Colorimetric method for detecting tobramycin based on double strand displacement and three-dimensional DNA structure
A technology for tobramycin and structure detection, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of personnel training and sample preparation complexity, long test cycle, high detection limit, etc., and achieve the expansion of detection range , Improve detection sensitivity and specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
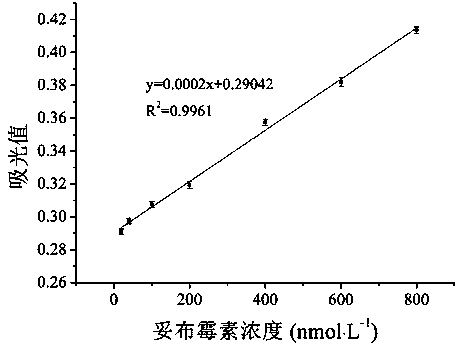
[0036] Example 1 Drawing of Tobramycin Concentration Standard Curve
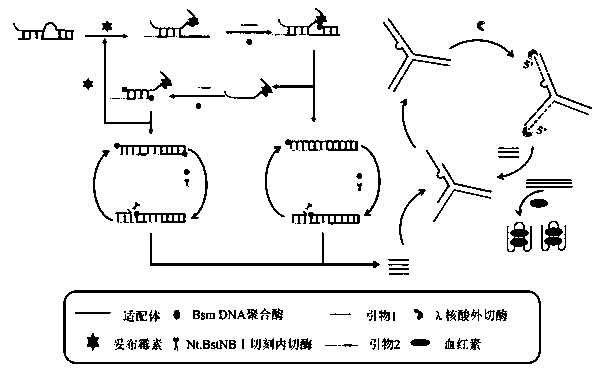
[0037] Mix T1 and T2 at the same concentration, denature at 95°C for 5 minutes, and then refold at 37°C for 120 minutes. 2 μL (10 μmol·L -1 ) double strands were mixed with 4 μL of tobramycin solutions of different concentrations, and incubated at 37°C for 30 min. Add 2 μL (10 μmol·L -1 ) Primer 1, 2 μL (10 μmol L -1 ) Primer 2, 5 U Nt.BstNBI nicking endonuclease, 8 U Bsm DNA polymerase and 2 μL (10 mmol·L -1 ) free deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate, 1× buffer (100 mmol·L -1 NaCl, 50mmol L -1 Tris-HCl, 10 mmol L -1 MgCl 2 , 0.1 mg·mL -1 BSA), mixed and incubated at 55°C for 120 min to generate a large amount of reporter probes, which were inactivated at 75°C for 10 min and stored at 4°C for use.
[0038] Mix 10 μL of S1, 10 μL of S2 and 10 μL of S3 (both 10 -6 mol L -1 ) were mixed, heated at 95 °C for 5 min, and then gradually cooled to room temperature. Thereafter, 30 μL of the DNA mixture ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The determination of tobramycin content in the actual water sample of embodiment 2
[0041] In order to further verify the accuracy of this method in the determination of tobramycin content in actual samples, Taihu Lake water without pretreatment was selected to dilute tobramycin to different concentrations. The reaction was carried out in exactly the same way as the tobramycin standard sample, and the resulting reaction solution was read with a UV-vis spectrophotometer at 420nm absorbance, which was substituted into the standard curve to calculate the tobramycin concentration.
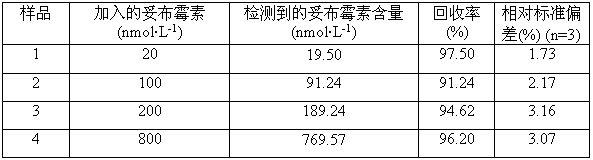
[0042] The specific samples and test results are shown in Table 1.
[0043] Table 1
[0044]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com