Method for analyzing residual stress of polyethylene pipe welded joint
A technology of welded joints and polyethylene pipes, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve the problems of explaining the creep and relaxation characteristics of polyethylene materials, complicated processes, and the application history of polyethylene materials is not as good as that of metal materials. Achieve reliability and integrity improvement and optimization, solve the effects of low accuracy and reduce actual measurement and manufacturing work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
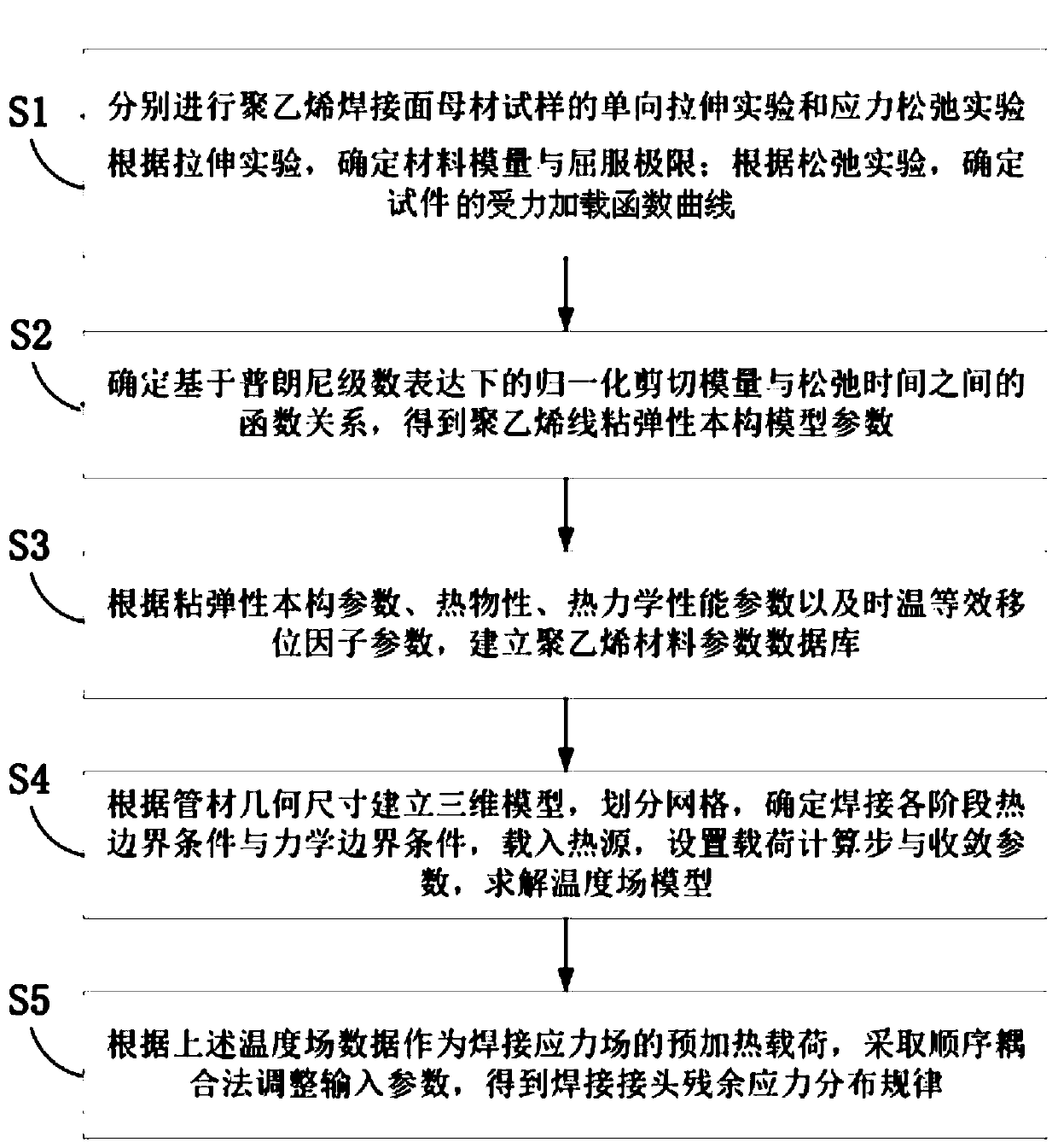
[0048] Such as figure 1 Shown is the analytical method of the residual stress of the polyethylene pipe welded joint of an embodiment of the present invention, and it comprises the steps:
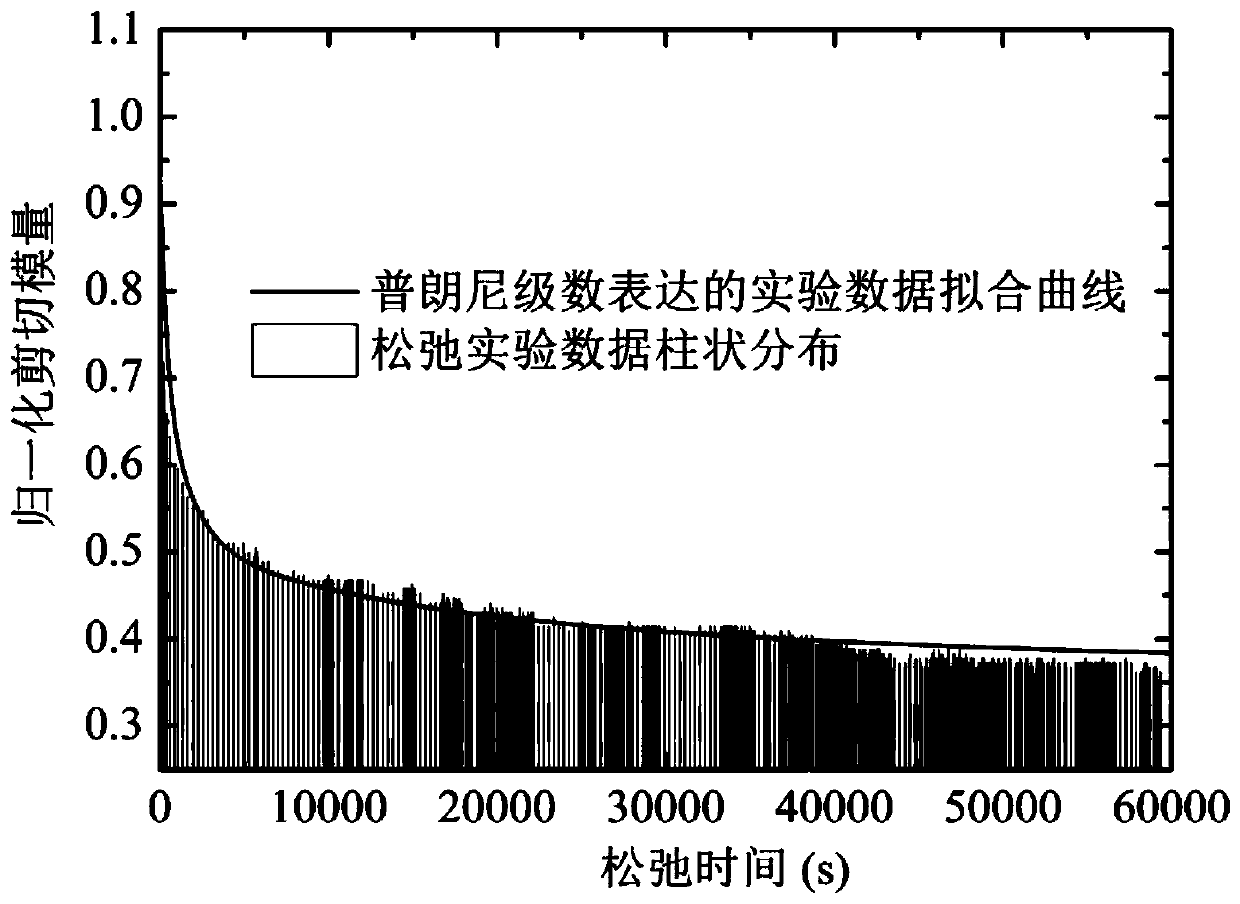
[0049] Step S1: Using a base metal sample of a polyethylene pipe welded joint to be tested, perform a uniaxial tensile test and a stress relaxation test respectively, and obtain the secant modulus of the polyethylene material according to the results of the uniaxial tensile test and the yield limit value, and according to the results of the stress relaxation experiment, the stress loading function curve of the polyethylene material under the unit strain is obtained. The ordinate of the obtained stress loading function curve is the applied load, the unit is kN, and the horizontal The coordinates are the loading time, the unit is s.
[0050] The present invention adopts the parameter setting of the stress relaxation experiment instead of the creep experiment, which avoids the problem that the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com