Glutamine synthetase mutant with glufosinate resistance and application and cultivation method of glutamine synthese mutant
A glutamine and synthetase technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of interfering with plant nitrogen metabolism, affecting plant growth and development, consumer resistance, etc., and achieve the effect of broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] This example provides a plurality of glutamine synthetase (hereinafter referred to as GS) mutants derived from rice (Oryza sativa), and these GS mutants are respectively named: OsA, OsC, OsD, OsE, OsF, OsG, OsH, OsI, OsK, OsP, OsT, OsV, OsY; these GS mutants are compared with the rice wild-type GS (ie reference sequence, SEQ ID NO.1), corresponding to the 59th position of the rice wild-type GS has a mutation, specifically The mutation types are shown in Table 1 below and figure 1 , the length of these GS mutants and the type of amino acid residues at the remaining positions are the same as those of rice wild-type GS.
[0091] Table 1
[0092]
Embodiment 2
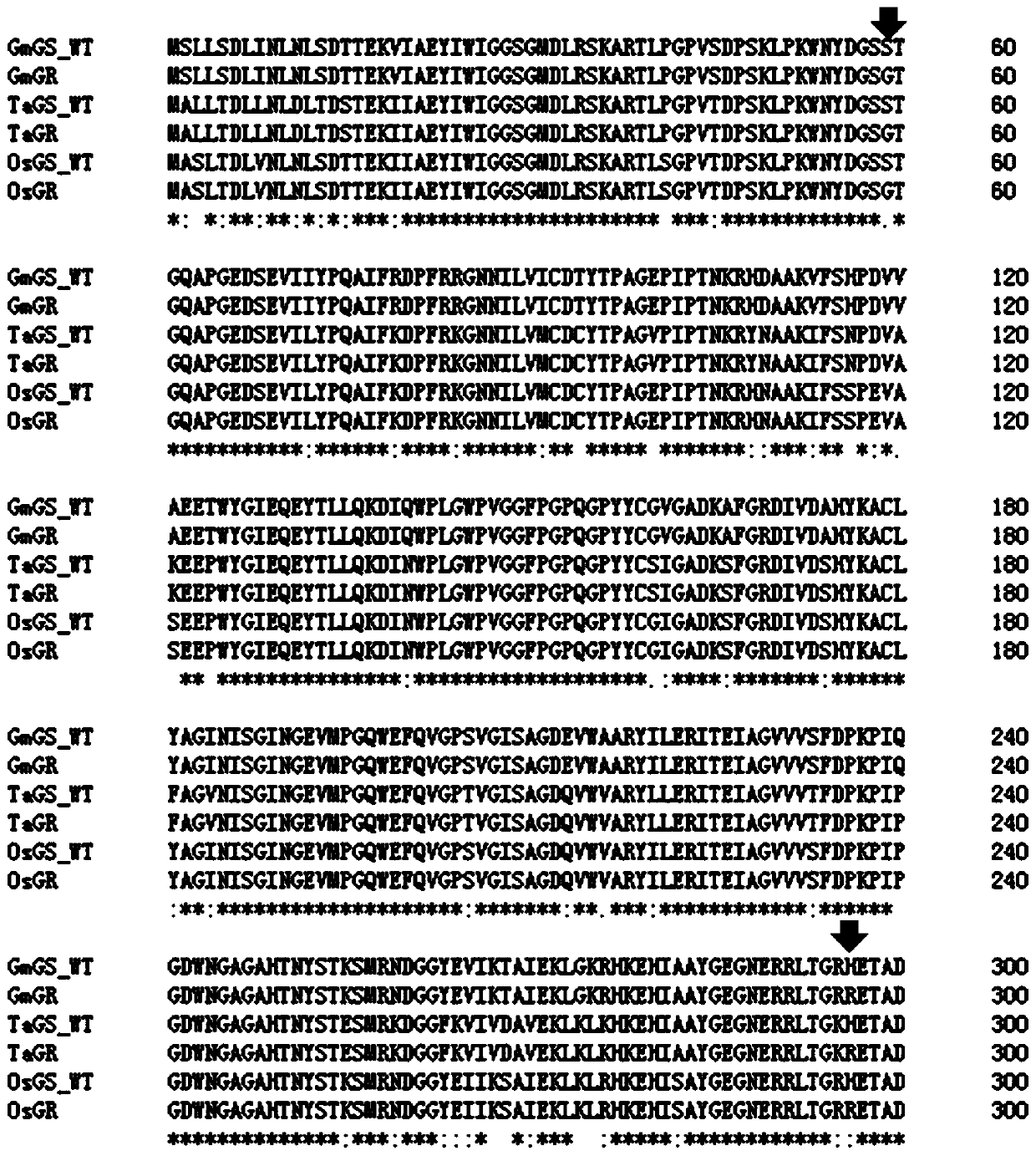
[0094] This example provides another GS mutant derived from rice, which is named OsGR. OsGR is compared with the rice wild-type GS (ie, the reference sequence, SEQ ID NO.1), corresponding to the 59th position of the rice wild-type GS and the 296th position have mutations, the specific mutation types are shown in Table 2 and figure 2 ; The length of OsGR and the amino acid residues of other sites are the same as those of rice wild-type GS (SEQ ID NO.1). That is, the 59th position of rice wild-type GS (SEQ ID NO.1) itself was mutated into G and the 296th position was mutated into R to obtain OsGR.
[0095] This embodiment also provides a GS mutant derived from wheat (Triticum aestivum), named TaGR, comparing TaGR with rice wild-type GS (ie, reference sequence, SEQ ID NO.1), corresponding to the first sequence of rice wild-type GS There are mutations at positions 59 and 296, and the specific mutation types are shown in Table 2 and figure 2 ; The length of TaGR and the types o...
Embodiment 3
[0104] This example provides a variety of additional GS mutants derived from rice, and these GS mutants are named: OA, OD, OE, OG, OI, OK, OM, OP, OQ, OR, OS, OT, OV. Comparing these GS mutants with rice wild-type GS (i.e. reference sequence, SEQID NO.1), there is a mutation corresponding to the 296th position of rice wild-type GS, and the specific mutation types are shown in Table 3 and image 3 , the length of these GS mutants and the amino acid residue types of the remaining positions are the same as those of rice wild-type GS (SEQ ID NO.1).
[0105] table 3
[0106]
[0107]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com