Method for preparing oxygen from chemical chain
A chemical chain and oxygen technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, oxygen preparation, etc., can solve the problems of low oxygen balance partial pressure of oxygen carrier, low utilization value of collected gas, low maximum oxygen concentration of collected gas, etc. To achieve the effect of improving the purity of oxygen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
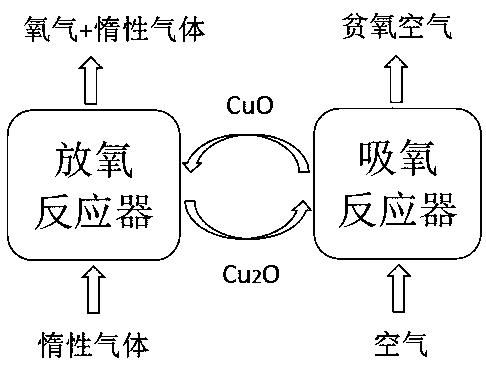
[0031] A method for preparing oxygen by chemical chains, comprising heating up and releasing oxygen, cooling down, and absorbing oxygen, the specific steps are as follows:
[0032] A. Heating and oxygen release process:
[0033] 1) Initially or after the oxygen absorption process, the atmospheric pressure reactor A contains molten salt at 750-780 °C and the active ingredient of the oxygen carrier immersed in it, and the mass ratio of the active ingredient of the oxygen carrier to the molten salt is 2:8; the molten salt for molten CaCl 2 -NaCl, oxygen solubility S≤100mol / m 3 , CaCl 2 The mass ratio to NaCl is 15:1; the active ingredient of oxygen carrier is CUO / CU 2 O, initially powdered CUO with a particle size of 0.01-0.2mm; CaCl 2 -NaCl molten salt on oxygen carrier active components CUO, CU 2 The solubility of O is 0.5%~5%;
[0034] 2) The reactor A is purged with water vapor, and other gases in the reactor A are evacuated;
[0035] 3) Indirectly heat the molten sal...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The difference between this example and Example 1 lies in the heating method of the temperature rise and oxygen release process. In Example 1, the molten salt is indirectly heated. In this example, the molten salt is used as the heat carrier to heat the molten salt in reactor A. The specific steps are as follows : 1) Heat transfer process of the heat carrier: During the process of temperature rise and oxygen release, after the reactor A is purged with water vapor, the heat carrier at 900~1000°C is added to the reactor A, and the heat carrier is the molten salt composition in the reactor A For the same molten salt, the temperature of the 750~780°C molten salt in reactor A is raised to 840~900°C by stirring; 840~900°C heat carrier, the heat carrier is converted into a 900~1000°C heat carrier after being directly contacted with flue gas at 1000~1200°C, and the 900~1000°C heat carrier is used in the heat release process of the heat carrier.
Embodiment 3
[0046] The present embodiment differs from Example 1 in that: 1) the molten salt adopts molten Na 2 CO 3 -K 2 CO 3 -Na 2 SiO 3 or Na 2 CO 3 -K 2 CO 3 -K 2 SiO 3 ; 2) During the process of heating up and releasing oxygen, the inside of reactor A is negative pressure, the pressure is -2000Pa~-10Pa; 3) During the process of oxygen absorption, the inside of reactor A is under positive pressure, and the pressure is 10Pa~2000Pa.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com