Unmanned forklift based on laser slam
An unmanned forklift and laser technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, navigation through speed/acceleration measurement, navigation calculation tools, etc., can solve cumulative map errors, inaccurate navigation, inaccurate cloud point information, etc. problem, achieve the effect of small navigation error and prevent the error of walking system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
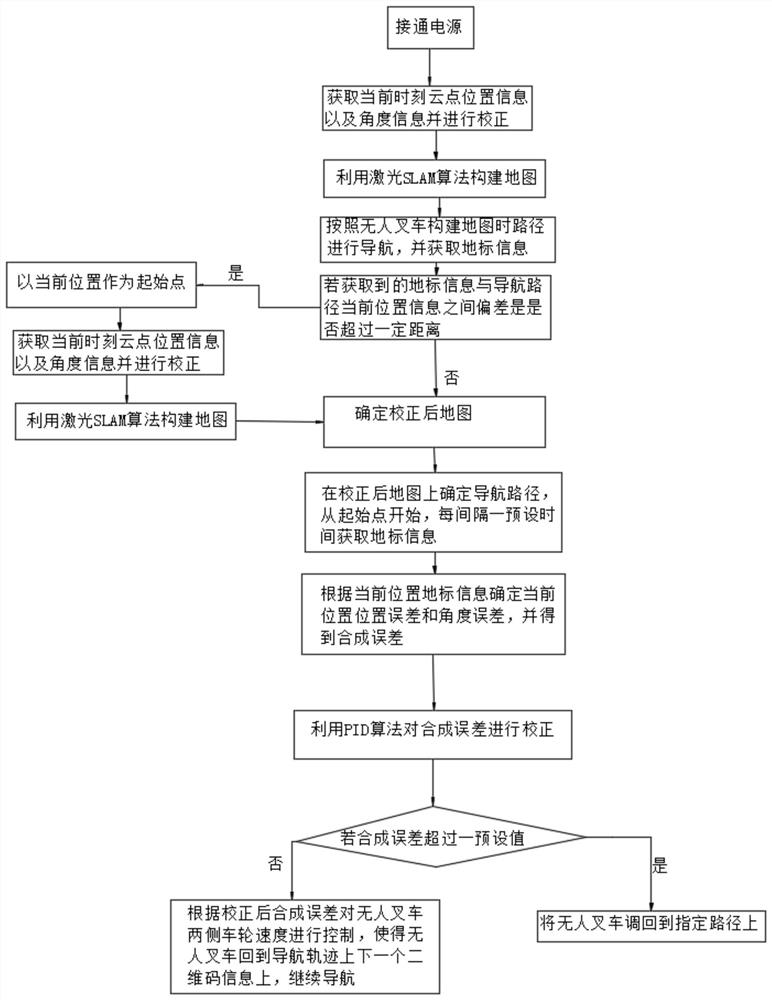
[0050] Such as Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 As shown, the unmanned forklift based on laser SLAM includes the car body, with wheels on the left and right sides of the car body, and landmark information on the ground where the unmanned forklift is walking. The landmark information can be binary code information, etc. In an embodiment, the landmark information is two-dimensional code information, and the control method of the unmanned forklift includes the following steps:
[0051] S1: Turn on the power;
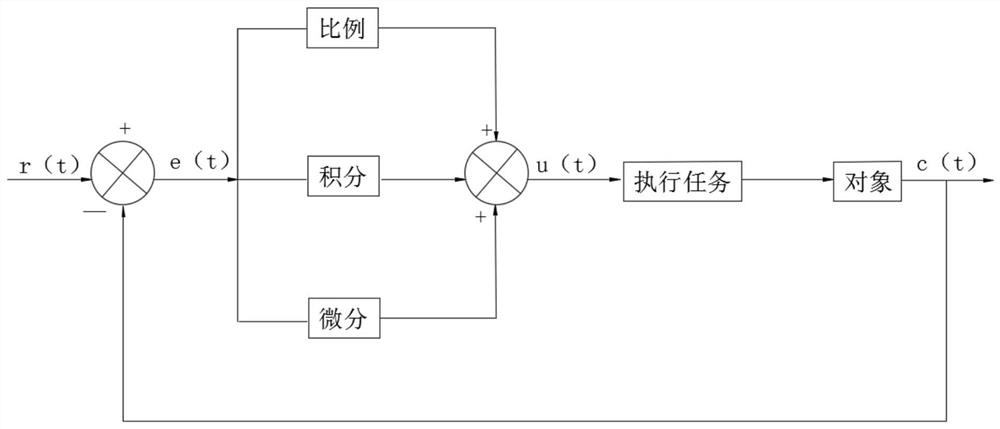
[0052] S2: The unmanned forklift constructs the map through the laser SLAM algorithm. The steps of constructing the map based on the laser SLAM algorithm include:
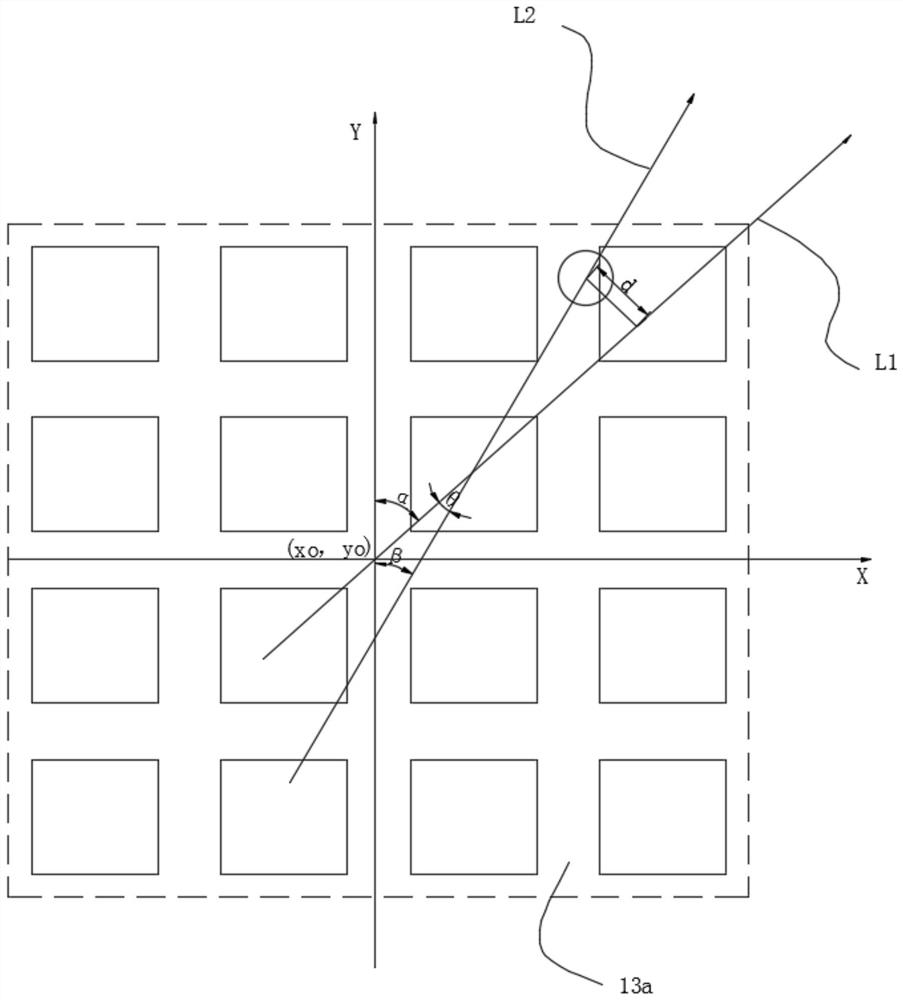
[0053] 1) Start the laser sensor to obtain the cloud point position information and cloud point angle information of the target near the unmanned forklift at the current moment, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com