Cutter changing assembly structure and method for large-size microstructure array relay machining
A microstructure array and large-scale technology, applied in metal processing equipment, metal processing machinery parts, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as difficult calibration, inability to accurately locate new tools to the processing stop point, and inconsistent reference coordinate systems. achieve the effect of avoiding damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
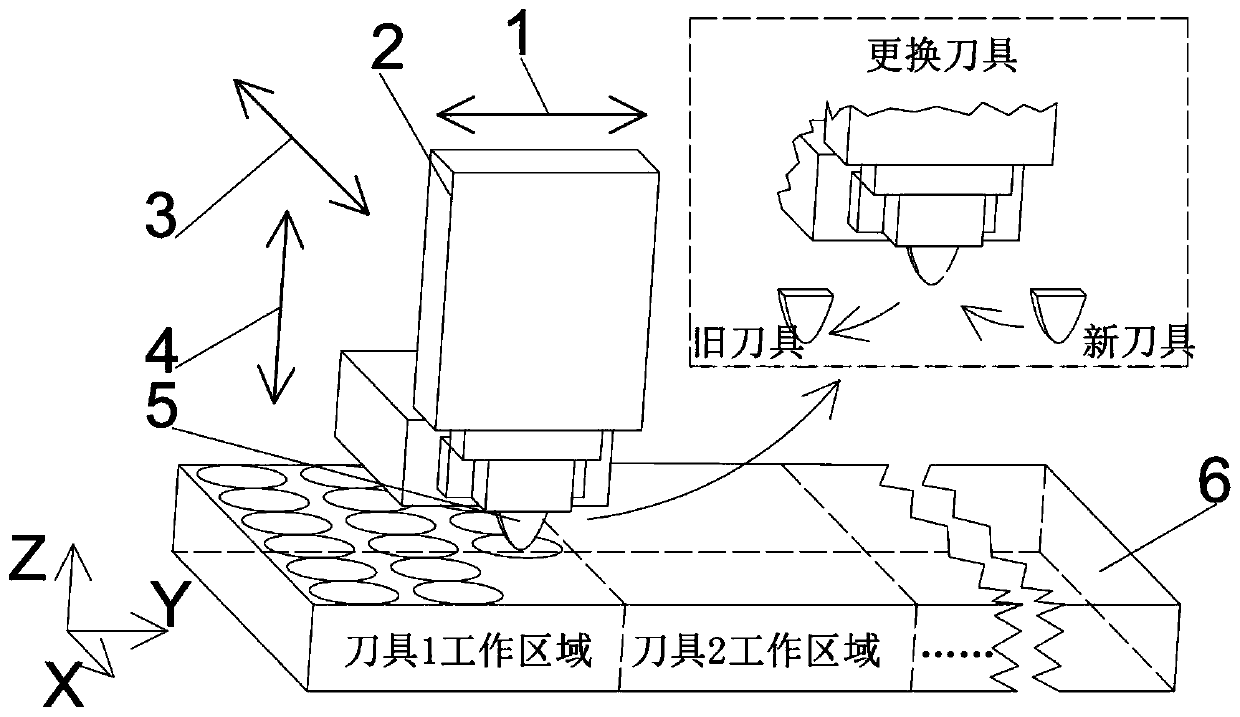
[0039] The schematic diagram of the tool change splicing structure of the first embodiment of the present invention is as follows: figure 1 Shown. Its main components are Y-direction slide 1 (including linear encoder), two-axis fast tool servo system with integrated force sensor 2, X-direction slide 3 (including linear encoder), Z-direction slide 4 (including linear encoder) 器), and replaceable tool 5, the figure also includes a large-size workpiece 6.
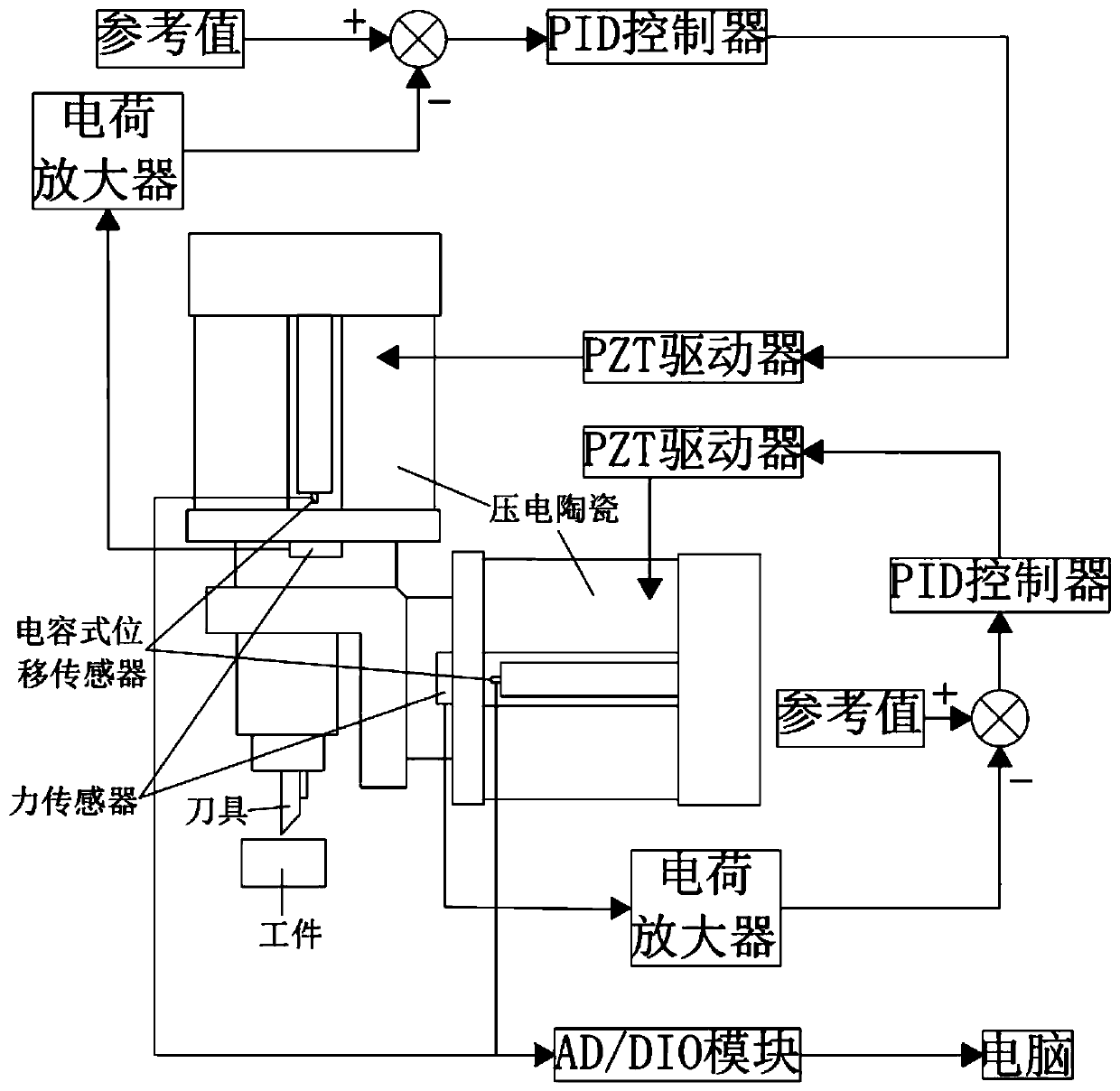
[0040] Also includes such as figure 2 In the control system shown, the two-axis fast tool servo system consists of a longitudinal fast tool servo and a horizontal fast tool servo. Servo control tool positioning adopts the method of force closed loop feedback control. The force sensor of the longitudinal fast tool servo detects the contact force between the tool and the workpiece in the longitudinal direction. After being amplified by the charge amplifier, it is compared with the reference signal as a feedback signal, and the comp...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The tool change splicing method of the second embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0045] 1) Detect the contact force between the tool and the workpiece in the longitudinal and transverse directions;
[0046] 2) Control the tool to perform displacement scanning along the topography of the processed microstructure on the surface of the workpiece, and at the same time, combine the reference signal to keep the magnitude of the longitudinal and lateral contact force constant through closed-loop control;
[0047] 3) Obtain the tool scanning path based on the tool displacement measured by the displacement sensor;
[0048] 4) Based on the acquired tool scan path, position the new tool to the processing stop point of the old tool.
[0049] Attached below figure 2 , 3 And 4(a)-(c) to explain in detail:
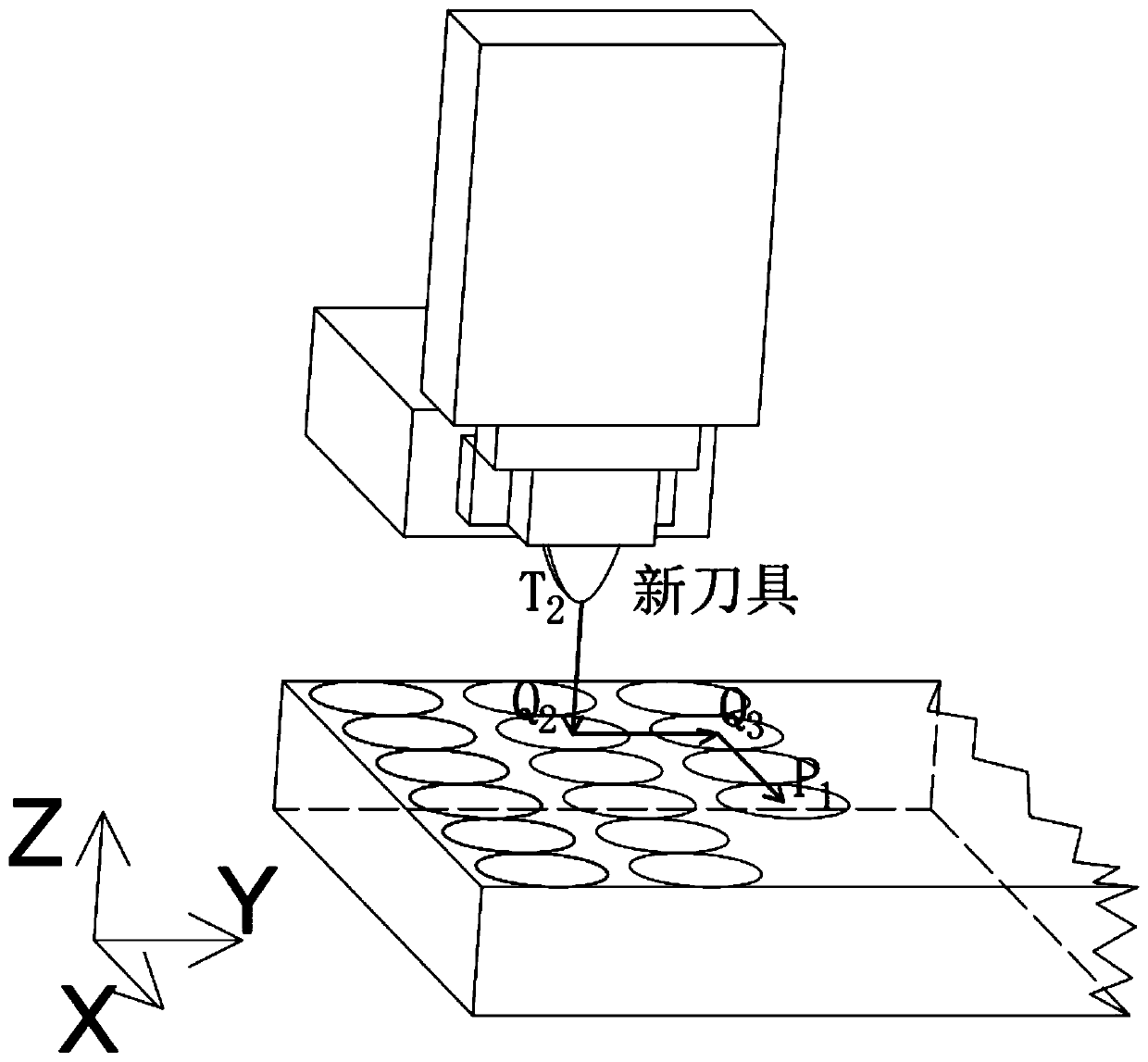
[0050] (1) In the process of splicing and changing tools, new tools are used to replace worn out tools. Such as image 3 As shown, suppose the position of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com