Biological inoculant having enhanced fertilizing and fungicidal activity
An inoculant and biological technology, applied in the direction of biocides, microorganisms, fungi, etc., can solve problems such as the combination of beneficial bacteria and biological antifungal agents that have not been considered
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] [Example 1: Determination of Antagonist Ability of Isolated Trichoderma (Trichoderma) Strains]
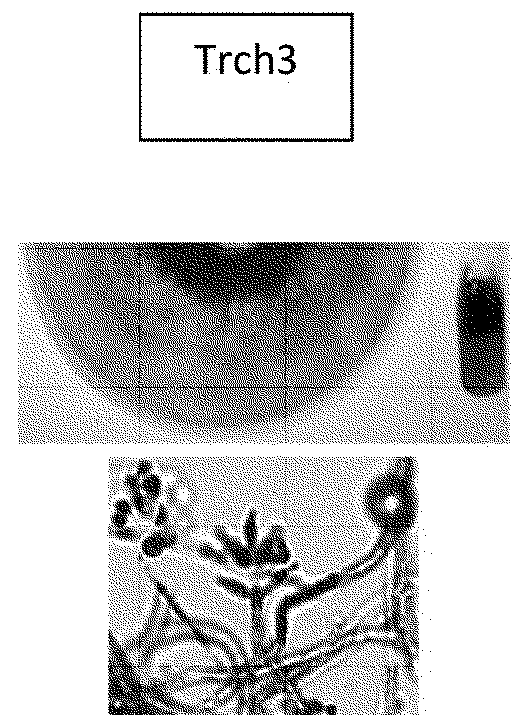
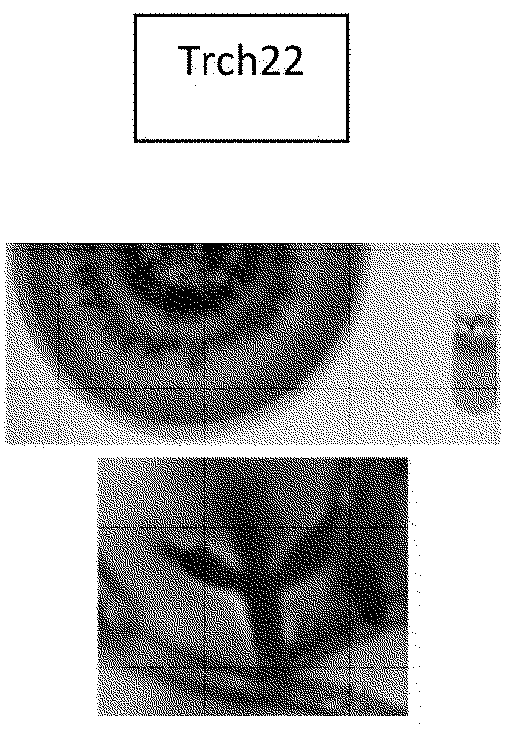
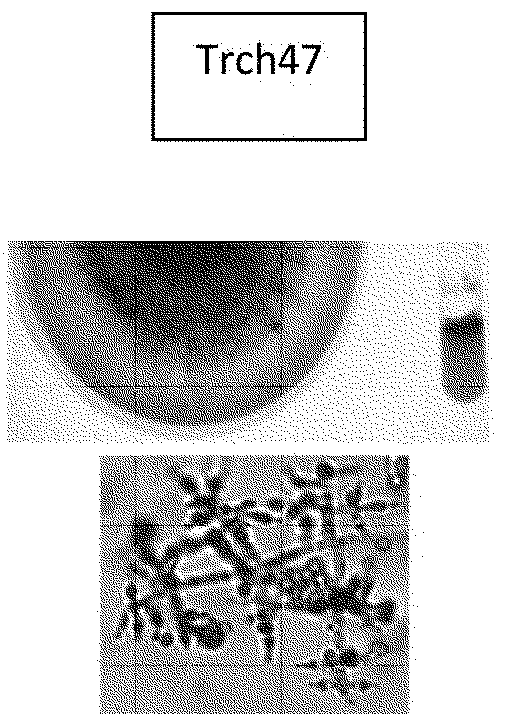
[0058] A total of 60 Trichoderma isolates were obtained from roots of crop plants as well as soil samples as described previously. These samples were identified by morphology, colony pigmentation and identification of the unique structure of the genus by microscopy techniques.
[0059] To determine the antagonistic activity of soil isolates, resistance tests were carried out with a series of phytopathogenic fungi, including those responsible for the most famous diseases in plant crops: Fusarium sp., Colletotrichum sp., Cercospora sp., Sclerotinia sp. and Rhizoctonia sp.
[0060] These fungal pathogens belong to many agronomically relevant crops such as soybean, wheat, corn, sunflower, cotton, sorghum, alfalfa, flax, canola, chickpea, rice, potato, onion, yerba mate (Ilexparaguariensis) , Tea And Vine.
[0061] During several growth rounds in the presence of the aforementi...
Embodiment 2
[0066] [Example 2: Characterization of the interaction of isolated Trichoderma strains with soybean]
[0067] The effect of three isolated Trichoderma strains on the growth of soybean plants under greenhouse conditions was determined. To achieve this, the most effective isolates for controlling the proliferation of pathogenic fungi were selected and the concentration of conidia in inoculated plants was optimized (Samuels & Hebbar, 2015). Build biological inoculants to produce in as little as 10 6 It is still effective at the concentration of spores / ml.
[0068] Subsequent measurements demonstrated that the three selected Trichoderma harzianum strains colonized the roots of soybean plants in the presence of B. japonicum without reducing their natural nodulation capacity. Furthermore, treatment of soybean seeds with these T. harzianum strains even resulted in an increase in the number of nodules per root weight, with Trch3 showing a greater effect and also maintaining the prop...
Embodiment 3
[0072] [Example 3: Trichoderma (Trichoderma)-Bradyrhizobium (Bradyrhizobium) interaction assay]
[0073] Crops were established and grown to evaluate the growth capabilities of two microorganisms: Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Trichoderma.
[0074] Soybean plants were also assessed for nodulation ability in the presence of Trichoderma compared to control plants. These trials were performed under controlled field crop conditions and allowed to evaluate the effect of fungal protection treatments on seeds, nodulation capacity, different growth parameters and final soybean yield.
[0075] The treatment is applied to premium soybeans. The experiment was carried out in the municipality of Pergamino, located in the north of the province of Buenos Aires (33°57'51.87"S 60°34'36.89"W), on soils of the Pergamino series, typical Argiudol, mixed family, Franca Soil texture, thermal, class I-2, IP=85. Sowing was carried out with soybean variety DM 4615STS with a row spacing of 0.40 m. Co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com