Method for preparing Cu-based two-dimensional sheet MOFs material
A flake-shaped, aminoterephthalic acid technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of metal-organic framework materials, can solve the problems of reduced catalytic performance, difficulty in large-scale production, and high requirements for experimental equipment, and achieves simple preparation methods, short experimental periods, and increased The effect of contact area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] In order to test the effect of the ratio of metal ions and ligands on the morphology of MOFs materials, the experiment was carried out by the control variable method.
[0031] The specific steps are:
[0032] Add Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 O stirred until completely dissolved, then added ligand 2-aminoterephthalic acid, 2-aminoterephthalic acid and Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 The molar ratio of O is 0.5:1, Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 The molar concentration of O is 0.005 mol / L. Stir for 30 minutes to mix the two evenly, then move the solution to a polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, and after installation, let it stand at 120°C for 24 hours. After the reactor was taken out and cooled to room temperature naturally, it was centrifuged at 6000r / min for 3min, and the supernatant was discarded to obtain a blue-green precipitate.
[0033] Add DMF to wash the blue-green precipitate, add 1 mL of DMF to each 1 mg of precipitate, sonicate for 10 min, centrifuge at the same speed for 3 min, and discard...
Embodiment 2-3
[0035] Other steps are the same as in Example 1, and the difference is that the amount of the ligand (2-aminoterephthalic acid) added is different, and the ligand and Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 The molar ratio of O is 1:1 and 1.5:1 in turn. The obtained MOFs materials are marked as No. 2 and No. 3 after drying.
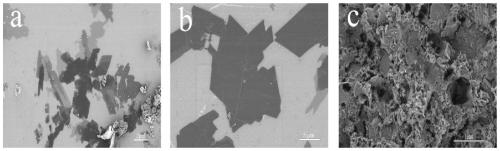
[0036] figure 1 a, figure 1 b, figure 1 c is the corresponding Cu(BDC-NH 2 ) SEM image of MOFs material, it can be seen that figure 1 The flake structure in b is more regular, and the flake diameter is about 8 μm. Therefore, Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 The optimum molar ratio of O to ligand is about 1:1. When the ligand ratio decreases, the formed flakes are smaller, about 2 μm. When the proportion of ligands increases, the increase of ligands makes the lamellar structure tightly combined and affects the lamellar separation. Therefore, suitable ligands with Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 The ratio of O molar weight is the 2 ) important conditions for MOFs materials.
Embodiment 4-6
[0038] In order to explore the relationship between 2-aminoterephthalic acid and Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 The molar concentration of O for Cu(BDC-NH 2 ) of MOFs material morphology, our implementation steps are as follows:
[0039] Add Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 O was stirred until completely dissolved, and the added 2-aminoterephthalic acid and Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 The molar ratio of O is 1:1. Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 The molar concentration of O is 0.001mol / L, 0.005mol / L, and 0.010mol / L in turn. Other steps are with embodiment 1. After drying, measure SEM to observe the morphology. Mark them as samples 4, 5, and 6 in turn.
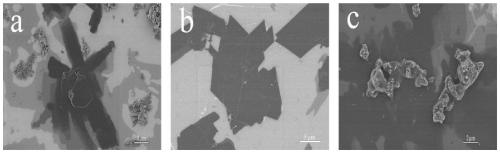
[0040] figure 2 a, figure 2 b, figure 2 c are the corresponding Cu(BDC-NH 2 ) of the MOFs material, it can be seen that the sheet structure in sample No. 5 is more regular and the edges are smoother, so the added Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 The optimum molar concentration of O and 2-aminoterephthalic acid is around 0.005mol / L. When the concentration decreases, the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com