Method for rapid dyeing and identification of zinc content in rice
A rapid dyeing and zinc content technology, which is applied in the direction of material analysis by observing the influence of chemical indicators, and analysis by making materials undergo chemical reactions, etc., to achieve the effects of wide applicability, fast identification and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
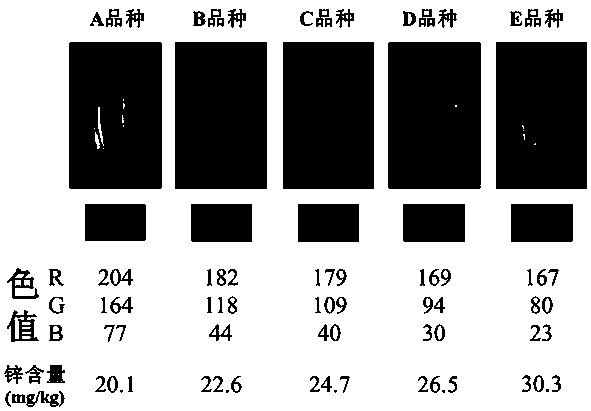
[0031] A rapid staining and identification method for zinc content in rice is based on the characteristic of a unique red complex (Zn-DTZ) formed between zinc ions (Zn) on the surface of rice grains and diphenylthiocarbazone (DTZ) reagents. The color depth of the complex can be used to determine the level of zinc content in rice grains by intuitive qualitative or indirect quantitative methods, that is, the darker the dyeing color, the higher the zinc content.
[0032] The rice grains in this example are derived from the field rice varieties (A, B, C, D, E) comparative experiments. In this example, at the maturity stage of rice, 50 grains of rice of different rice varieties in the field were collected respectively, and the chaff of the rice was removed manually or by a huller, and then put into 15 mL centrifuge tubes respectively, and then added 500 mg L -1 Submerge the grains in about 10 ml of dithizone solution, cover and shake well, soak at room temperature 25±5°C for 30 min...
Embodiment 2
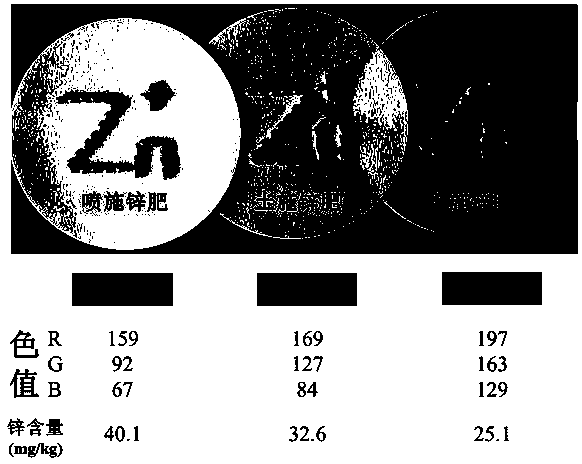
[0034] It is basically the same as Example 1, the difference is that the rice grains of this example are derived from the treatment experiments of different zinc fertilizer application methods in the field (no zinc fertilizer, soil zinc fertilizer, spray zinc fertilizer), soil zinc fertilizer treatment 50 kg / hm 1 day before rice transplanting 2 Zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O) Soil application, spraying zinc fertilizer at 800 L / hm at the tillering stage of rice and 7 days after flowering 2 The concentration of 0.3% zinc sulfate was sprayed on the leaves, and the rice grains treated with different zinc fertilizer amounts and application methods during the harvest period were removed from the glumes and quickly stained with DTZ for identification. the result shows( figure 2 ), the effect of foliar spraying zinc fertilizer on enhancing the zinc content of rice grains was significantly higher than that of soil application, and the results of dyeing identification amo...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Substantially the same as Examples 1 and 2, the difference is that the rice grains of the present embodiment are derived from different zinc fertilizer varieties in the field (ionic state zinc fertilizer ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O. Comparative test of organic chelated zinc fertilizer (HBED-Zn) and application methods (soil application, foliage spraying), soil application of zinc fertilizer treatment is 50 kg / hm 1 day before rice transplanting 2 Zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O) Soil application, spraying zinc fertilizer at 800 L / hm at the tillering stage of rice and 7 days after flowering 2 The concentration of 0.3% zinc sulfate was sprayed on the leaves, and the rice grains treated with different zinc fertilizer varieties and application methods at the harvest period were removed from the glumes and then quickly stained with DTZ for identification. the result shows( image 3 ), the effect of soil application of organic chelated zinc fertilizer on enhancing the zinc co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com