multi-dimensional entangled light, including a single-mode laser 100 and an adjustment component 200, wherein,
[0050] The single-mode laser 100 is used to bidirectionally output two beams of laser light; wherein, the two beams of laser light are generated by stimulated emission, and the two beams of laser light are in a multi-photon entangled state satisfying the law of parity conservation;
[0051] The adjustment component 200 is arranged on the optical path 300 of the two laser beams, and is used to adjust the laser beam volume of the two laser beams to be smaller than the coherent volume of the single-mode laser 100, and adjust the laser beam area of the two laser beams to be smaller than the single-mode laser 100 The coherent area of , output macroscale multi-ph...
Embodiment 2
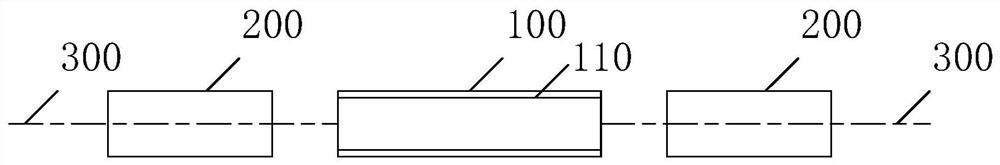
[0070] see figure 2 , is a schematic structural diagram of a multi-photon entanglement light source provided in this embodiment. in, figure 2 The multiphoton entangled light source shown is composed of figure 1 The multiphoton entanglement source optimization shown is obtained.
[0071] see figure 2 , the single-mode laser 100 has an axisymmetric structure, and is used to coaxially and bidirectionally output two laser beams with the same power.
[0072] In this embodiment, the bidirectional output laser light of the single-mode laser 100 has the same power, and the adjustment and control of photons in the single-mode laser 100 are not limited in this embodiment. It can be understood that the output laser light only needs to have the same power.
[0073] As an optional implementation, the resonant cavity of the single-mode laser 100 adopts a parallel planar standing wave cavity 110 , which is used to generate two laser beams in a multiphoton coherently superimposed enta...
Embodiment 3
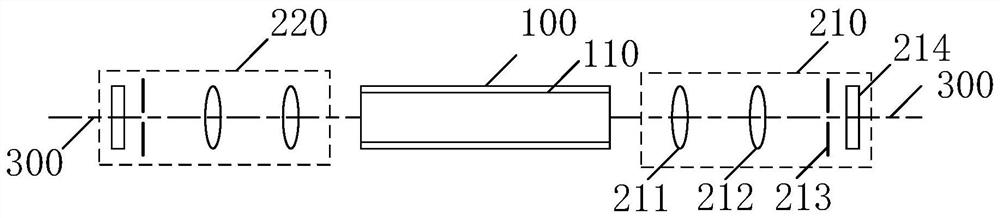
[0127] see image 3 , is a schematic structural diagram of a multi-photon entanglement light source provided in this embodiment. in, image 3 The multiphoton entangled light source shown is composed of figure 2 The multiphoton entanglement source optimization shown is obtained.
[0128] see image 3 , the adjustment assembly 200 includes a first optical assembly 210 and a second optical assembly 220 arranged on the optical path 300 of the two laser beams, the first optical assembly 210 and the second optical assembly 220 have the same optical elements and the optical elements are axisymmetrically arranged .
[0129] In this embodiment, the first optical component 210 and the second optical component 220 are mirror-symmetrically arranged on the basis of the central section of the single-mode laser 100 .
[0130] As an optional implementation manner, the first optical assembly 210 includes a first lens 211 , a second lens 212 , an aperture stop 213 , and an interference fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com