Curbing toxic emissions from remediated substrate
一种基质、毒性金属的技术,应用在抑制修复基质中的毒性排放领域
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
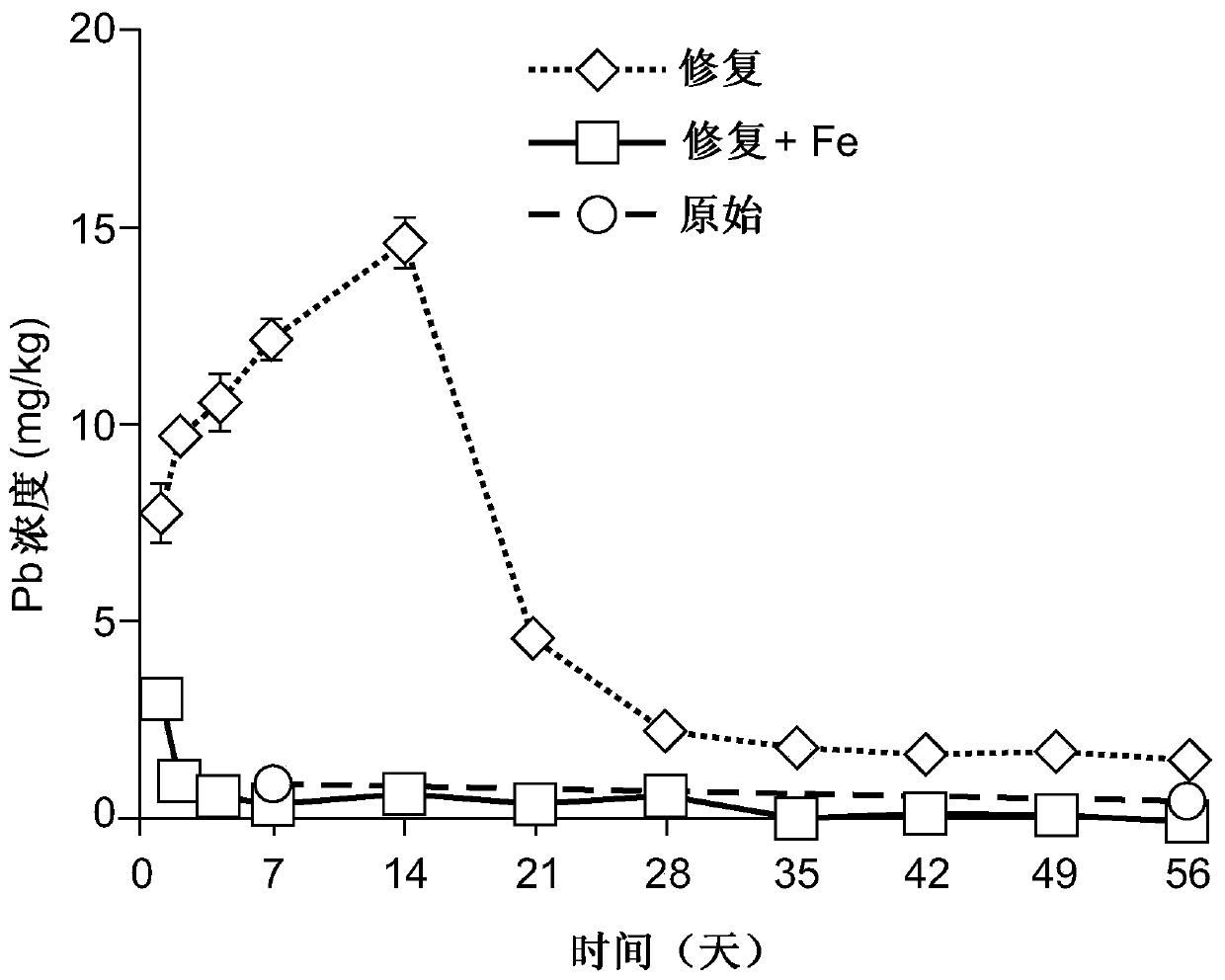
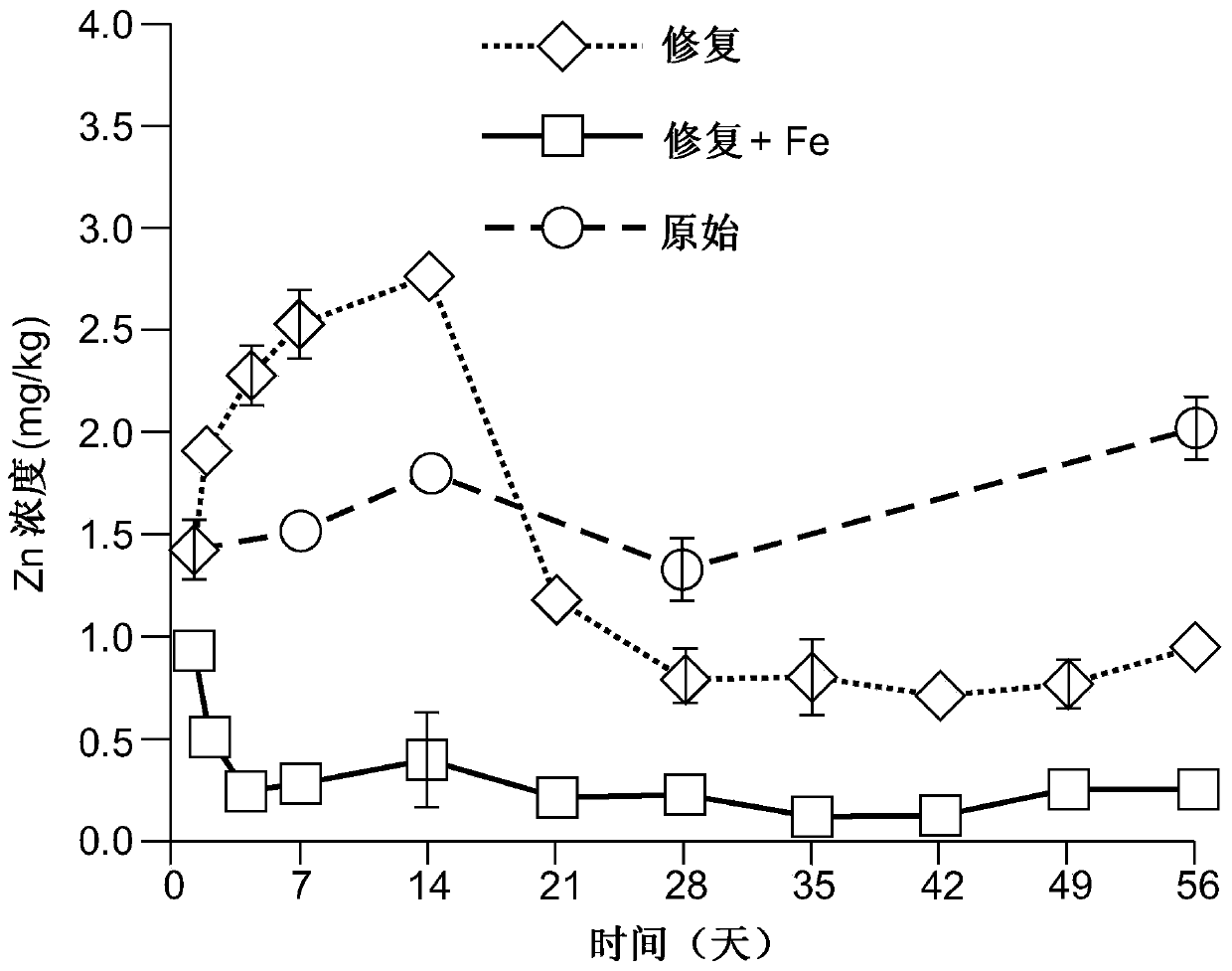
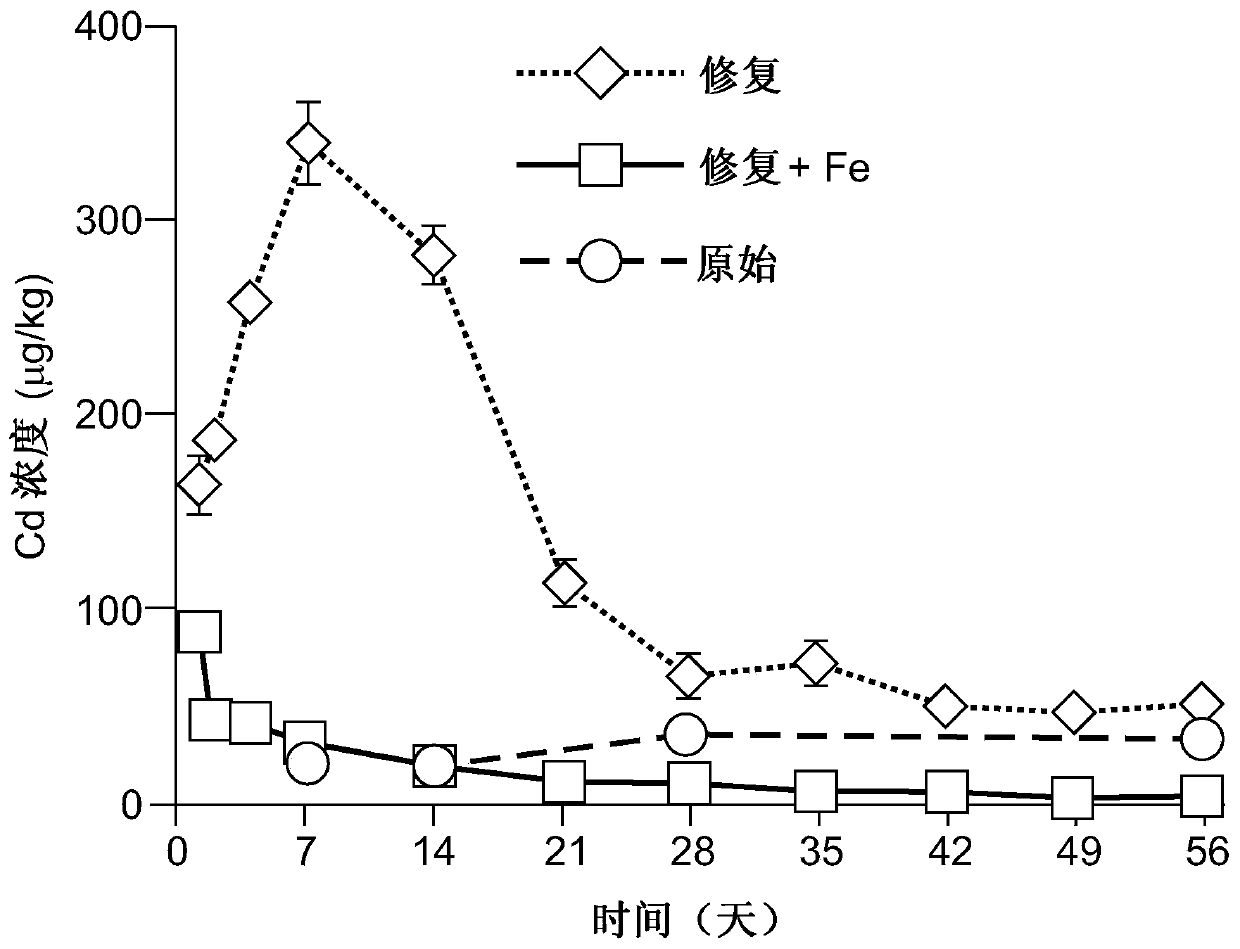
[0017] From Austria (Austria) has 860mg·kg -1 Pb, 330mg·kg -1 Zn and 3mg·kg -1 Acidic (pH = 5.1) industrially contaminated soil (50 kg, dry weight) of Cd was treated with 60 mM EDTA kg in a mixing vessel -1 solution (w:V ratio=1:1). According to the method of the invention, 1% (w / w) of zero-valent Fe (<0.5mm particles) was added to the soil slurry phase. The soil solids phase was then separated from the slurry using a chamber filter press and rinsed in press with 3 volumes of wash rinse solution to remove large amounts of toxic chelates. The rinse solution is washed and recovered as described in the patent application "Soil and sediment remediation" EP 3153246A1.
[0018] The soil washed with EDTA removed 78%, 20% and 83% of Pb, Zn and Cd, respectively. Lower levels of soil Zn extraction are known to those skilled in the art.
[0019] The washed (remediated) soil contained 28% moisture and was stored at room temperature for 8 weeks. Periodically 30 g samples were collec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com