Spinal surgery minimally invasive surgery navigation system
A minimally invasive surgery and navigation system technology, applied in the field of spinal surgery minimally invasive surgery navigation system, can solve the problems of long time for intraoperative image registration, long time for accurate three-dimensional reconstruction, and inability to accurately position, so as to improve clinical practicability and Generalization, precise and stable control of puncture angle and depth, and the effect of avoiding damage to normal tissues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
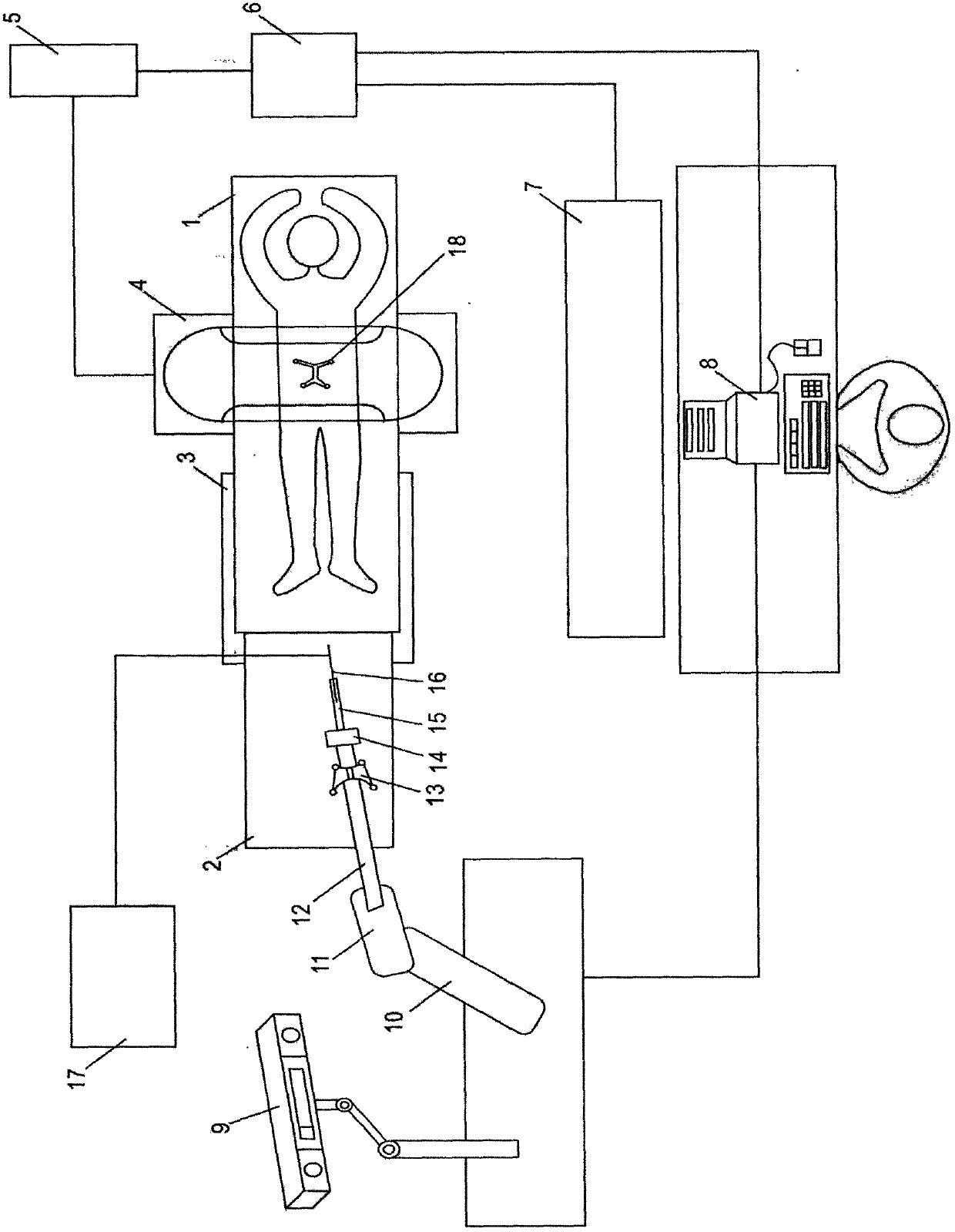
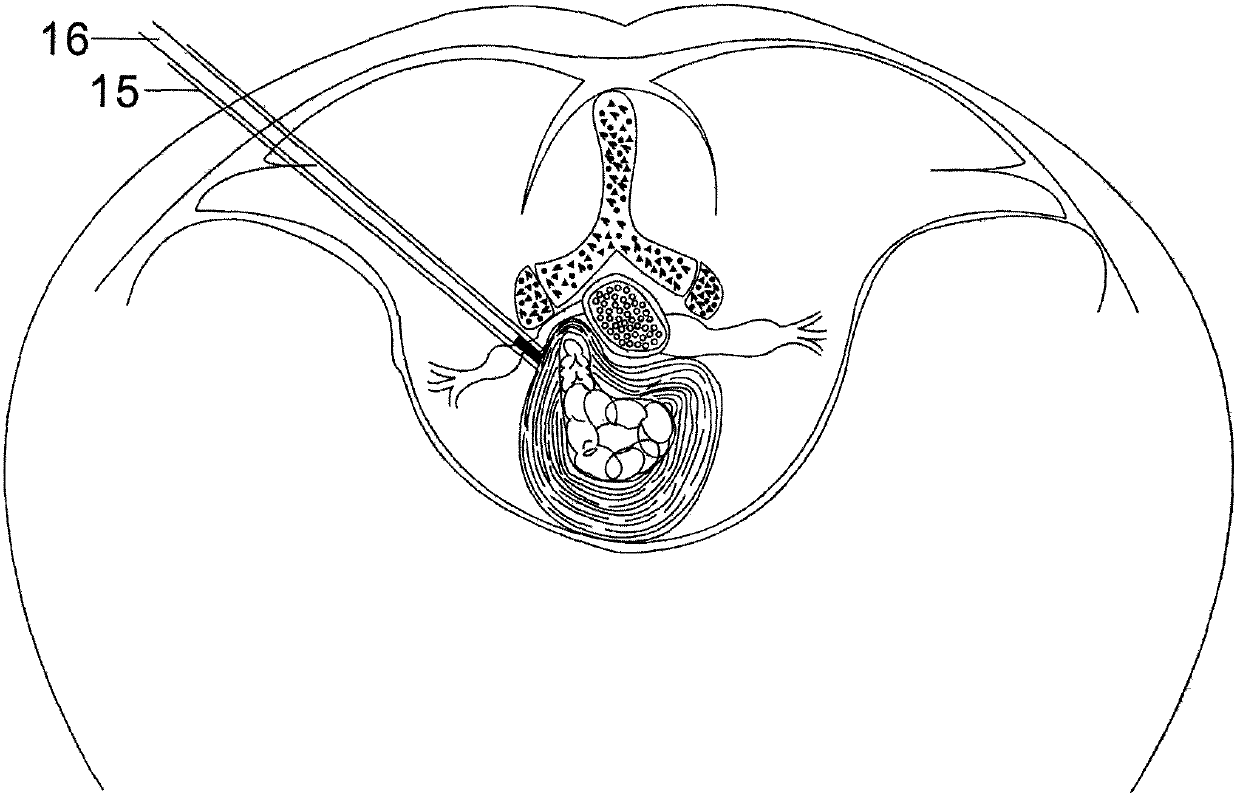
[0030] Embodiment one: if figure 1 , figure 2 , Figure 5 As shown in the figure, a navigation system for minimally invasive spinal surgery uses CT, MRI and other imaging equipment to obtain image data of the patient's spinal lesion area before the operation and inputs it into the system controller 8 for storage. The image processor 6 reads the image data of the system controller 8. The CT and MRI image information of the patient's preoperative spinal lesion is fused, the useful data is extracted for image segmentation, and the three-dimensional image model is reconstructed to display the patient's vertebrae, joints, nerves, blood vessels, and intervertebral disc tissue that compresses the nerve as a whole. Ligaments, preoperative surgical path planning based on the position of herniated disc and compressed nerve.
[0031] During the operation, the patient lies prone on the operating table 1, and the operating table 1 is connected to the lower base 3 through the slide rail as...
Embodiment 2
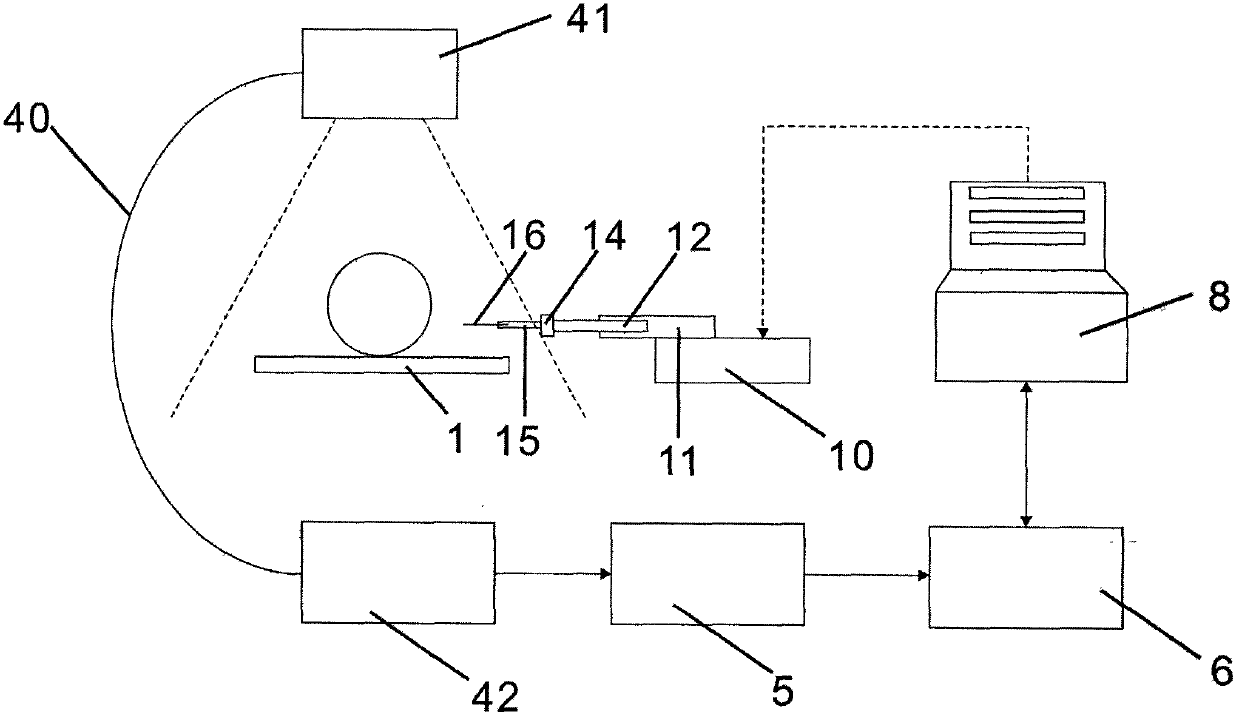
[0036] Embodiment two: if figure 1 , figure 2 , Figure 5 Shown, a kind of spinal surgery minimally invasive operation navigation system, this embodiment is compared with the first embodiment, the difference is: in this embodiment, the scanner 4 that is used to scan patient's spinal lesion is two-dimensional C Arm 40, the scanner 4 irradiates the patient with X-rays through the X-ray light source 41, and receives the X-ray information passing through the patient through the X-ray imaging device 42. After the X-rays penetrate the human body, the attenuation degree of different parts Different image information is obtained, and the image signal converter 5 converts the analog signal information obtained with different attenuation degrees into digital signal information, and the digital signal information is processed by the image processor 6 to obtain a two-dimensional bone image of the patient's spinal lesion, which is controlled by the system Under the control of the device...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Embodiment three: as figure 1 , Figure 5 , Figure 6 Shown, a kind of spinal surgery minimally invasive surgery navigation system, this embodiment is compared with the first embodiment, the difference is: in this embodiment, the scanner 4 that is used to scan patient's spinal lesion is O-shaped arm 43. After the X-ray penetrates the human body, the image information is obtained from the different attenuation degrees of different parts, and the image signal converter 5 converts the analog signal information obtained by the different attenuation degrees into digital signal information, and the digital signal information passes through the image processor 6 Computing and processing to obtain the two-dimensional bone image of the patient's spinal lesion. Under the control of the system controller 8, the image processor 6 performs three-dimensional reconstruction on the two-dimensional bone image, and the obtained three-dimensional reconstructed image is fused with the pat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com