A Method for Microstructure After Vacuum Carburizing
A technology of vacuum carburizing and vacuum low-pressure carburizing, which is applied in furnaces, heat treatment equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems affecting material mechanics and performance, ineffective effects, and difficult to refine the surface structure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0020] The method for refining structure after vacuum carburizing of the present invention, its preferred embodiment is:
[0021] Including vacuum low-pressure carburizing stage, also includes slow cooling stage after carburizing, cycle slow cooling stage, secondary quenching stage;
[0022] The slow cooling stage after carburizing includes: after carburizing, the workpiece continues to be in the heating chamber, the heating is stopped, and nitrogen is filled in pulse mode, and slowly lowered to 600°C;
[0023] The cycle slow cooling stage refers to multiple rapid heating and multiple slow cooling;
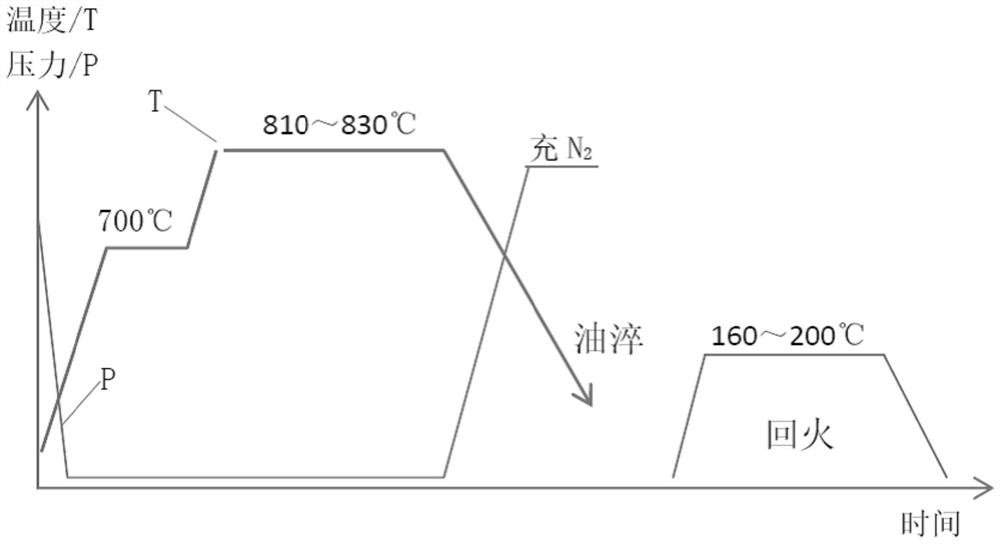
[0024] The secondary quenching stage refers to a quenching method in which the first quenching solidifies and refines the crystal grains after the slow cooling cycle is completed, and the second quenching takes into account both the surface and the core.
[0025] In the slow cooling stage after carburizing, the heating chamber is charged with nitrogen gas in a pulsed manner with ...
Embodiment 1
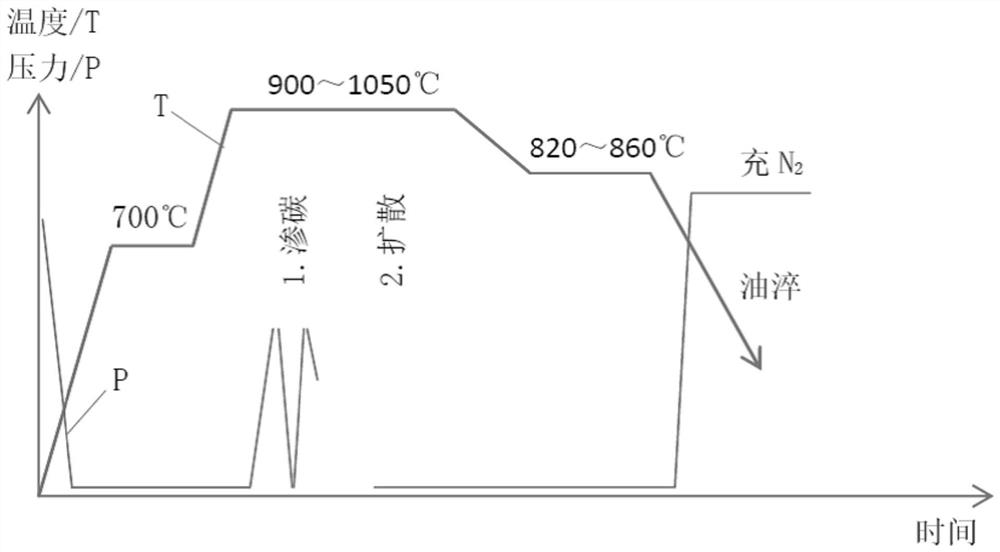
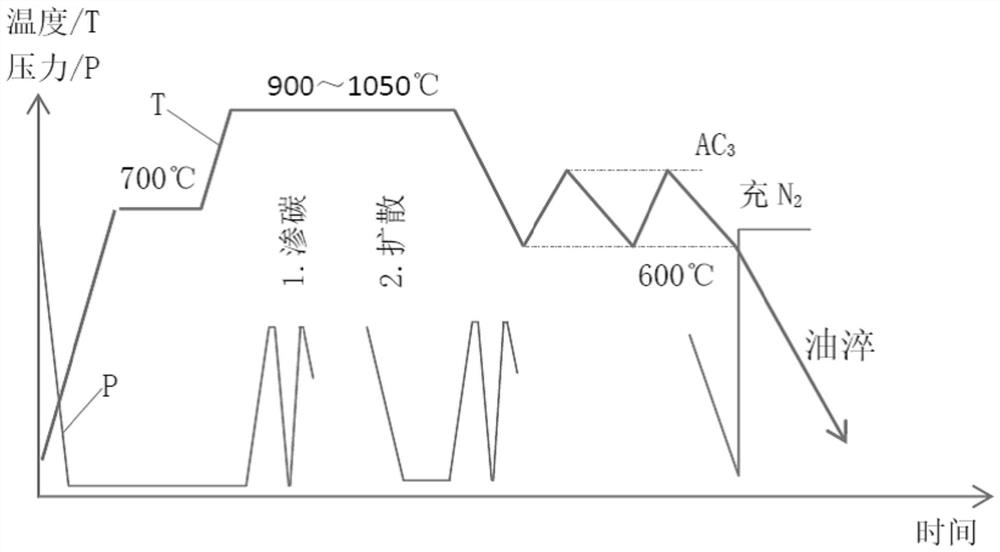
[0045] see Figure 2~3 (and compare figure 1 ), in an embodiment of the present invention, a method for refining surface and core tissue during cooling after vacuum carburizing, including the following stages:
[0046] (1) Vacuum low-pressure carburizing stage: Set the carburizing time and diffusion time according to the technical requirements of the workpiece, and after preparing the corresponding process curve, put the workpiece in a vacuum furnace to evacuate, start heating, and preheat at 700°C for a period of time. After heating up to the carburizing temperature of 900-1050°C, the low-pressure carburizing process is started, and acetylene or propane is charged in pulses, with a pressure of generally 1.3-6.6kpa. After carburizing and diffusion stages, vacuum low-pressure carburizing is completed.
[0047] (2) Slow cooling stage after carburizing: After carburizing, stop heating and start pulse-type air-inflation cooling. The pulse cycle is generally 4-5min, and the air-in...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2 – Gears
[0054] Dimensions (mm): addendum circle diameter φ630, inner hole φ270, tooth width 80, module 5mm
[0055] Material: 18CrNiMo7-6.
[0056] Heat treatment technical requirements: standard JB / T6141.3-1992 vacuum carburizing carbide ≤ 2 grades, surface martensite and retained austenite ≤ 2 grades, core structure ≤ 2 grades, carburized layer 0.9 ~ 1.2mm , Surface hardness HRC60~62.
[0057] Carburizing process: compare the traditional process of vacuum low-pressure carburizing with the microstructure process.
[0058] like Figure 4~5 It is the surface martensite structure obtained by the traditional process of vacuum low-pressure carburizing. According to JB / T6141.3-1992 rating: Martensite structure is 4 grades, and the needles are relatively thick; heart structure: 2 grades.
[0059] like Figure 6~7 It is the surface martensite structure obtained by vacuum low-pressure carburizing refinement process. According to JB / T6141.3-1992 rating: martensi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap