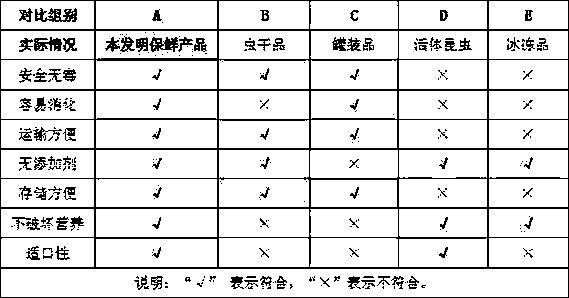
Preservation process of animal edible insect
A technology for treating insects, which is applied in the field of light industrial animal food, can solve the problems of insect color changes and processing methods that need to be further improved, and achieve the effects of extending the shelf life, avoiding spoilage, and avoiding infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1, take fresh-keeping Tenebrio molitor (mealworm) as example:
[0035] A fresh-keeping treatment process for animal edible insects, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0036] S1, cleaning insects from live bodies, and carrying out a disinfection and sterilization;
[0037] S2, insect inactivation, immobilizing insect protein;
[0038] S3, drain the surface of the insects, and carry out secondary disinfection and sterilization;
[0039] S4. Aseptic packaging, using aluminum foil bags or sealed bags;
[0040] S5, carrying out the third disinfection and sterilization;
[0041] S6, quenching is carried out after processing is completed, at -20 ℃ temperature, guarantees the original color of fresh-keeping insect.
[0042] Preferably, in step S1, use normal temperature water to wash cleanly, and use 10±3°C, molar concentration of 10% ozone water to soak for 3 minutes after washing.
[0043] Preferably, in step S2, the insect protein is im...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Embodiment 2, take fresh-keeping grasshopper as example:
[0053] A fresh-keeping treatment process for animal edible insects, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0054] S1, cleaning insects from live bodies, and carrying out a disinfection and sterilization;
[0055] S2, insect inactivation, immobilizing insect protein;
[0056] S3, drain the surface of the insects, and carry out secondary disinfection and sterilization;
[0057] S4. Aseptic packaging, using aluminum foil bags or sealed bags;
[0058] S5, carrying out the third disinfection and sterilization;
[0059] S6, quenching is carried out after processing is completed, at -20 ℃ temperature, guarantees the original color of fresh-keeping insect.
[0060] Preferably, in step S1, use normal temperature water to wash cleanly, and use 10±3°C, molar concentration of 10% ozone water to soak for 3 minutes after washing.
[0061] Preferably, in step S2, the insect protein is immobilized by soa...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Embodiment 3, take the fresh-keeping Dubia cockroach as example:
[0070] A fresh-keeping treatment process for animal edible insects, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0071] S1, cleaning insects from live bodies, and carrying out a disinfection and sterilization;
[0072] S2, insect inactivation, immobilizing insect protein;
[0073] S3, drain the surface of the insects, and carry out secondary disinfection and sterilization;
[0074] S4. Aseptic packaging, using aluminum foil bags or sealed bags;
[0075] S5, carrying out the third disinfection and sterilization;
[0076] S6, quenching is carried out after processing is completed, at -20 ℃ temperature, guarantees the original color of fresh-keeping insect.
[0077] Preferably, in step S1, use normal temperature water to clean, and use 10±3°C, molar concentration of 10% ozone water to soak for 2 minutes after washing.
[0078] Preferably, in step S2, the insect protein is immobilized by so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com