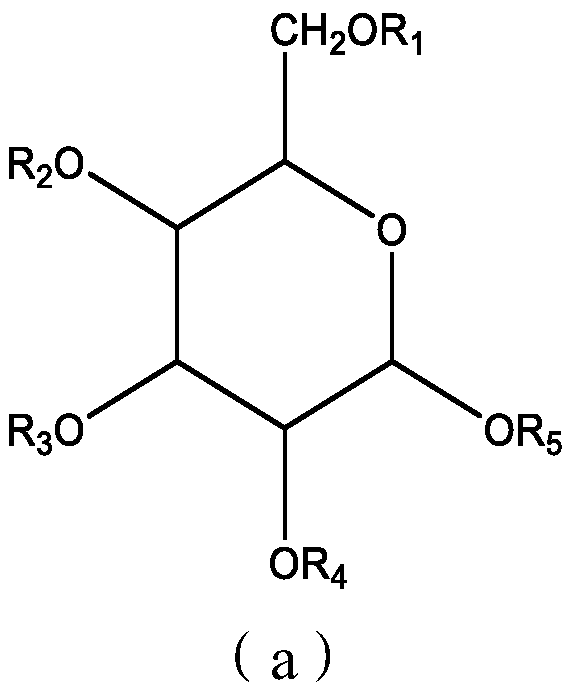
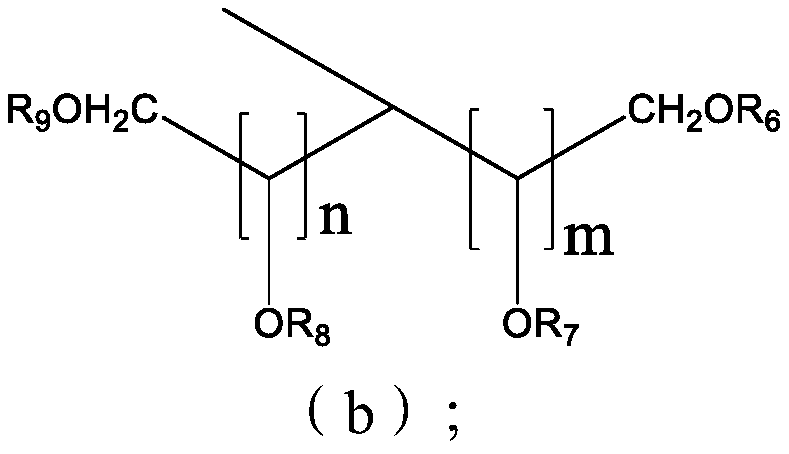
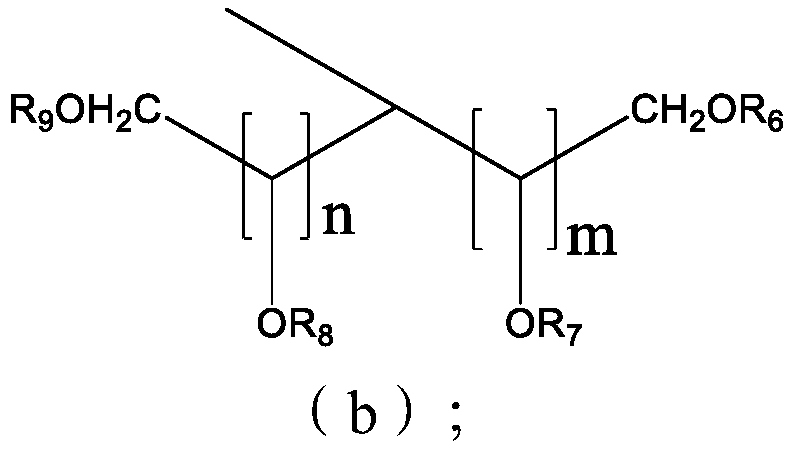
Low oxide trench dishing chemical mechanical polishing
A chemical mechanical, inorganic oxide technology, applied in the direction of other chemical processes, chemical instruments and methods, polishing compositions containing abrasives, etc., can solve problems that do not involve the importance of oxide trench depression reduction, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0213] The working stock had 0.15% by weight of chemical additives, which was added to the reference stock.
[0214] Observe the effect of various selected chemical additives on membrane removal rate and selectivity.
[0215] Test the removal rate (RR, in count). The test results are listed in Table 1.
[0216] As the results shown in Table 1, slurries based on ceria-coated silica provided higher removal rates for TEOS.
[0217] Table 1. Chemical Additives on Membrane RR and TEOS:SiN selectivity effects
[0218]
[0219] As the results further shown in Table 1, the chemical additives D-sorbitol, D-mannitol, D-mannose, and xylitol inhibited the SiN removal rate relative to the reference, except meso-erythritol, while Still provides high TEOS and HDP film removal rates and provides high oxide:SiN selectivity.
Embodiment 2
[0221] In Example 2, a formulation based on 0.2% by weight of ceria-coated silica abrasive without chemical additives was used as reference.
[0222] The chemical additives were used at a concentration of 0.15% by weight (0.15X), respectively, with 0.2% by weight of ceria-coated silica as the abrasive in the working slurry.
[0223] The test results are listed in Table 2. HDP RRs in Table 1 are also listed in Table 2.
[0224] Table 3 lists the oxide trench recess rates Removal rate of relative blank HDP membrane The ratio.
[0225] Table 2. Effects of Chemical Additives on Oxide Trench Recession and HDP RR Impact
[0226]
[0227] The test results are listed in Table 2. HDP RRs in Table 1 are also listed in Table 2.
[0228] Table 3 lists the oxide trench recess rates Removal rate of relative blank HDP membrane The ratio.
[0229] Table 3. Trench Depression Rates / blank HDP RR The ratio
[0230]
[0231] As the results shown in Tables 2 and 3, ad...
Embodiment 3
[0241] Observe the effect of various selected chemical additives on the membrane removal rate (RR, expressed as count) and selectivity effects. These chemical additives were each used in a concentration of 0.1% by weight, with 0.2% by weight of ceria-coated silica as abrasive.
[0242] The test results are listed in Table 5.
[0243] Table 5. Effect of chemical additives on film RR and TEOS:SiN selectivity effects
[0244]
[0245] The results are shown in Table 5. These chemical additives D-sorbitol, D-(-)-fructose, maltitol, and dulcitol inhibited the SiN removal rate compared to the reference, while still providing high TEOS and HDP films removal rate.
[0246] The CMP composition with D-(-)-fructose inhibited the removal of TEOS in addition to SiN, but still provided high TEOS:SiN selectivity.
[0247] The effect of various selected chemical additives on oxide trench recessing relative to overpolish time was observed.
[0248] The test results are listed in Tabl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com