Use of K-252A derivative for treatment of peripheral or central nerve disorders, and cytokine overproduction
A kind of use, interleukin technology, applied in the direction of nervous system disease, respiratory system disease, skin disease, etc., can solve the problem of slow recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Pharmacological activity on dopaminergic neurons
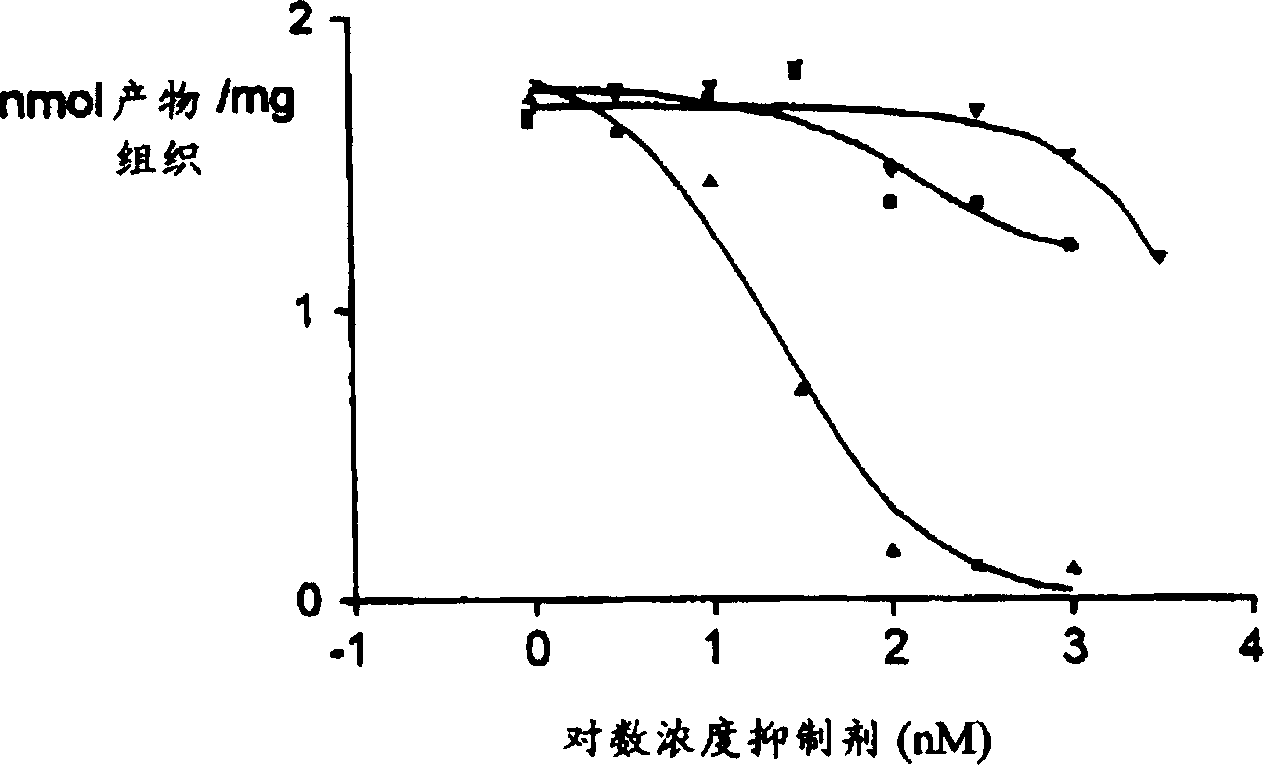
[0065] Experiments with Compound A were performed on MPTP-injured dopaminergic neurons in mice (MPTP mouse model). Subcutaneous administration of a single dose of MPTP (20 mg / kg) to C57 black mice resulted in a loss of approximately 60% of striatal tyrosine hydroxylase activity. Daily administration of 0.01-10 mg / kg (sc) of Compound A to the MPTP-treated mice reduced the loss of striatal tyrosine hydroxylase activity. These data are listed in Table 2.
[0066] Table 2
[0067] deal with
striatal TH activity
(±SEM)
% of uninjured control
undamaged
MPTP-impaired
MPTP-lesioned (vector)
MPTP-impaired + Compound A
19.06±1.06
7.40±1.07
6.99±0.75
100±5.6
39±5.6
37±4.0
(0.01mg / kg)
(0.03mg / kg)
(0.10mg / kg)
(0.30mg / kg)
(1.0mg / kg)
(3.0mg / kg)
(10.0mg / kg)
7.76±1.23
10.48±0.92 *
11.51±0.80 *
...
Embodiment 2
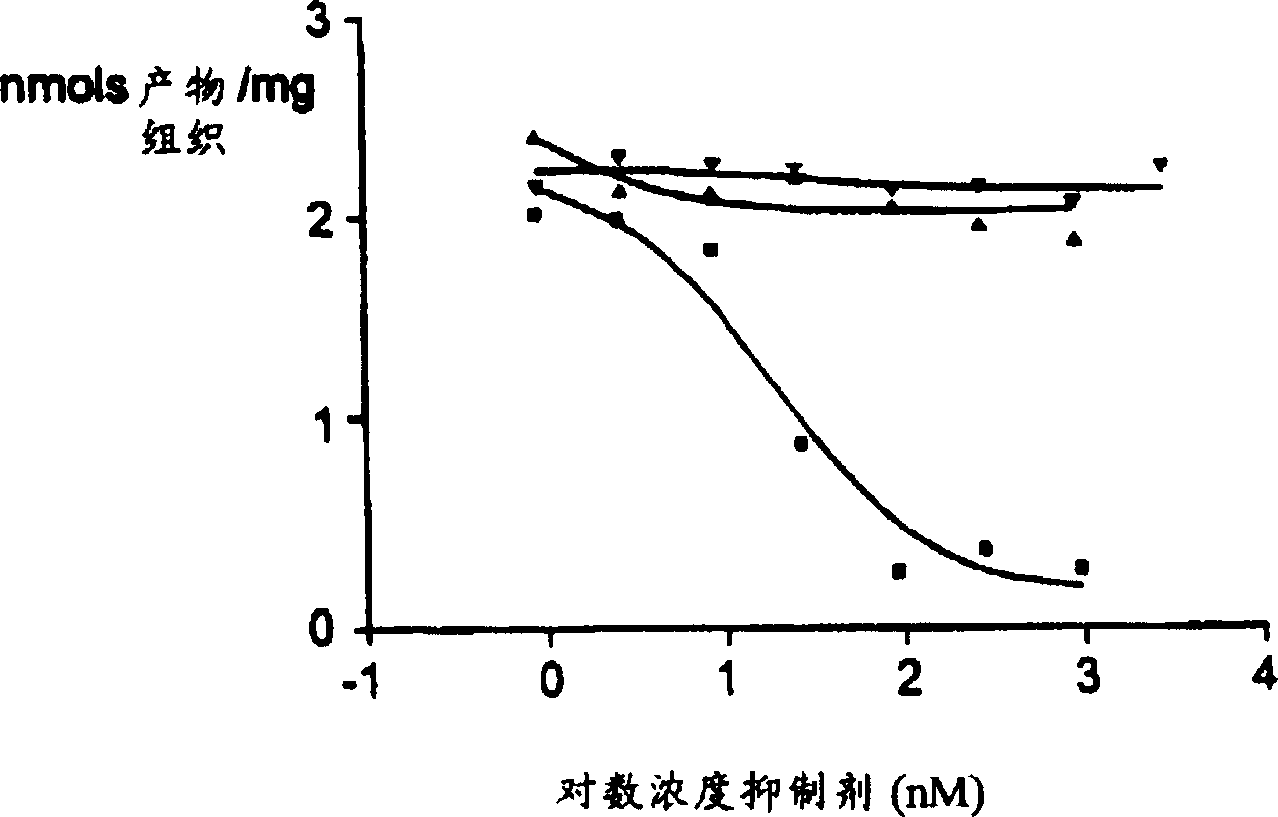
[0078] Pharmacological activity on GABAergic neurons
[0079] Compound A was tested for its ability to inhibit the loss of GABAergic neurons (eg, enhance survival) in the macrocellular inferior olivary nucleus using the well-known ibotenic acid injury model. Ibotenic acid, an excitotoxin, is known to reduce the number of GABA-expressing neurons in the nbm region (Lindefors et al., Neurosci. Lett., 135:262-264, 1992; Shaugnessy et al. Brain Res., 637 : 15-26, 1994).
[0080] Ibotenic acid (5.0 g) was injected into the side of the nbm of adult male Sprague-Dawley rats. Eighteen hours after injury, administration of compound A (0.03 mg / kg) to rats was started by subcutaneous injection, every other day, and continued until 18 days after injury. Tissue sections of the whole nbm rostral-caudalextent were then collected and processed for detection of glutamate decarboxylase, an enzyme required for the biosynthesis of GABA. The number of glutamate decarboxylase-expressing neurons w...
Embodiment 3
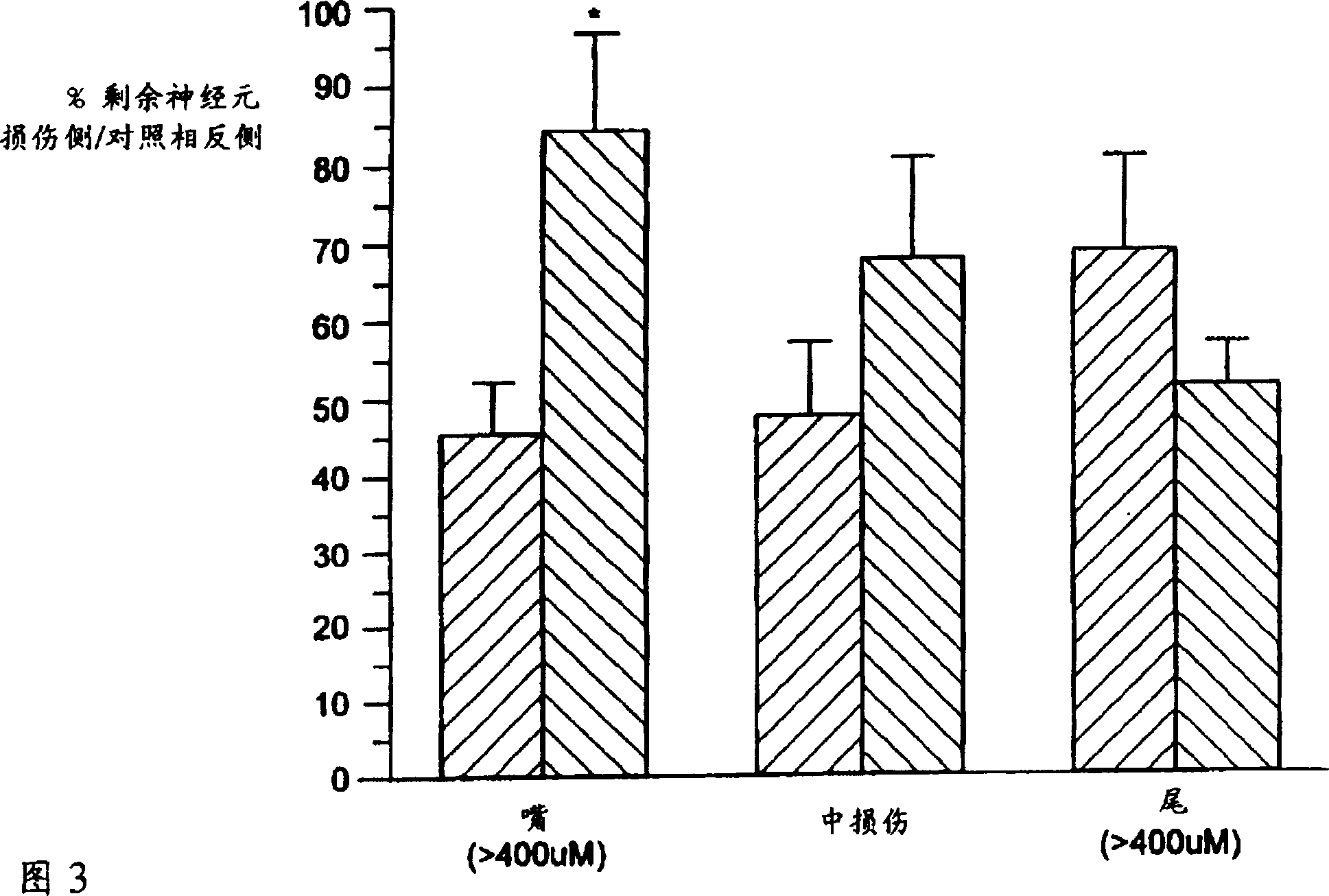
[0084] Pharmacological activity on NBM neurons
[0085]To directly test the ability of Compound A to prevent excitatory neuronal death, nbm neurons in adult Sprague-Dawley rats were first labeled with a long-lived marker. The labeling is done by injecting Fluoro-Gold (FG), a protein that is absorbed by nerve endings and transported back to cells (Book et al., J. Neuropath. Exp. Neurology, 53:95-102, 1994), before entering and Neuronal tracers of NBM neuronal targets within the parietal cortex. After 7-10 days, animals received unilateral NBM injury with 5 μg ibotenic acid. Beginning 18 hours after the injury, the animals were subcutaneously injected with Compound A (0.03 mg / kg) every other day until 18 days after the injury. Tissue sections of the entire anterior-caudal region of the nbm on both sides of the brain were collected, and the number of nbm neurons labeled with FG was counted. Count values were corrected for magnitude differences using standard methods and re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com