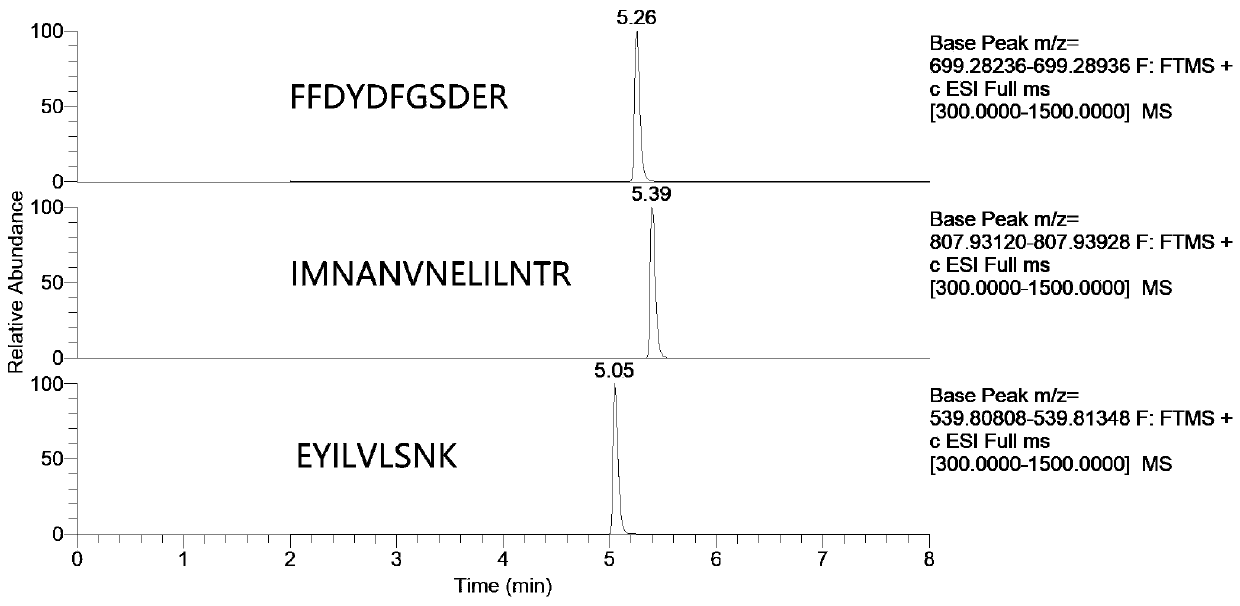
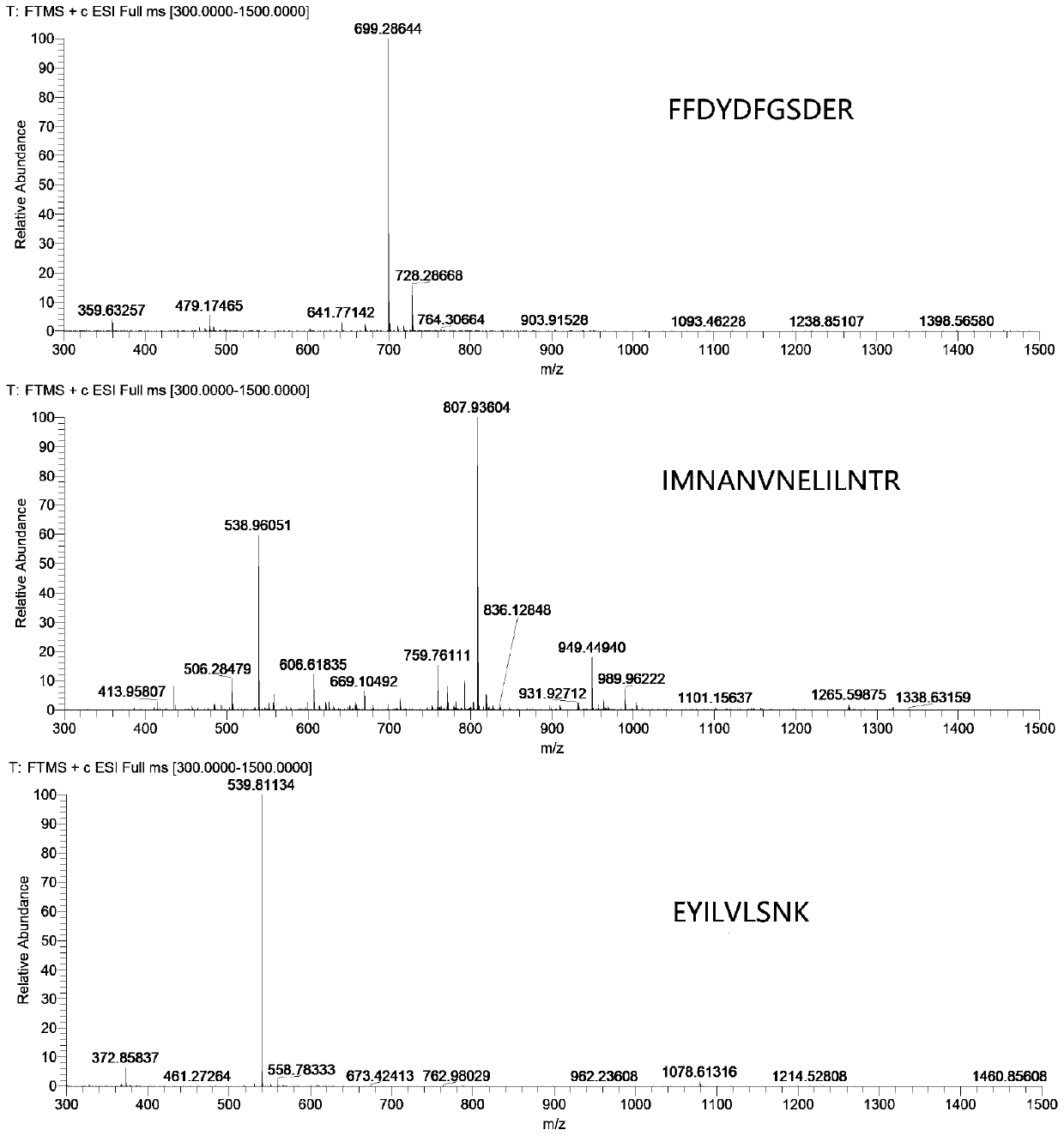
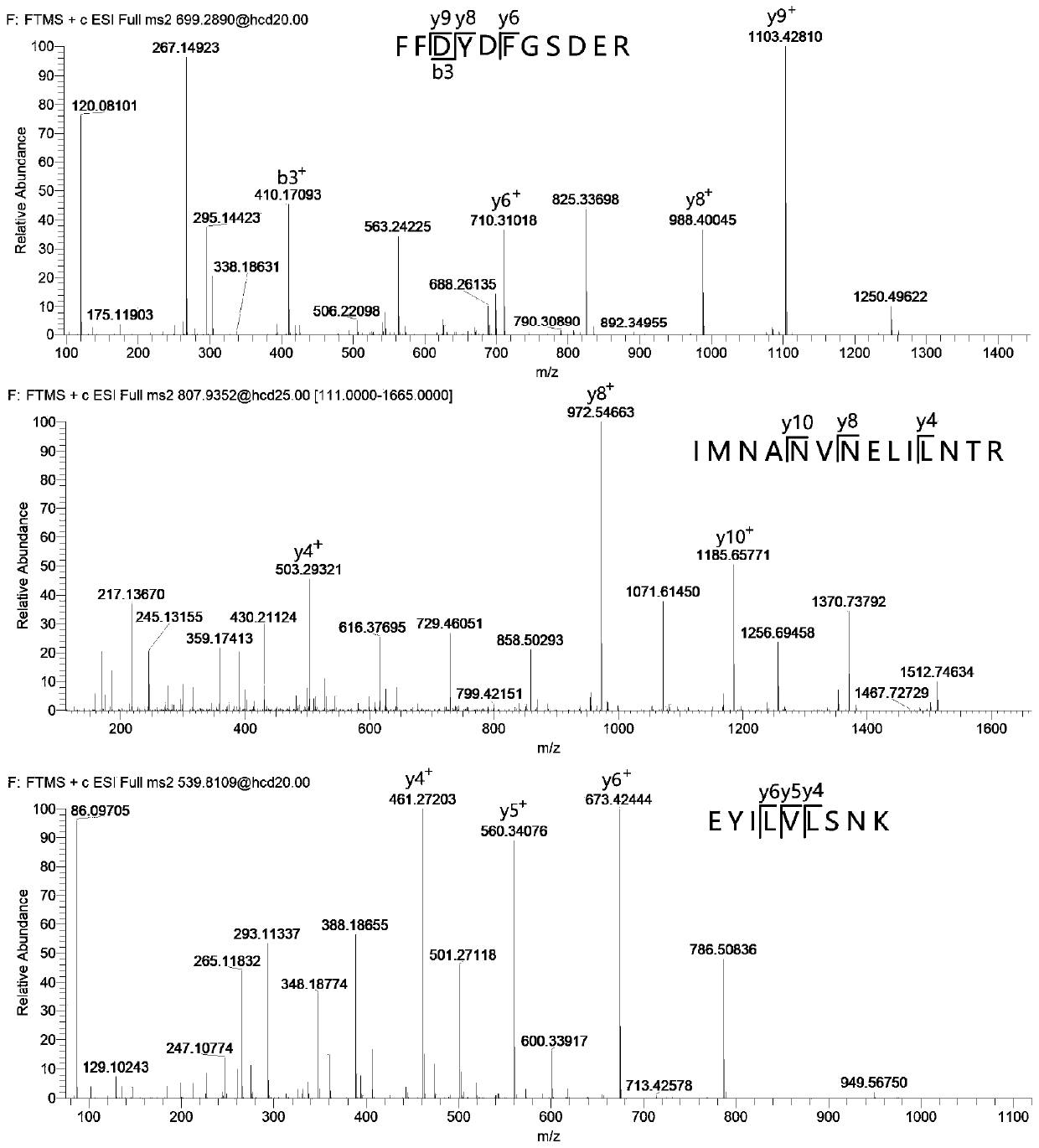
Method for measuring content of apis mellifera MRJP1 protein in honey by using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
A technology of liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry, applied in the field of food testing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] Example 1 Method for determining the protein content of Italian bee MRJP1 in honey by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
[0102] 1. Sample source
[0103] A total of 80 common honey samples were purchased from the market or beekeepers, such as acacia honey, wattle honey, rapeseed honey, jujube honey, linden honey, etc.
[0104] 2. Experimental steps
[0105] (1) Solution preparation
[0106] 5M Urea solution: Weigh 4.5g of Urea, and dilute to 15mL with ultrapure water;
[0107] Lysis buffer (LB): 8M urea, 2M thiourea, 4% CHAPS, 20mM Tris base;
[0108] The 100mM DTT 100mL system configuration is as follows: Weigh 48.06g of urea, 4% sulfur CHAPS, 20mM Tris base, 15.22g, CHAPS 4.00g, Tris base 0.24g and DTT 0.46g, dissolve with ultrapure water, mix and make up to 100mL, store in -20°C refrigerator until use.
[0109] 40mM NH 4 HCO 3 Solution: weigh 0.316g NH 4 HCO 3 , dilute to 100 mL with ultrapure water, and store in a 4°C refrigerator until use. ...
Embodiment 2
[0179] Quantitative detection of embodiment 2 honey adulteration
[0180] 1. Sample source
[0181] Buy real honey samples and syrups from markets or beekeepers.
[0182] 2. Experimental steps
[0183] (1) Solution preparation
[0184] With embodiment 1.
[0185] (2) Blending of honey: mix syrup into honey in different proportions.
[0186] Mix syrup into honey according to the ratio of 5%, 10%, 20%, 50%, 80%.
[0187] (3) Pretreatment of honey samples
[0188] ① Accurately weigh 10g of the honey to be tested into a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 10mL of deionized water, and vortex until the honey is fully dissolved. Centrifuge at 12000rpm, 4°C for 10min. Collect the supernatant in a new 2mL centrifuge tube.
[0189] ② Pipette 200 μL of protein solution, add 800 μL 40mM NH 4 HCO 3 mix. Add 100 μL of 30 mM DTT solution to the above mixed solution, react at room temperature for 60 min, and then add 500 μL of 100 mM IAA solution and react in dark at room temperature for 60 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com