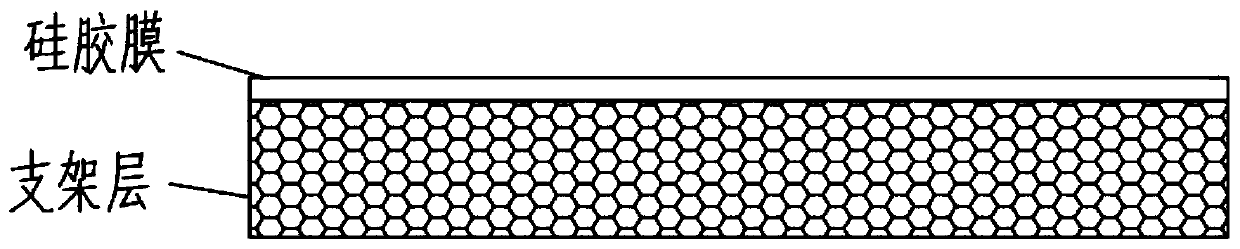
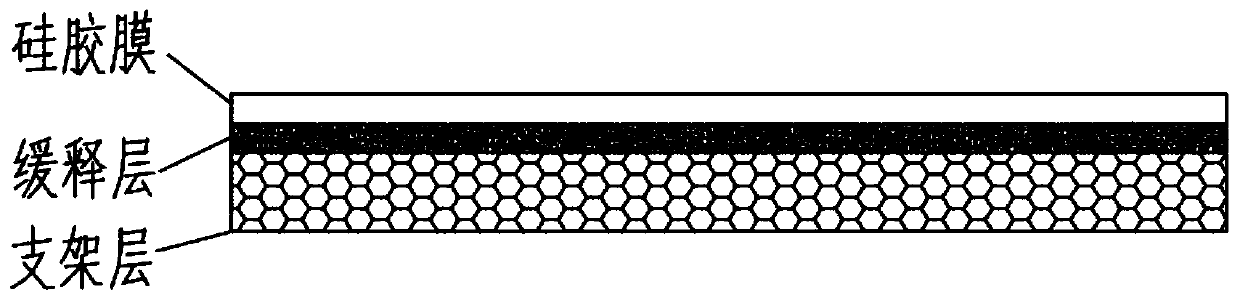
Slow-release and micro-organism-inhibition type artificial dermis model and construction method thereof
A construction method, artificial technology, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, coatings, pharmaceutical sciences, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] Antibacterial agent selects a kind of embodiment-silver nitrate of soluble component for use;
[0087] Step 1, the construction of the slow-release layer:
[0088] Because silver nitrate is a water-soluble inorganic salt, when the slow-release layer meets water, the silver ions become free, and driven by the concentration difference, they penetrate the dense fiber structure of the cellulose film and reach the wound surface to play a role in continuous sterilization. Therefore, in this embodiment, a denser and thicker biocellulose film should be selected to ensure the slow release of silver ions.
[0089] Take the density as 10mg / cm 3 A biological cellulose film with a thickness of about 1 cm is soaked in a 5% silver nitrate solution for 10 hours to fully absorb the silver nitrate. Pre-freeze the expanded biological cellulose membrane at -20°C, then transfer it to a vacuum freeze dryer, freeze-dry for 10 hours, make it incompletely freeze-dried and become a film with a...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Antibacterial agent selects a kind of embodiment-sodium zirconium phosphate of micron-sized particle for use;
[0100] Step 1, the construction of slow-release layer;
[0101] Since the particle size of sodium silver zirconium phosphate is relatively micron, it is necessary to choose a biocellulose membrane with a low density and a moderate thickness. To ensure that the sodium zirconium phosphate silver particles can be evenly adsorbed in the biocellulose membrane. When the biological cellulose membrane changes from the expanded state to the thin film state, the pores of the biological cellulose membrane change from micrometer to nanometer, so that the silver zirconium phosphate particles are wrapped between the biological cellulose membranes. Because the biological fiber has the function of absorbing liquid, when the body fluid enters the slow-release layer, the silver ions loaded by sodium zirconium phosphate enter the body fluid and become free, so that they can ent...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Antibacterial agent selects a kind of embodiment of nano-scale particle-nano-silver particle;
[0114] Step 1, the construction of slow-release layer;
[0115] In this embodiment, nano-silver particles are selected as the antibacterial agent, taking into account the adsorption and release of nano-silver. In this embodiment, a biocellulose film with moderate density and thick thickness is selected as the slow-release layer.
[0116] Take the dry weight as 5mg / cm 3 A wet biological cellulose film with a thickness of about 0.8cm±0.1cm is soaked in a 10% nano-silver suspension for 10 hours to fully absorb the nano-silver. Pre-freeze the biocellulose membrane in the above-mentioned expanded state at -20°C, then transfer it to a vacuum freeze dryer, freeze-dry for 10 hours, make it incompletely freeze-dried and become a thin film with a thickness of about 1mm, so that the silver nanoparticles Encased in cellulose. The biocellulose film was then dried at 30° C. for 24 hour...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com