Method for preparing battery grade iron phosphate from waste and old lithium iron phosphate batteries
A lithium iron phosphate battery, lithium iron phosphate technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the economic value of products, affecting the purity of iron phosphate, increasing recovery costs, etc., and reducing lithium recovery. cost, corrosion mitigation, recovery effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
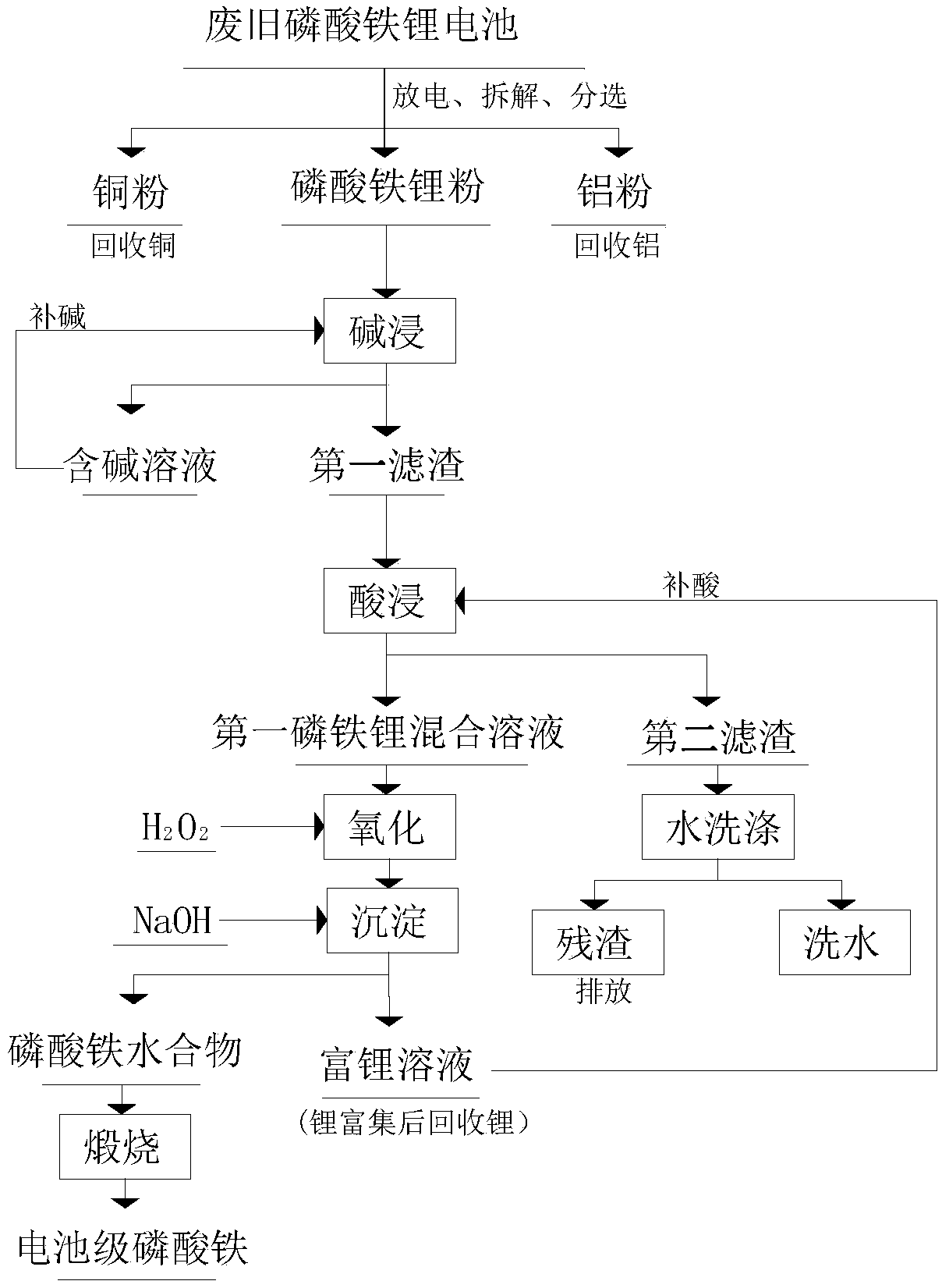
[0048] This embodiment provides a method for preparing battery-grade iron phosphate from waste lithium iron phosphate batteries, which mainly includes the following steps:
[0049] (1) Battery dismantling and separation: Discharge the waste lithium iron phosphate battery to below 2.0V, put it into a crusher for disassembly, and then separate it by vibrating screening and airflow screening to obtain the first lithium iron phosphate powder, Aluminum powder and copper powder;
[0050] (2) Alkaline leaching: put 300 g of the first lithium iron phosphate powder recovered from waste lithium iron phosphate batteries into 1.5 L of sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 3 mol / L and stir for 1 hour at a stirring speed of 500 r / min. room temperature (28°C), then filter and wash to obtain the first filter residue and alkali-containing filtrate, and the alkali-containing solution is supplemented with a second preset concentration of alkali and then continue to leach new second l...
Embodiment 2
[0056] This embodiment provides a method for preparing battery-grade iron phosphate from waste lithium iron phosphate batteries, which mainly includes the following steps:
[0057] (1) Battery dismantling and separation: Discharge the waste lithium iron phosphate battery to below 2.0V, put it into a crusher for disassembly, and then separate it by vibrating screening and airflow screening to obtain the first lithium iron phosphate powder, Aluminum powder and copper powder;
[0058] (2) Alkaline leaching: Put 300 g of the first lithium iron phosphate powder recovered from waste lithium iron phosphate batteries into 2.0 L of sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 1 mol / L and stir for 3 hours at a stirring speed of 600 r / min. room temperature (32° C.), then filter and wash to obtain the first filter residue and alkali-containing filtrate, and the alkali-containing solution is supplemented with a second preset concentration of alkali and then continue to leach new secon...
Embodiment 3
[0064] (1) Battery dismantling and separation: Discharge the waste lithium iron phosphate battery to below 2.0V, put it into a crusher for disassembly, and then separate it by vibrating screening and airflow screening to obtain the first lithium iron phosphate powder, Aluminum powder and copper powder;
[0065] (2) Alkaline leaching: put 300 g of the first lithium iron phosphate powder recovered from waste lithium iron phosphate batteries into 2.0 L of sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 4 mol / L and stir for 0.5 h at a stirring speed of 600 r / min. The temperature is room temperature (31°C), and then filtered and washed to obtain the first filter residue and alkali-containing filtrate. The alkali-containing solution is supplemented with a second preset concentration of alkali and continues to leach new second lithium iron phosphate powder. The first filter residue enters the next step ;
[0066] (3) Acid leaching: the first filter residue obtained in step (2) is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com