Modified Y-type molecular sieve and a preparation method thereof
A molecular sieve and modification technology, applied in molecular sieve catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, and hydrocarbon oil treatment, can solve the problems of destroying zeolite structure, low conversion rate of heavy oil, and reducing zeolite selectivity, etc., and achieve high conversion efficiency, heat and The effect of high hydrothermal stability and low coke selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0052] One embodiment of the present invention further provides a method for preparing the above-mentioned modified Y-type molecular sieve, comprising the following steps:
[0053] (1) carry out ion exchange reaction with NaY molecular sieve and rare earth salt solution, to obtain the Y-type molecular sieve that the unit cell size containing rare earth that sodium oxide content reduces does not change;
[0054] (2) Roasting the Y-type molecular sieve whose unit cell size containing the rare earth after ion exchange does not change, to obtain the Y-type molecular sieve whose unit cell constant is reduced;
[0055] (3) carry out phosphorus modification treatment to the Y-type molecular sieve with reduced unit cell constant after roasting, to introduce phosphorus in the molecular sieve;
[0056] (4) reacting the molecular sieve after phosphorus modification treatment with silicon tetrachloride to carry out dealumination and silicon supplementation to obtain a gas-phase ultrastabl...
Embodiment 1
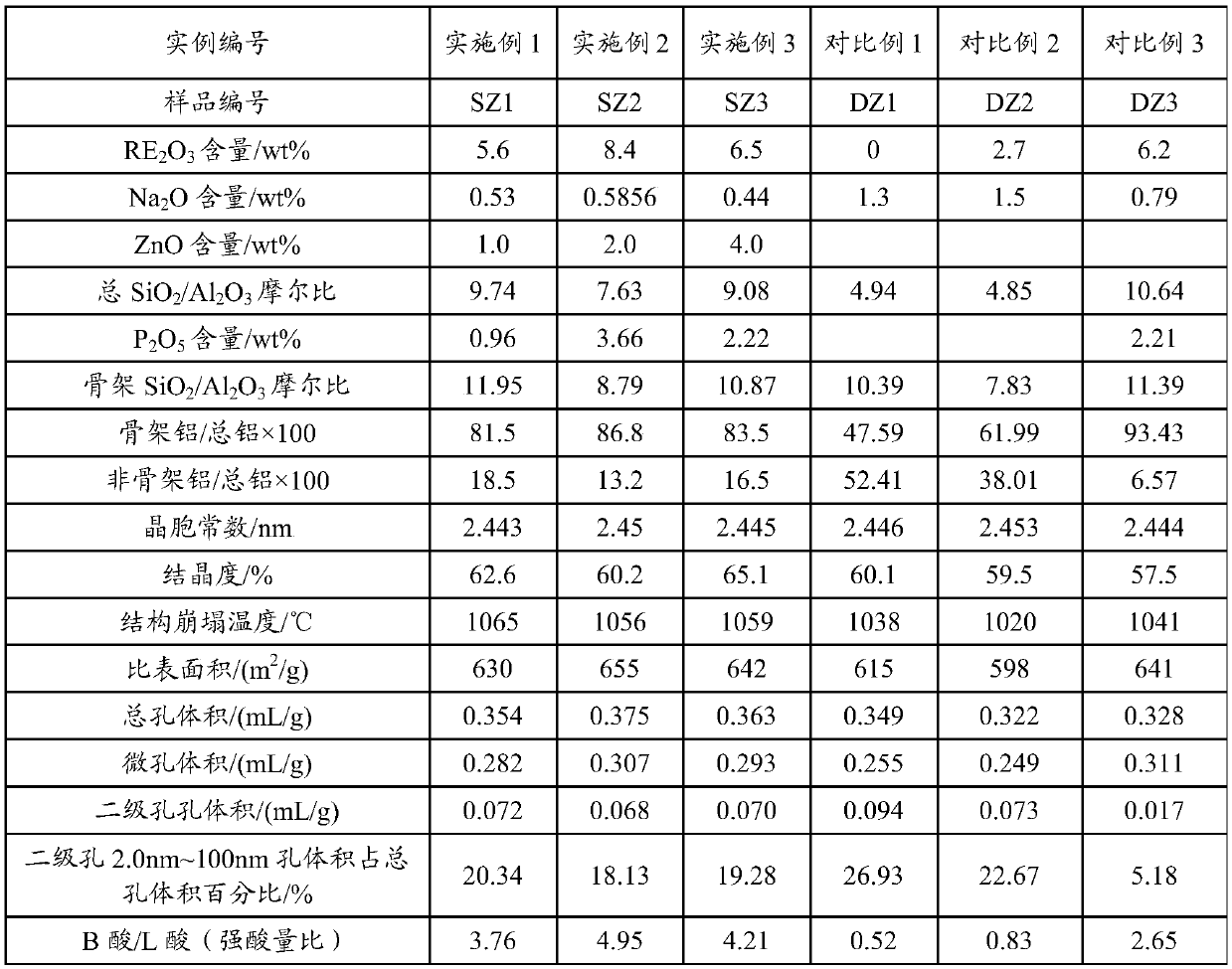
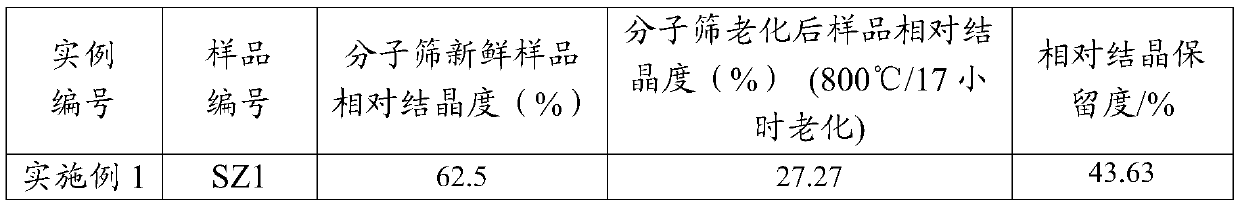
[0106] Get 2000 grams of NaY molecular sieves (calculated on a dry basis) and add them to 20 liters of decationized aqueous solution and stir to make them evenly mixed. Add 600ml of RE(NO 3 ) 3 Solution (concentration of rare earth salt solution in RE 2 o 3 Calculated as 319g / L, RE is a mixed rare earth of La and Ce, and La is calculated by the mass of rare earth oxide 2 o 3 : Ce 2 o 3=3:2), stirred, heated up to 90-95°C for 1 hour, then filtered, washed, and the filter cake was dried at 120°C to obtain a unit cell constant of 2.471nm, a sodium oxide content of 7.0wt%, and RE 2 o 3 A Y-type molecular sieve with a total rare earth content of 8.8wt%.
[0107] Afterwards, the molecular sieve was calcined for 6 hours at a temperature of 390° C. in an atmosphere containing 50 volume percent water vapor and 50 volume percent air to obtain a Y-type molecular sieve with a unit cell constant of 2.455 nm.
[0108] After cooling, add Y-type molecular sieve with a unit cell consta...
Embodiment 2
[0114] Get 2000 grams of NaY molecular sieves (on a dry basis) and add them to 25 liters of decationized aqueous solution and stir to make them evenly mixed. Add 800 ml of RECl 3 solution (in RE 2 o 3 The calculated solution concentration is: 319g / L, RE is a mixed rare earth of La and Ce, and La is calculated by the mass of rare earth oxide 2 o 3 : Ce 2 o 3 =3:2), stirred, heated to 90-95°C for 1 hour, then filtered and washed, and the filter cake was dried at 120°C to obtain a unit cell constant of 2.471nm and a sodium oxide content of 5.5wt%, expressed as RE 2 o 3 A Y-type molecular sieve with a total rare earth content of 11.3 wt%.
[0115] Afterwards, the molecular sieve was calcined at a temperature of 450° C. under 80% water vapor for 5.5 hours to obtain a Y-type molecular sieve with a unit cell constant of 2.461 nm.
[0116] After cooling, add a Y-type molecular sieve with a unit cell constant of 2.461nm into 6 liters of aqueous solution in which 268 grams of amm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cell constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Cell constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Cell constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com