High-precision interference alignment narrowband interference suppression algorithm for broadband private network system
A narrow-band interference and interference alignment technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as high complexity of recovery algorithms, uneven error distribution, and low estimation accuracy, and achieve the effects of improving BER performance, increasing accuracy, and reducing spectrum leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
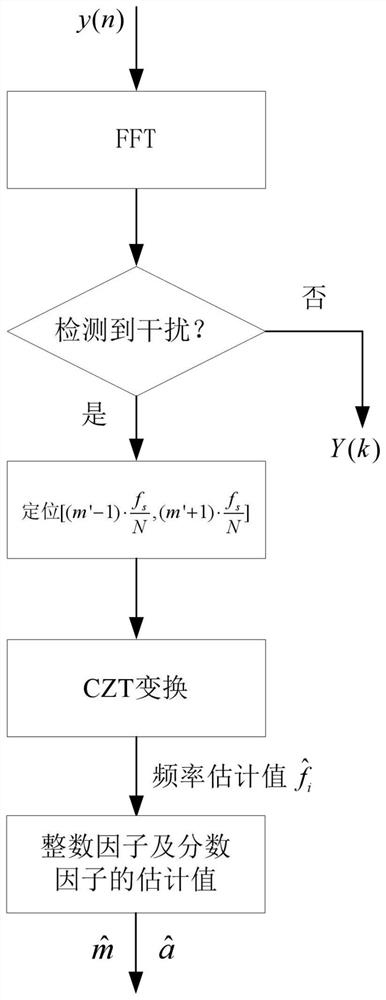
[0071] according to figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the present invention provides a high-precision interference alignment narrowband interference suppression algorithm for a broadband private network system, comprising the following steps:
[0072] Step 1: Use FFT to detect narrowband signal interference clusters on the in-band spectrum, start detection from low frequencies, and filter out interference clusters with interference. If there is no interference, perform baseband processing on the received signal in a traditional OFDM system;
[0073] Step 2: Model the form of narrowband interference as single-tone interference, and all interference clusters correspond to multiple single-tone interferences. The single-tone interference in each interference cluster is used to locate the frequency of the narrow-band interference signal in the interference cluster. The j corresponding to the maximum value of |Y(j)| in the interference cluster is denoted as m′, according to the ener...
specific Embodiment 2
[0131] according to Figure 6 to Figure 8 , aiming at improving the NBI frequency estimation accuracy and reducing the NBI spectrum leakage narrowband interference suppression problem in the OFDM-based broadband private network system group service of the present invention, a Monte Carlo simulation verification is carried out, and the relevant simulation parameters are set as shown in Table 1.
[0132] Table 1
[0133]
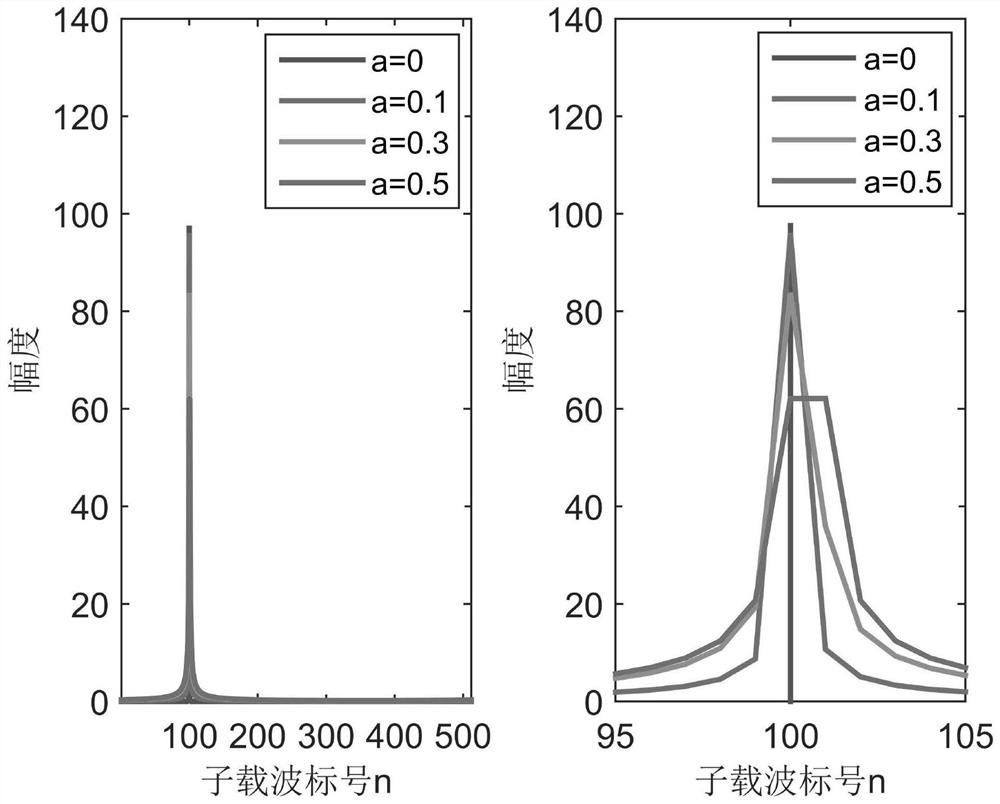
[0134] To compare the frequency estimation accuracy of CZT, Image 6 gives m=100, a=0.3, A 0 = 4, the spectrum near the interference frequency after FFT of the received signal and the spectrum refined by CZT. It can be seen from the figure that compared with the spectrum obtained by direct FFT, the spectrum peak after CZT refinement is closer to the actual interference frequency, and the interference frequency estimation based on CZT has higher accuracy.
[0135] In order to compare the impact of different fractional factors a on the system performance, ...
specific Embodiment 3
[0138] The NBI time-domain sampling of one OFDM symbol period at the receiving end is expressed as:
[0139]
[0140] Among them, t s is the sampling interval in the time domain.
[0141] After NBI undergoes FFT, the frequency domain interference at the kth subcarrier position can be expressed as:
[0142]
[0143] Pushed further:
[0144]
[0145] When a=0,
[0146]
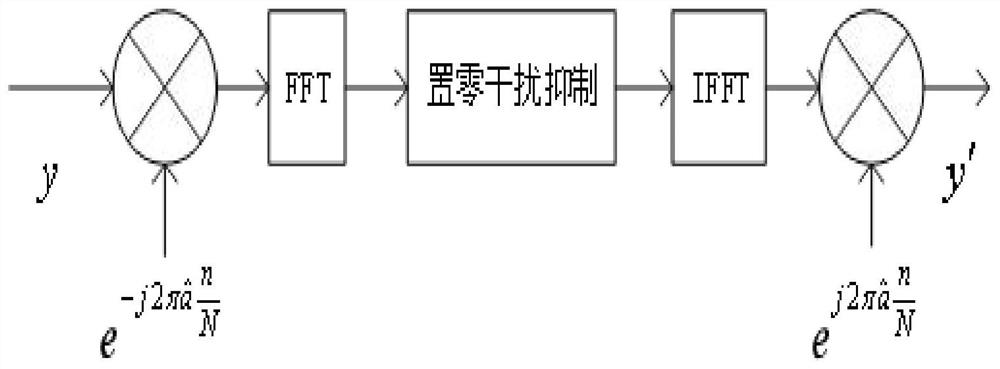
[0147] At this time, the single-tone interference is orthogonal to the OFDM subcarrier, and the interference only affects the subcarrier labeled m, and has no influence on other subcarriers. A good effect can be obtained by using the frequency domain zeroing interference suppression method for the subcarrier m.
[0148] When a≠0,
[0149]
[0150] It can be seen that single-tone interference produces spectrum leakage to adjacent multiple subcarriers. A 0 =4, the monotone interference of the interference frequency integer factor m=100 is an example, the monotone interference spectrum corresp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com