Implantable auricular cartilage composite stent
A composite stent, implantable technology, applied in nose implants, medical science, prostheses, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient support, poor stability, poor hardness, etc., to improve stability, increase support, increase The effect of its own strength and hardness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
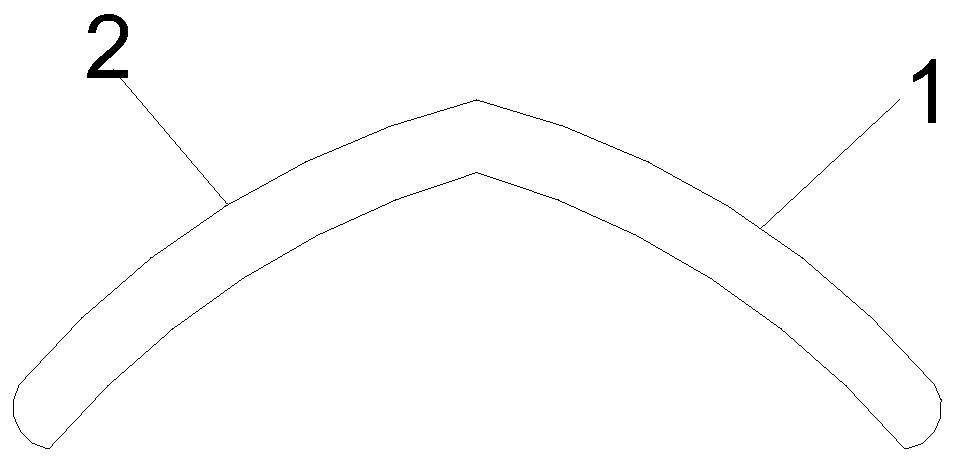
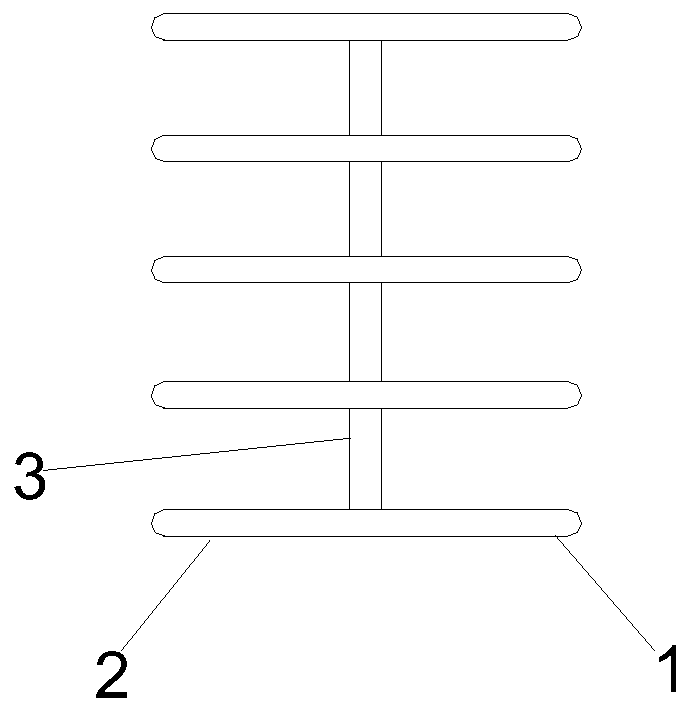
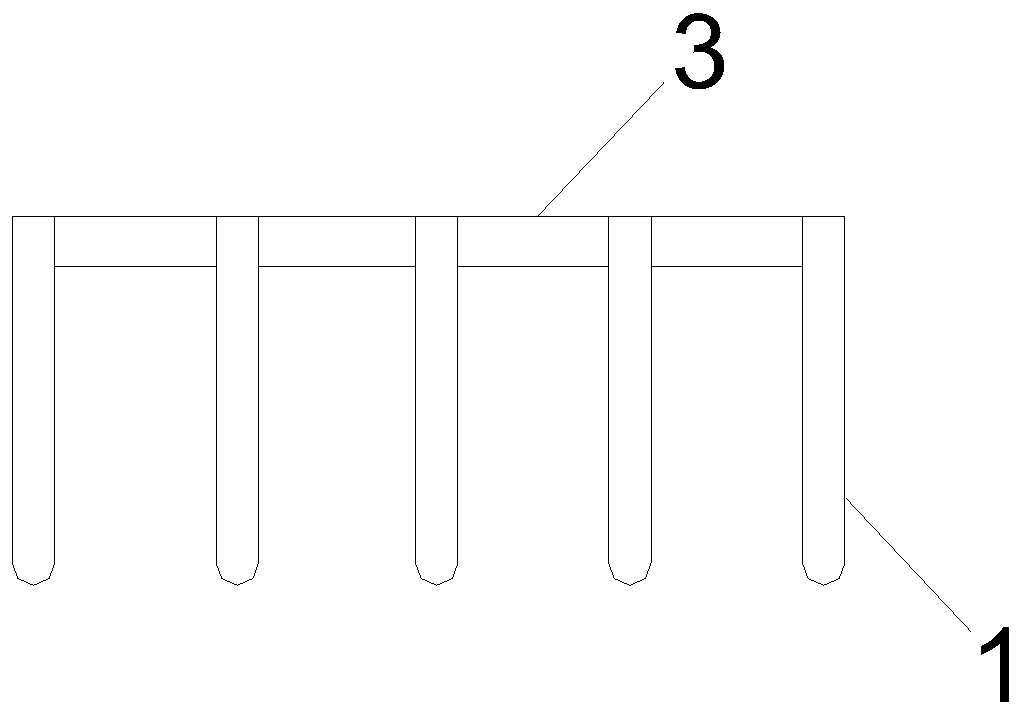
[0052] Such as Figure 1-4 As shown, an implantable ear cartilage composite bracket; includes a first bracket 1 and a second bracket 2; one end of the first bracket 1 and the second bracket 2 is connected with a connecting frame 3, and the first bracket 1 and the second bracket 2 are connected to each other. The second support 2 forms a "human" structure through the connection frame 3; the first support 1, the second support 2 and the connection frame 3 all include a line carving fiber core 4 and an ear cartilage support layer 5, and the line carving line The outside of the fiber core 4 is wrapped with an ear cartilage support layer 5 .
[0053] The thread-carving fiber core 4 has a helical structure. The acute angle included in the "human" shape of the first bracket 1 and the second bracket 2 ranges from 35° to 50°.
[0054] In addition, during the preparation of the ear cartilage scaffold, the removed ear cartilage tissue was minced, washed three times with phosphate hydro...
Embodiment 2
[0059] The preparation method of the implantable ear cartilage composite bracket comprises the following steps:
[0060] S1: Add the thread carving thread into the N,N-dimethylformamide solvent and stir it, after ultrasonic treatment, let it stand for a period of time, add alkaline solution to solidify, stretch while solidifying, wash, dry, and get the thread carving thread fiber Core 4;
[0061] S2: Take the hyaline ear cartilage tissue, cut it into pieces, add active agent and protease inhibitor for centrifugation, remove the supernatant, and keep the precipitated part of the solution;
[0062] S3: add active agent and protease inhibitor buffer solution to the precipitation solution obtained in S2, oscillate and mix well, and wash the precipitated part repeatedly after centrifugation to obtain cartilage particles for later use;
[0063] S4: spread the cartilage particles obtained in S3 evenly on a culture dish, and then vacuum freeze-dry them in a freeze dryer to obtain car...
Embodiment 3
[0072] The difference from Examples 1 and 2 is that in order to further increase the stability of the ear cartilage scaffold, the specific surface area A of the ear cartilage cell particles is 850-1920 cm 2 / g; PH value is 7-8 to increase the adhesion of ear chondrocytes, and at the same time increase the contact area with the cross-linking agent, which is beneficial to the proliferation and growth of ear chondrocytes. The specific surface area A of the ear chondrocyte particles and the pH value satisfy: A·PH is greater than or equal to 5950 and less than or equal to 15360.
[0073] The cell content M of the extracellular matrix of the ear cartilage, the specific surface area A of the ear chondrocytes and the pH value satisfy the following relationship:
[0074] A=μ·(PH) 3 / M 1 / 2 ;
[0075] In the above formula, μ is the specific surface area coefficient, and the value range is 3.24-6.65; only numerical calculations are performed here.
[0076] In order to improve the bioa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com